|
Roland (Lully)
''Roland'' is an opera with music by Jean-Baptiste Lully and a libretto by Philippe Quinault. It was first performed on January 8, 1685, at the Palace of Versailles by the Académie Royale de Musique (Paris Opera) and later, beginning on March 8, 1685, at the company's public theatre in Paris, the Théâtre du Palais-Royal. The story is derived from Ariosto's epic poem '' Orlando Furioso''. The opera takes the form of a tragédie en musique with an allegorical prologue and five acts. Roles There is also a chorus of Fairies, Islanders, Shepherds and Shepherdesses, Heroes and followers of Glory. Synopsis The opera opens with an allegorical prologue in which Démogorgon, King of the Fairies, sings the praises of Louis XIV and asks to see the story of the famous paladin Roland. Roland, the nephew of Charlemagne loves Angélique, the daughter of the King of Cathay, but, unbeknown to him, she is in love with Médor, a soldier in the army of Africa. In Act One, Roland gives A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roland (opera By Jean-Baptiste Lully)
Roland (; ; or ''Rotholandus''; or ''Rolando''; died 15 August 778) was a Frankish military leader under Charlemagne who became one of the principal figures in the literary cycle known as the Matter of France. The historical Roland was military governor of the Breton March, responsible for defending Francia's frontier against the Bretons. His only historical attestation is in Einhard's ''Vita Karoli Magni'', which notes he was part of the Frankish rearguard killed in retribution by the Basques in Iberia at the Battle of Roncevaux Pass. The story of Roland's death at Roncevaux Pass was embellished in later medieval and Renaissance literature. The first and most famous of these epic treatments was the Old French ''Chanson de Roland">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''Chanson de Roland'' of the 11th century. Two masterpieces of Italian Renaissance poetry, the ''Orlando Innamorato'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haute-contre
The ''haute-contre'' (plural ''hautes-contre'') was the primary French operatic tenor voice, predominant in French Baroque and Classical opera, from the middle of the seventeenth century until the latter part of the eighteenth century. History This voice was predominantly used in male solo roles, typically heroic and amatory ones, but also in comic parts, even '' en travesti'' (see apropos the portrait reproduced below and representing Pierre Jélyotte made up for the female title role of Rameau's ''Platée ''Platée'' is an opera in a prologue and three acts by Jean-Philippe Rameau with a libretto by Adrien-Joseph Le Valois d'Orville. Rameau bought the rights to the libretto ''Platée ou Junon jalouse'' (''Plataea, or Juno Jealous'') by Jacques Autr ...''). Lully wrote 8 out of 14 leading male roles for the voice; Charpentier, who was an haute-contre himself, composed extensively for the voice-part, as did Rameau and, later, Gluck. The leading ''hautes-contre'' of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niccolò Piccinni
Niccolò Piccinni (; 16 January 1728 – 7 May 1800) was an Italian composer of symphonies, sacred music, chamber music, and opera. Although he is somewhat obscure today, Piccinni was one of the most popular composers of opera—particularly the Neapolitan opera buffa—of the Classical period. Life Piccinni was born in Bari, in the Apulia region. From the age of fourteen, he was educated at the Conservatory of San Onofrio by Leonardo Leo and Francesco Durante,. thanks to the intervention of the Bishop of Bari (his father, although himself a musician, was opposed to his son following the same career). Piccinni's first opera, ''Le donne dispettose'', was produced in 1755 with the patronage of Prince Vintimille. In 1760 he composed, at Rome, the ''chef d'œuvre'' of his early life, '' La Cecchina, ossia la buona Figliuola'', an ''opera buffa'' with a libretto by Carlo Goldoni, which "enjoyed a two-year run in Rome and was played in all the important European capitals. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roland (Piccinni)
