|
Rokiškis Music School
Rokiškis Music School () was a music school sponsored by the Tyzenhaus family that operated in Rokiškis (present-day Lithuania) from 1873 to 1904. While it focused on preparing church organists, several prominent Lithuanian interwar musicians were its alumni (e.g. Mikas Petrauskas, Juozas Gruodis, Juozas Tallat-Kelpša, etc.). History The first music school was transferred to Rokiškis from Hrodna by the Tyzenhaus family in 1785, but information about this school has not survived. The Tyzenhaus family reestablished a music school in 1873. The family had similar music schools in Aknīste (present-day Latvia) and Pastavy (present-day Belarus) that were closed in 1883 once the school in Rokiškis became more professional. It first taught orchestra and choir. In 1883, it added fortepiano, church organ, and hymns sections, but four years later it was downsized to just teach church organs. The school also had a branch in Obeliai, but it closed around 1884. The school was located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyzenhaus
The Tyzenhauz family (, , , ) was a noble family of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth of Baltic Germans, German extraction.Butterwick, R. (2021). ''The Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1733–1795''. Cambridge University Press. It was active in the Duchy of Livonia, Duchy of Courland and the northern Grand Duchy of Lithuania.Stone, D. Z. (2014). ''The Polish-Lithuanian State, 1386–1795''. University of Washington Press. Among the best-known members of the family were Gothard Jan Tyzenhaus, Gothard Jan Tyzenhauz, the Dorpat Voivodeship, Voivode of Dorpat (1634–1640), Konstanty Tyzenhauz (1786–1853), ornithologist, and Antoni Tyzenhaus, Antoni Tyzenhauz (1733–1785), the manager of royal property during the reign of Stanisław August Poniatowski. Antoni built Tyzenhaus Palace, Tyzenhauz Palace in Vilnius, Lithuania. In Rokiškis, northern Lithuania, the family also built the neogothic church of St. Matthias and Rokiškis Manor, which now houses Rokiškis Regional Museum. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( ; ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions to musical form have led him to be called "Father of the Symphony" and "Father of the String quartet". Haydn arose from humble origins, the child of working people in a rural village. He established his career first by serving as a chorister at St. Stephen's Cathedral, Vienna, then through an arduous period as a freelance musician. Eventually he found career success, spending much of his working life as Kapellmeister, music director for the wealthy Esterházy family at their palace of Eszterháza in rural Hungary. Though he had his own orchestra there, it isolated him from other composers and trends in music so that he was, as he put it, "forced to become original". During this period his music circulated widely in publication, eventuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Institutions Disestablished In 1904
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are disagreements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1873 Establishments In The Russian Empire
Events January * January 1 ** Japan adopts the Gregorian calendar. ** The California Penal Code goes into effect. * January 17 – American Indian Wars: Modoc War: First Battle of the Stronghold – Modoc Indians defeat the United States Army. February * February 11 – The Spanish Cortes deposes King Amadeus I, and proclaims the First Spanish Republic. * February 12 ** Emilio Castelar, the former foreign minister, becomes prime minister of the new Spanish Republic. ** The Coinage Act of 1873 in the United States is signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant. Coming into effect on April 1, it ends bimetallism in the U.S., and places the country on the gold standard. * February 20 ** The University of California opens its first medical school in San Francisco. ** British naval officer John Moresby discovers the site of Port Moresby in Papua New Guinea, and claims the land for Britain. March * March 3 – Censorship: The United States Congress enacts the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Institutions Established In 1873
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are disagreements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visuotinė Lietuvių Enciklopedija
The ''Visuotinė lietuvių enciklopedija'' or VLE () is a 25-volume universal Lithuanian-language encyclopedia published by the Science and Encyclopaedia Publishing Institute from 2001 to 2014. VLE is the first published universal encyclopedia in post-Soviet Lithuania (it replaces the former ''Lietuviškoji Tarybinė Enciklopedija'' which was published in thirteen volumes from 1976 to 1985). The last volume, XXV, was published in July 2014. An additional volume of updates, error corrections, and indexes was published in 2015. The encyclopedia's twenty-five volumes contain nearly 122,000 articles and about 25,000 illustrations. Since June 2017, VLE is published as an online encyclopedia being updated to present day. Description VLE is an encyclopedia published in Lithuanian; therefore, it focuses on Lithuania, Lithuanians and Lithuanian topics (Lithuanian personalities, organizations, language, culture, national activities). These articles make up about 20–25% of all articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Lithuania
Music of Lithuania refers to all forms of music associated with Lithuania, which has a long history of the folk, popular and classical musical development. Music was an important part of polytheistic, pre-Christian Lithuania – rituals were accompanied by music instruments and singing, deeds of the heroes and those who didn't return from the war were celebrated in songs. History Music was very important part of ancient Lithuanian polytheistic belief. It is known that, at the start of the 2nd millennium, Baltic tribes had special funeral traditions in which the deeds of the dead were narrated using recitation, and ritual songs about war campaigns, heroes and rulers also existed. First professional music was introduced to Lithuania with travelling monks in the 11th century. After the christianization of Lithuania in 1387, religious music started to spread, Gregorian chant was introduced. Travelling musicians arranged concerts in the manors and castles of the Lithuanian nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
František Zdeněk Skuherský
František Zdeněk Xavier Alois Skuherský (July 31, 1830 – August 19, 1892) was a Czech composer, pedagogue, and theoretician. Born in Opočno to František Alois Skuherský, the doctor of Duke Colloredo-Mansfeld and founder of the Opočno hospital. He graduated from the Hradec Králové gymnasium and studied philosophy and shortly medicine at Charles University. Also in Prague, he graduated from an organ school. In music, especially composing, he paid attention since childhood. He signed his first works in the pseudonym ''Opocensky.'' After his studies, he made a living by teaching people music in their homes. In the years 1854 to 1866 he was a theatre kapellmeister in Innsbruck and conductor of the town's singing choir, and later director of the University's cathedral. During this time he composed six operas, some of which premiered at Innsbruck. After the death of his wife, who gave him three children, he came back to Prague where in 1866 he became the director of a promine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Otto Grimm
Julius Otto Grimm (6 March 1827 in Pernau, Livonia, now Pärnu, Estonia – 7 December 1903 in Münster) was a German composer, conductor and musician who spent the majority of his professional life in Westphalia. He is most-often remembered today as one of the best friends of Johannes Brahms, whom he met in Leipzig in 1853. Brahms went on to dedicate his 4 Ballades, Op. 10 to Grimm in 1854. Life and career After studying philology and philosophy at the University of Tartu (then the University of Dorpat), concluding his exams in 1848, Grimm began his career and avocation as a tutor in Saint Petersburg. His first compositions were published around this time. From 1851/2, he pursued further studies in Dresden. In 1855, Grimm took the position of Professor of Music and Choral Conductor in Göttingen. In 1860, he accepted the post of conductor of the Musikverein (Music Association) of Münster. During his 40-year-long career in Münster, he received many honors and appointments. Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass (music)
The Mass () is a form of sacred musical composition that sets the invariable portions of the Christian Eucharistic liturgy (principally that of the Catholic Church, the Anglican Communion, and Lutheranism), known as the Mass. Most Masses are settings of the liturgy in Latin, the sacred language of the Catholic Church's Roman Rite, but there are a significant number written in the languages of non-Catholic countries where vernacular worship has long been the norm. For example, there have been many Masses written in English for a United States context since the Second Vatican Council, and others (often called "communion services") for the Church of England. Masses can be ''a cappella'', that is, without an independent accompaniment, or they can be accompanied by instrumental '' obbligatos'' up to and including a full orchestra. Many masses, especially later ones, were never intended to be performed during the celebration of an actual mass. History Middle Ages The earliest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aria
In music, an aria (, ; : , ; ''arias'' in common usage; diminutive form: arietta, ; : ariette; in English simply air (music), air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrument (music), instrumental or orchestral accompaniment, normally part of a larger work. The typical context for arias is opera, but vocal arias also feature in oratorios and cantatas, or they can be stand-alone concert arias. The term was originally used to refer to any expressive melody, usually, but not always, performed by a singer. Etymology The Italian term ''aria'', which derives from the Greek ἀήρ and Latin ''aer'' (air), first appeared in relation to music in the 14th century when it simply signified a manner or style of singing or playing. By the end of the 16th century, the term 'aria' refers to an instrumental form (cf. Santino Garsi da Parma lute works, ('Aria del Gran Duca'). By the early 16th century, it was in common use as meaning a simple setting of strophe, strophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
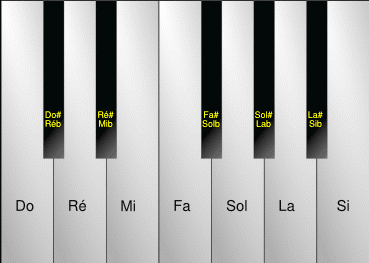
Solfège
In music, solfège (British English or American English , ) or solfeggio (; ), also called sol-fa, solfa, solfeo, among many names, is a mnemonic used in teaching aural skills, Pitch (music), pitch and sight-reading of Western classical music, Western music. Solfège is a form of solmization, though the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Syllables are assigned to the notes of the Scale (music), scale and assist the musician in Gordon music learning theory#Audiation, audiating, or mentally hearing, the pitches of a piece of music, often for the purpose of singing them aloud. Through the Renaissance music, Renaissance (and much later in some shapenote publications) various interlocking four-, five- and six-note systems were employed to cover the octave. The tonic sol-fa method popularized the seven syllables commonly used in English-speaking countries: ''do'' (spelled ''doh'' in tonic sol-fa),''Oxford English Dictionary'' 2nd Ed. (1998) ''re'', ''mi'', ''fa'', ''so(l)'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |