|
Rodolphe Töpffer
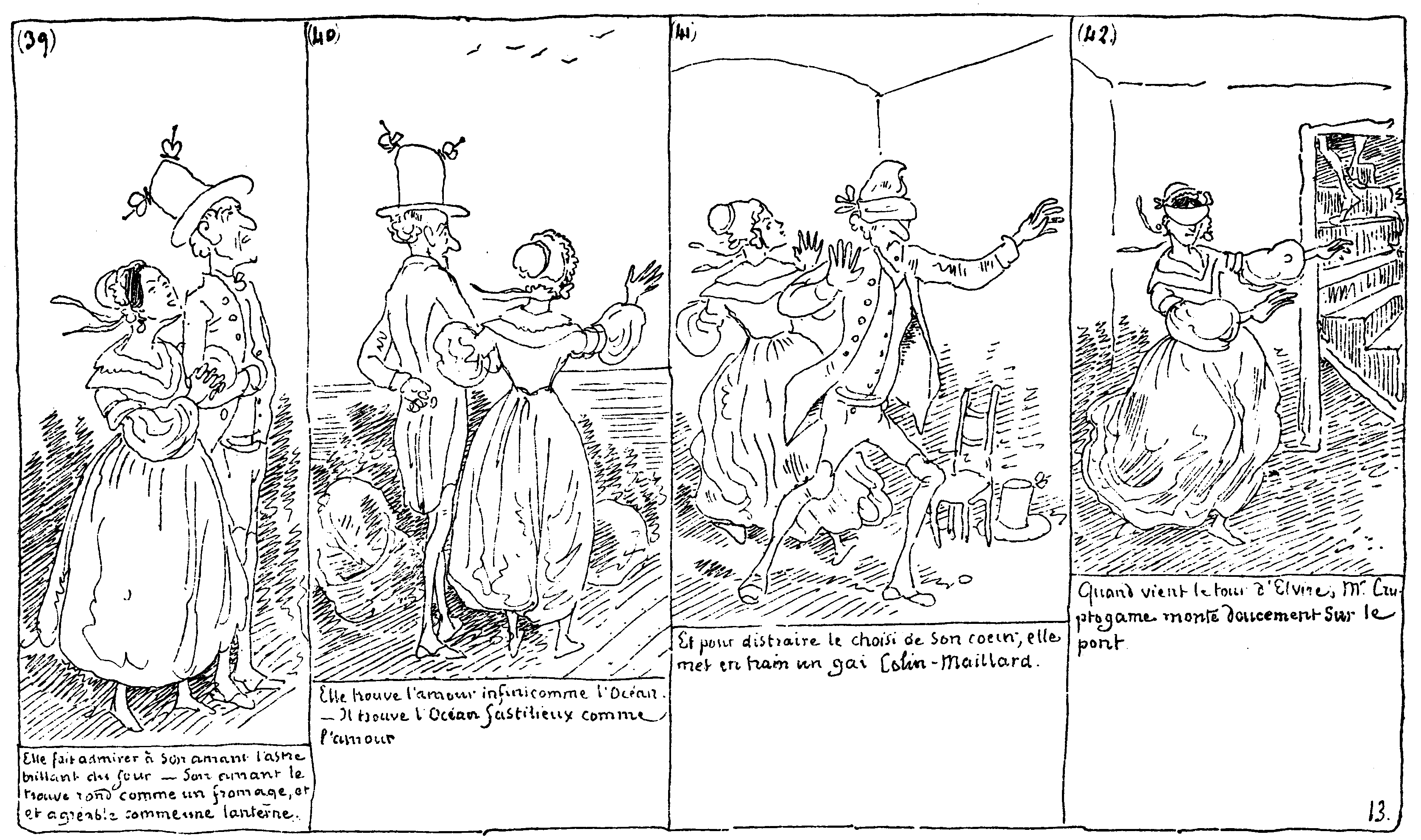
Rodolphe Töpffer ( , ; 31 January 1799 – 8 June 1846) was a Swiss teacher, author, painter, cartoonist, and caricaturist. He is best known for his illustrated books (''littérature en estampes'', " graphic literature"), which are possibly the earliest European comics. He is known as the father of comic strips and has been credited as the "first comics artist in history." Paris-educated, Töpffer worked as a schoolteacher at a boarding school, where he entertained students with his caricatures. In 1837, he published (published in the United States in 1842 as ''The Adventures of Obadiah Oldbuck''). Each page of the book had one to six captioned cartoon panels, much like modern comics. Töpffer published several more of these books, and wrote theoretical essays on the form. Biography Töpffer was born on 12 pluviôse of the seventh year of the French Republican calendar at ten hours after noon (« dix heures après midi »), that is on 31 January 1799, in Geneva, Lém ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situated in the south west of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Republic and Canton of Geneva. The city of Geneva () had a population 201,818 in 2019 (Jan. estimate) within its small municipal territory of , but the Canton of Geneva (the city and its closest Swiss suburbs and exurbs) had a population of 499,480 (Jan. 2019 estimate) over , and together with the suburbs and exurbs located in the canton of Vaud and in the French departments of Ain and Haute-Savoie the cross-border Geneva metropolitan area as officially defined by Eurostat, which extends over ,As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined Functional Urban Area of Geneva was made up of 93 Swiss communes and 158 French communesFederal Statistical O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone ( lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for musical scores and maps.Meggs, Philip B. A History of Graphic Design. (1998) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 146 Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meggs. Typographic Design: Form and Communication, Third Edition. (2002) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 11 Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography. Originally, the image to be printed was drawn with a greasy substance, such as oil, fat, or wax onto the surface of a smooth and flat limestone pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journalist
A journalist is an individual that collects/gathers information in form of text, audio, or pictures, processes them into a news-worthy form, and disseminates it to the public. The act or process mainly done by the journalist is called journalism. Roles Journalists can be broadcast, print, advertising, and public relations personnel, and, depending on the form of journalism, the term ''journalist'' may also include various categories of individuals as per the roles they play in the process. This includes reporters, correspondents, citizen journalists, editors, editorial-writers, columnists, and visual journalists, such as photojournalists (journalists who use the medium of photography). A reporter is a type of journalist who researches, writes and reports on information in order to present using sources. This may entail conducting interviews, information-gathering and/or writing articles. Reporters may split their time between working in a newsroom, or from home, and goin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccentricity (behaviour)
Eccentricity (also called quirkiness) is an unusual or odd behavior on the part of an individual. This behavior would typically be perceived as unusual or unnecessary, without being demonstrably maladaptive. Eccentricity is contrasted with normal behavior, the nearly universal means by which individuals in society solve given problems and pursue certain priorities in everyday life. People who consistently display benignly eccentric behavior are labeled as "eccentrics". Etymology From Medieval Latin ''eccentricus'', derived from Greek ', "out of the center", from '-, '- "out of" + ', "center". ''Eccentric'' first appeared in English essays as a neologism in 1551 as an astronomical term meaning "a circle in which the earth, sun, etc. deviates from its center." Five years later, in 1556, an adjective form of the word was used. In 1685, the definition evolved from the literal to the figurative, and ''eccentric'' is noted to have begun being used to describe unconventional or odd b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutor
TUTOR, also known as PLATO Author Language, is a programming language developed for use on the PLATO system at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign beginning in roughly 1965. TUTOR was initially designed by Paul Tenczar for use in computer assisted instruction (CAI) and computer managed instruction (CMI) (in computer programs called "lessons") and has many features for that purpose. For example, TUTOR has powerful answer-parsing and answer-judging commands, graphics, and features to simplify handling student records and statistics by instructors. TUTOR's flexibility, in combination with PLATO's computational power (running on what was considered a supercomputer in 1972), also made it suitable for the creation of games — including flight simulators, war games, dungeon style multiplayer role-playing games, card games, word games, and medical lesson games such as ''Bugs and Drugs'' (''BND''). TUTOR lives on today as the programming language for the Cyber1 PLATO Sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Class
Upper class in modern societies is the social class composed of people who hold the highest social status, usually are the wealthiest members of class society, and wield the greatest political power. According to this view, the upper class is generally distinguished by immense wealth which is passed on from generation to generation. Prior to the 20th century, the emphasis was on '' aristocracy'', which emphasized generations of inherited noble status, not just recent wealth. Because the upper classes of a society may no longer rule the society in which they are living, they are often referred to as the old upper classes, and they are often culturally distinct from the newly rich middle classes that tend to dominate public life in modern social democracies. According to the latter view held by the traditional upper classes, no amount of individual wealth or fame would make a person from an undistinguished background into a member of the upper class as one must be born into a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dandy
A dandy is a man who places particular importance upon physical appearance, refined language, and leisurely hobbies, pursued with the appearance of nonchalance. A dandy could be a self-made man who strove to imitate an aristocratic lifestyle despite coming from a middle-class background, especially in late 18th- and early 19th-century Britain. Previous manifestations of the ''petit-maître'' (French for "small master") and the Muscadin have been noted by John C. Prevost, but the modern practice of dandyism first appeared in the revolutionary 1790s, both in London and in Paris. The dandy cultivated cynical reserve, yet to such extremes that novelist George Meredith, himself no dandy, once defined cynicism as "intellectual dandyism". Some took a more benign view; Thomas Carlyle wrote in ''Sartor Resartus'' that a dandy was no more than "a clothes-wearing man". Honoré de Balzac introduced the perfectly worldly and unmoved Henri de Marsay in '' La fille aux yeux d'or'' (1835), a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Class
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Common definitions for the middle class range from the middle fifth of individuals on a nation's income ladder, to everyone but the poorest and wealthiest 20%. Theories like "Paradox of Interest" use decile groups and wealth distribution data to determine the size and wealth share of the middle class. From a Marxist standpoint, middle class initially referred to the 'bourgeoisie,' as distinct from nobility. With the development of capitalist societies and further inclusion of the bourgeoisie into the ruling class, middle class has been more closely identified by Marxist scholars with the term ' petite bourgeoisie.' There has been significant global middle-class growth over time. In February 2009, '' The Economist'' asserted that over half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newspaper
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sports and art, and often include materials such as opinion columns, weather forecasts, reviews of local services, obituaries, birth notices, crosswords, editorial cartoons, comic strips, and advice columns. Most newspapers are businesses, and they pay their expenses with a mixture of subscription revenue, newsstand sales, and advertising revenue. The journalism organizations that publish newspapers are themselves often metonymically called newspapers. Newspapers have traditionally been published in print (usually on cheap, low-grade paper called newsprint). However, today most newspapers are also published on websites as online newspapers, and some have even abandoned their print versions entirely. Newspapers developed in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gespräche Mit Goethe
''Gespräche mit Goethe'' (translation: ''Conversations with Goethe'', ''Conversations with Eckermann'') is a book by Johann Peter Eckermann recording his conversations with Johann Wolfgang von Goethe during the last nine years of the latter's life, while Eckermann served as Goethe's personal secretary. It was first released (in two volumes) in 1836 and substantially augmented (with the addition of another volume) in 1848. Eckermann published the book at a time when Goethe's popularity was diminishing in Germany, and the book initially sold poorly there. It rapidly became very popular among international readers and subsequently played an important role in reviving interest in and appreciation of Goethe's work both in Germany and around the world. Some editions go so far as to publish the book as ''Conversations with Eckermann'', with Goethe listed as the author. This practice mistakenly implies Eckermann played a role of editor rather than author; on the contrary, the book is ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Peter Eckermann
Johann Peter Eckermann (21 September 1792 – 3 December 1854), German poet and author, is best known for his work '' Conversations with Goethe'', the fruit of his association with Johann Wolfgang von Goethe during the last years of Goethe's life. Biography Eckermann was born at Winsen (Luhe) in Harburg, of humble parentage, and was brought up in penury and privation. After serving as a volunteer in the War of Liberation (1813–1814), he obtained a secretarial appointment under the war department at Hanover. In 1817, although twenty-five years of age, he was enabled to attend the gymnasium of Hanover and afterwards the university of Göttingen, which, however, after one year's residence as a student of law, he left in 1822. His acquaintance with Goethe began in the following year, when Eckermann sent to Goethe the manuscript of ''Beiträge zur Poesie'' (1823). Soon afterwards he went to Weimar, where he supported himself as a private tutor. For several years he also instructed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benoît Peeters
Benoît Peeters (; born 1956) is a French comics writer, novelist, and comics studies scholar. Biography After a degree in Philosophy at Université de Paris I, Peeters prepared his Master's at the École des Hautes Études en Sciences Sociales (EHESS‚ Paris) under the direction of Roland Barthes. He holds a '' habilitation à diriger les recherches'' (HDR), i.e. a supplementary PhD enabling him to supervise the work of PhD candidates (Université de Paris I, 2007). He published his first novel, ''Omnibus'', by Les Éditions de Minuit in 1976, followed by his second, ''La Bibliothèque de Villers'', Robert Laffont, 1980. Since then, he has published over sixty works on a wide variety of subjects. His best-known work is '' Les Cités obscures'', an imaginary world which mingles a Borgesian metaphysical surrealism with the detailed architectural vistas of the series' artist, François Schuiten. The series began with ''Les Murailles de Samaris'' (''The Walls of Samaris'') in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)