''Roland'' is a tragédie lyrique in three acts by the composer Niccolò Piccinni. The opera was a new setting of a libretto written by Philippe Quinault for Jean-Baptiste Lully in 1685, specially adapted for Piccinni by Jean-François Marmontel and based on Ludovico Ariosto's epic poem ''Orlando Furioso'' (''The Frenzy of Orlando''). The opera was first performed on 27 January 1778 by the Académie Royale de Musique (Paris Opera) at the Théâtre du Palais-Royal. Background and performance history ''Roland'' was the first opera Piccinni wrote for Paris. He had been hired by the Académie royale de musique in 1776, in spite of his ignorance of the French language. Piccinni still knew no French when he was composing ''Roland'' and had to be helped all the way by his librettist Marmontel, who provided a translation of every word along with details on how to accentuate it correctly. Marmontel also helped Piccinni come to terms with the French style of opera, which was very different fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-François Marmontel
Jean-François Marmontel (; 11 July 1723 – 31 December 1799) was a French historian, writer and a member of the Encyclopédistes movement. Biography He was born of poor parents at Bort, Limousin (today in Corrèze). After studying with the Jesuits at Mauriac, Cantal, he taught in their colleges at Clermont-Ferrand and Toulouse; and in 1745, acting on the advice of Voltaire, he set out for Paris to try for literary success. From 1748 to 1753 he wrote a succession of tragedies: ''Denys le Tyran'' (1748); ''Aristomene'' (1749); ''Cleopâtre'' (1750); ''Heraclides'' (1752); ''Egyptus'' (1753). These literary works, though only moderately successful on the stage, secured Marmontel's introduction into literary and fashionable circles. He wrote a series of articles for the '' Encyclopédie'' evincing considerable critical power and insight, which in their collected form, under the title ''Eléments de Littérature'', still rank among the French classics. He also wrote se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Chanson De Roland
The ''Song of Roland'' () is an 11th-century based on the deeds of the Frankish military leader Roland at the Battle of Roncevaux Pass in AD 778, during the reign of the Emperor Charlemagne. It is the oldest surviving major work of French literature. It exists in various manuscript versions, which testify to its enormous and enduring popularity in Medieval and Renaissance literature from the 12th to 16th centuries. The epic poem written in Old French is the first and one of the most outstanding examples of the ''chanson de geste'', a literary form that flourished between the 11th and 16th centuries in Medieval Europe and celebrated legendary deeds. An early version was composed around 1040 AD, with additions and alterations made up to about 1115 AD. The final poem contains about 4,000 lines. Manuscripts and dating Although set in the Carolingian era, the ''Song of Roland'' was written centuries later. There is a single extant manuscript of the ''Song of Roland''. It is held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques-Bénigne Bossuet
Jacques-Bénigne Lignel Bossuet (; 27 September 1627 – 12 April 1704) was a French Bishop (Catholic Church), bishop and theology, theologian. Renowned for his sermons, addresses and literary works, he is regarded as a brilliant orator and literary stylist of the French language. A native of Dijon, Bossuet was educated at a Jesuits, Jesuit school before enrolling in the College of Navarre in Paris, where he studied philosophy and theology. In 1652, he was ordained a priest and became a Doctor of Divinity. He spent the next seven years at Metz, where he honed his skills in oratory and politics, before returning to Paris and establishing his reputation as a great preacher. By the early 1660s, Bossuet was preaching regularly before the court of King Louis XIV at Palace of Versailles, Versailles. He was appointed tutor to the Louis, Grand Dauphin, Dauphin in 1670 and elected to the Académie Française a year later. In 1681, he was appointed Roman Catholic Diocese of Meaux, Bishop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Françoise D'Aubigné, Marquise De Maintenon
Françoise d'Aubigné (27 November 1635 – 15 April 1719), known first as Madame Scarron and subsequently as Madame de Maintenon (), was a French nobility, French noblewoman and the second wife of Louis XIV, Louis XIV of France from 1683 until his death in 1715. Although she was never considered queen of France, as the marriage was carried out in secret, Madame de Maintenon had considerable political influence as one of the King's closest advisers and the Governess of the Children of France, governess of the royal children. Born into an impoverished Huguenots, Huguenot noble family, Françoise married the poet Paul Scarron in 1652, which allowed her access to the Parisian high society. She was widowed in 1660, but later saw her fortunes improve through her friendship with Louis XIV's mistress, Françoise-Athénaïs de Rochechouart, Marquise de Montespan, Madame de Montespan, who tasked her with the upbringing of the king's extramarital children. She was made royal governess whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reigning monarchs, longest of any monarch in history. An emblem of the Absolutism (European history), age of absolutism in Europe, Louis XIV's legacy includes French colonial empire, French colonial expansion, the conclusion of the Thirty Years' War involving the Habsburgs, and a controlling influence on the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture, style of fine arts and architecture in France, including the transformation of the Palace of Versailles into a center of royal power and politics. Louis XIV's pageantry and opulence helped define the French Baroque architecture, French Baroque style of art and architecture and promoted his image as absolute ruler of France in the early modern period. Louis XIV began his personal rule of France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armide (Lully)
''Armide'' is an opera in five acts by Jean-Baptiste Lully. The libretto by Philippe Quinault is based on Torquato Tasso's poem ''La Gerusalemme liberata'' (''Jerusalem Delivered''). The work is in the form of a tragédie en musique, a genre invented by Lully and Quinault. Critics in the 18th century regarded ''Armide'' as Lully's masterpiece. It continues to be well-regarded, featuring some of the best-known music in French baroque opera and being arguably ahead of its time in its psychological interest. Unlike most of his operas, ''Armide'' concentrates on the sustained psychological development of a character – not Renaud, who spends most of the opera under Armide's spell, but Armide, who repeatedly tries without success to choose vengeance over love. Performance history ''Armide'' was first performed on 15 February 1686 by the Paris Opera at the Théâtre du Palais-Royal (rue Saint-Honoré), Théâtre du Palais-Royal, with scenery by Jean Bérain the Elder, Bérain, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amadis (Lully)
''Amadis'' or ''Amadis de Gaule'' (Amadis of Gaul) is a ''tragédie en musique'' in a prologue and five acts by Jean-Baptiste Lully to a libretto by Philippe Quinault based on Nicolas Herberay des Essarts' adaptation of Garci Rodríguez de Montalvo's ''Amadis de Gaula''. It was premiered by the Paris Opera at the Théâtre du Palais-Royal (rue Saint-Honoré), Théâtre du Palais-Royal sometime from January 15 to 18, 1684. There was a later production at Palace of Versailles, Versailles without scenery or machines in 1685.Rosow 1992, pp. 103–104. Performance history ''Amadis'' was the first ''tragédie en musique'' to be based on Chivalry, chivalric rather than Mythology, mythological themes; Lully's last three completed operas followed in this course. Louis XIV of France chose the theme. In the dance troupe the principal male dancers were Pierre Beauchamp, Louis-Guillaume Pécour and Lestang, and the principal female dancers were La Fontaine, Carré and Pesan. There were eigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
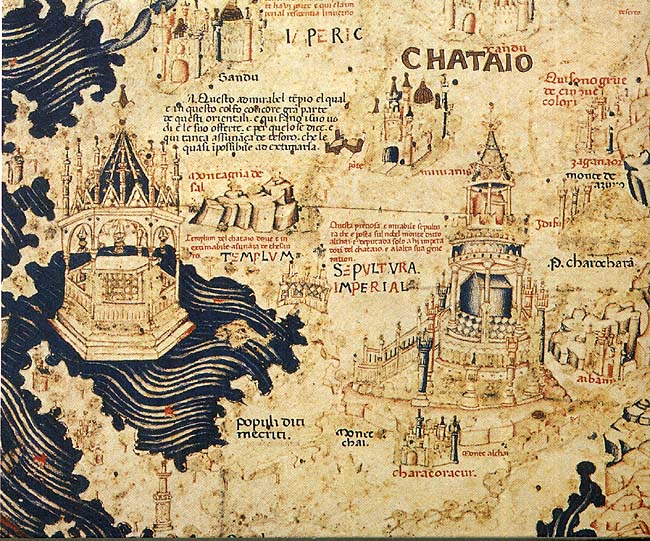
Cathay
Cathay ( ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from ''China'', which was a reference to southern China. As knowledge of East Asia increased, Cathay came to be seen as the same polity as China as a whole. The term ''Cathay'' became a poetic name for China. The name ''Cathay'' originates from the term '' Khitan'' ( zh, c=契丹, p=Qìdān), a para-Mongolic nomadic people who ruled the Liao dynasty in northern China from 916 to 1125, and who later migrated west after they were overthrown by the Jin dynasty to form the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty) for another century thereafter. Originally, this name was the name applied by Central and Western Asians and Europeans to northern China; the name was also used in Marco Polo's book on his travels in Yuan dynasty China (he referred to southern China as '' Mang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |