|
Robert McNeill Alexander
Robert McNeill (Neill) Alexander, CBE FRS (7 July 1934 – 21 March 2016) was a British zoologist and a leading authority in the field of biomechanics. For thirty years he was Professor of Zoology at the University of Leeds. Early life and education Alexander was born in Lisburn, Northern Ireland, one of the four sons of Robert Alexander and his wife Janet McNeill. His father was the chief engineer of the city of Belfast. His mother was a novelist and playwright who wrote more than 20 children's books and two opera libretti. He was educated at Tonbridge School and at Trinity Hall, Cambridge where he gained an MA and a PhD. His PhD research at Cambridge was supervised by Professor Sir James Gray, FRS. Subsequently, he was awarded a DSc by the University of Wales. Academic career Alexander was a Lecturer at the University College of North Wales (now Bangor University) from 1958 to 1969 and then Professor of Zoology at the University of Leeds from 1969 until his retirement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomechanics
Biomechanics is the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems, at any level from whole organisms to Organ (anatomy), organs, Cell (biology), cells and cell organelles, using the methods of mechanics. Biomechanics is a branch of biophysics. Etymology The word "biomechanics" (1899) and the related "biomechanical" (1856) come from the Ancient Greek βίος ''bios'' "life" and μηχανική, ''mēchanikē'' "mechanics", to refer to the study of the mechanical principles of living organisms, particularly their movement and structure. Subfields Biofluid mechanics Biological fluid mechanics, or biofluid mechanics, is the study of both gas and liquid fluid flows in or around biological organisms. An often studied liquid biofluid problem is that of blood flow in the human cardiovascular system. Under certain mathematical circumstances, blood flow can be modeled by the Navier–Stokes equations. ''In vivo'' whole blood is assum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangor University
Bangor University () is a Public university, public Research university, research university in Bangor, Gwynedd, Wales. It was established by Royal charter, Royal Charter in 1885 as the University College of North Wales (UCNW; ), and in 1893 became one of the founding institutions of the federal University of Wales. In 1996, after structural changes to the University of Wales it became known as the University of Wales, Bangor (UWB; ). It became independent of the University of Wales in 2007, adopting its current name and awarding its own degrees. It has over 10,000 students across 3 academic colleges and 11 schools, as well as several large research institutes. Its campus makes up a large part of Bangor, and extends to nearby Menai Bridge as well, with a second campus in Wrexham for some healthcare courses. Its total income for 2022/23 was £178.0 million, of which 19% came from research grants, and it has an endowment of £8.2 million. Its alumni includes multiple Fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whipsnade Zoo
Whipsnade Zoo, formerly known as ZSL Whipsnade Zoo and Whipsnade Wild Animal Park, is a zoo located in Whipsnade, near Dunstable, Bedfordshire, England. It is one of two zoos (the other being London Zoo in Regent's Park, London) that is owned by the Zoological Society of London (ZSL), a charity devoted to the worldwide conservation of animals and their habitats. Description The park covers , and can be located from miles to the north and from the air because of the Whipsnade White Lion, a large hill figure carved into the side of the Dunstable Downs (part of the Chiltern Hills) below the White rhinoceros, white rhino enclosure. Due to its size, inside the park, visitors may walk or drive their cars between the various animal enclosures, or through an 'Asian' area where some animals are allowed to roam free around the cars. There is also a train service, the Narrow-gauge railway, narrow-gauge Great Whipsnade Railway, also known as the "Jumbo Express." Whipsnade Zoo is the UK' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Zoo
London Zoo, previously known as ZSL London Zoo or London Zoological Gardens and sometimes called Regent's Park Zoo, is the world's oldest scientific zoo. It was opened in London on 27 April 1828 and was originally intended to be used as a collection for scientific study. In 1831 or 1832, the Tower of London menagerie animals were transferred to the zoo's collection. It was opened to the public in 1847. As of December 2022, it houses a collection of 14,926 individuals, making it one of the largest collections in the United Kingdom. It is managed under the aegis of the Zoological Society of London (established in 1826) and is situated at the northern edge of Regent's Park, on the boundary line between the City of Westminster and the borough of Camden (the Regent's Canal runs through it). The Society also has a more spacious site at Whipsnade Zoo in Bedfordshire where larger animals, such as elephants and rhinos, have been moved. As well as being the first scientific zoo, Lond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Society Of London
The Zoological Society of London (ZSL) is a charity and organization devoted to the worldwide animal conservation, conservation of animals and their habitat conservation, habitats. It was founded in 1826. Since 1828, it has maintained London Zoo, and since 1931 Whipsnade Zoo. History On 29 November 1822, the birthday of John Ray, "the father of modern zoology", a meeting held in the Linnean Society in Soho Square led by Rev. William Kirby (entomologist), William Kirby, resolved to form a "Zoological Club of the Linnean Society of London". Between 1816 and 1826, discussions between Stamford Raffles, Humphry Davy, Joseph Banks and others led to the idea that London should have an establishment similar to the Jardin des Plantes in Paris. It would house a zoological collection "which should interest and amuse the public." The society was founded in April 1826 by Stamford Raffles, Sir Stamford Raffles, the Henry Petty-Fitzmaurice, 3rd Marquess of Lansdowne, Marquess of Lansdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
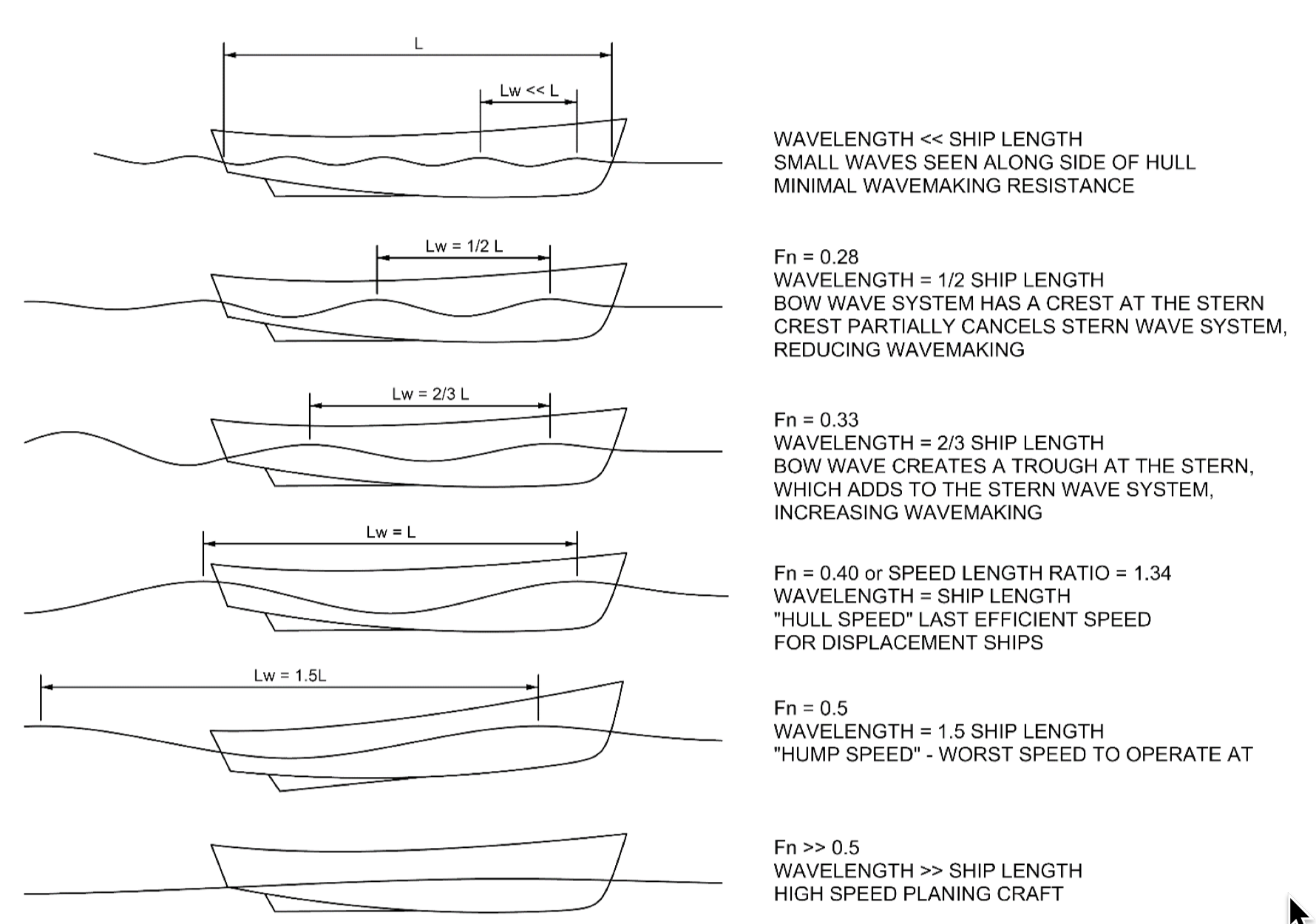
Froude Number
In continuum mechanics, the Froude number (, after William Froude, ) is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the flow inertia to the external force field (the latter in many applications simply due to gravity). The Froude number is based on the speed–length ratio which he defined as: \mathrm = \frac where is the local flow velocity (in m/s), is the local gravity field (in m/s2), and is a characteristic length (in m). The Froude number has some analogy with the Mach number. In theoretical fluid dynamics the Froude number is not frequently considered since usually the equations are considered in the high Froude limit of negligible external field, leading to homogeneous equations that preserve the mathematical aspects. For example, homogeneous Euler equations are conservation equations. However, in naval architecture the Froude number is a significant figure used to determine the resistance of a partially submerged object moving through water. Origins In open c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutionary history, evolution of dinosaurs is a subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya and their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, Evolution of birds, having evolved from earlier Theropoda, theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomy (biology), taxonomic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology. Anatomy is a complex and dynamic field that is constantly evolving as discoveries are made. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
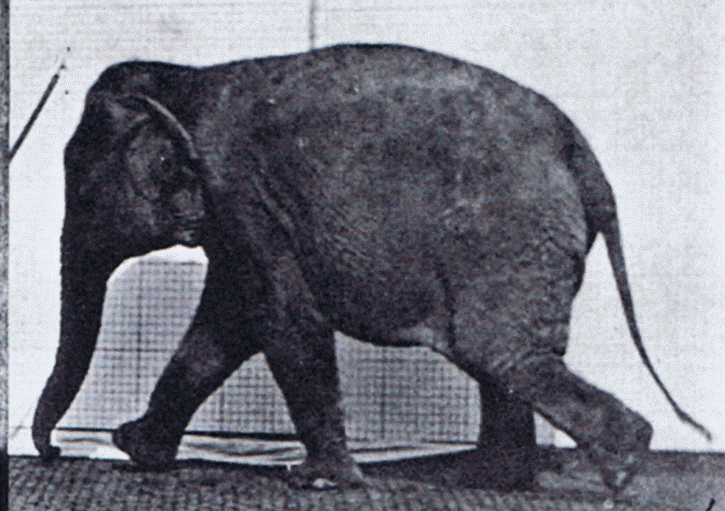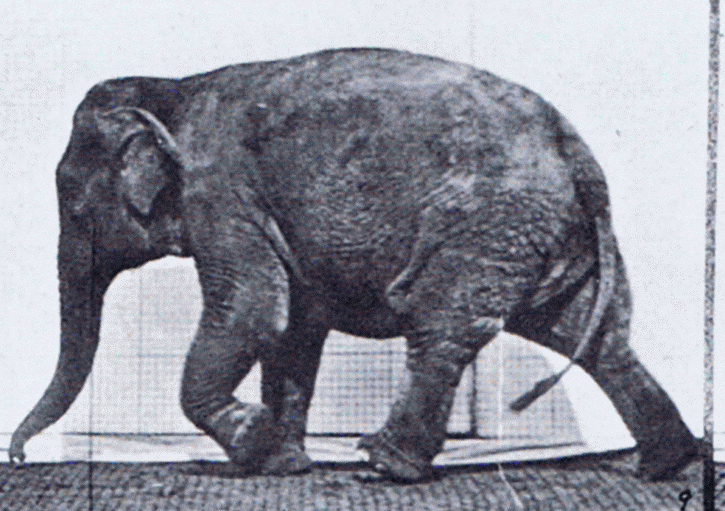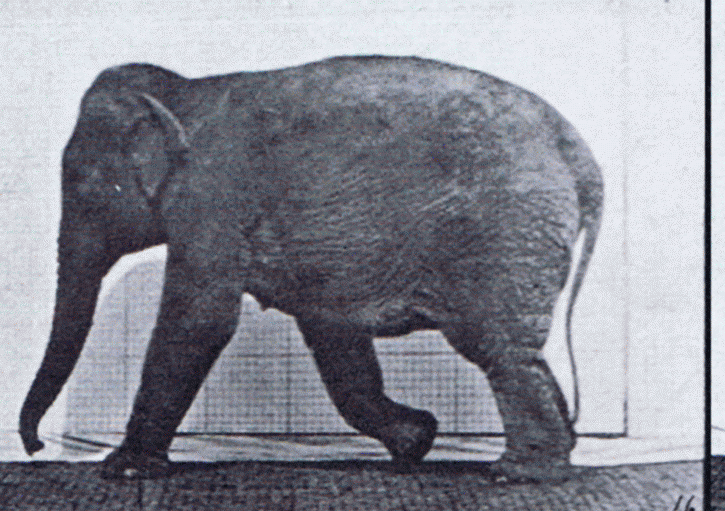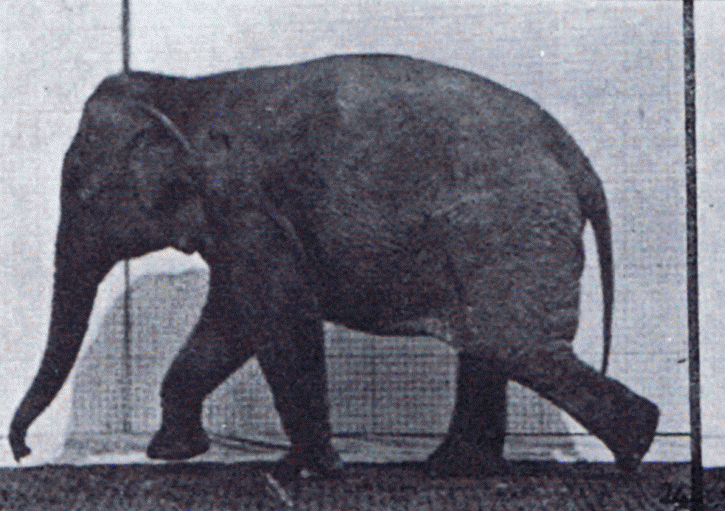
Gait
Gait is the pattern of Motion (physics), movement of the limb (anatomy), limbs of animals, including Gait (human), humans, during Animal locomotion, locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to wikt:maneuver, maneuver, and energetic efficiency. Different animal species may use different gaits due to differences in anatomy that prevent use of certain gaits, or simply due to evolved innate preferences as a result of habitat differences. While various gaits are given specific names, the complexity of biological systems and interacting with the environment make these distinctions "fuzzy" at best. Gaits are typically classified according to footfall patterns, but recent studies often prefer definitions based on mechanics. The term typically does not refer to limb-based propulsion through fluid mediums such as water or air, but rather to propulsion across a solid substrate by generating reactive forces against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Locomotion
Terrestrial locomotion has evolution, evolved as animals adapted from ecoregion#Marine, aquatic to ecoregion#Terrestrial, terrestrial environments. Animal locomotion, Locomotion on land raises different problems than that in water, with reduced friction being replaced by the increased effects of gravity. As viewed from evolutionary taxonomy, there are three basic forms of animal locomotion in the terrestrial environment: *#Legged locomotion, legged – moving by using appendages *#Limbless locomotion, limbless locomotion – moving without legs, primarily using the body itself as a propulsive structure. *#Rolling, rolling – rotating the body over the substrate Some terrains and land cover, terrestrial surfaces permit or demand alternative locomotive styles. A sliding component to locomotion becomes possible on slippery surfaces (such as ice and snow), where locomotion is aided by potential energy, or on loose surfaces (such as sand or scree), where friction is low but purchase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
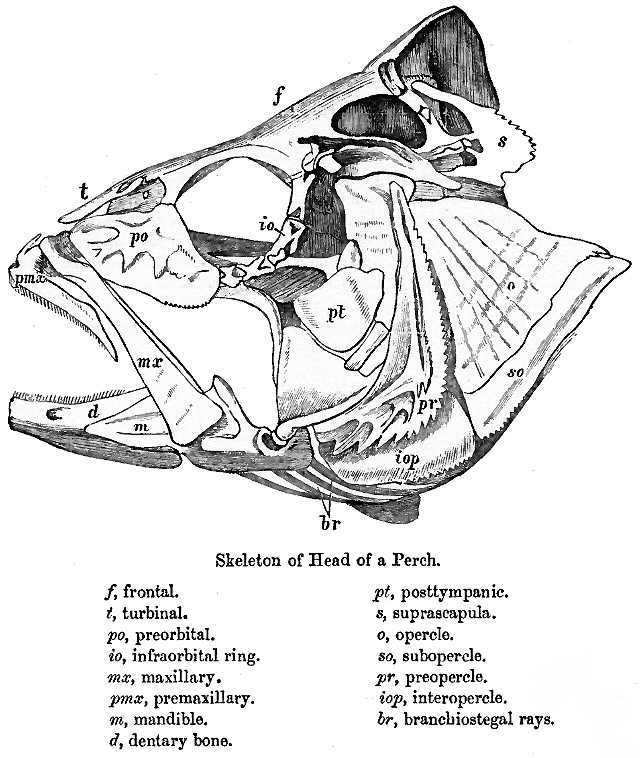
Fish Jaw
Most bony fishes have two sets of jaws made mainly of bone. The primary oral jaws open and close the mouth, and a second set of pharyngeal jaws are positioned at the back of the throat. The oral jaws are used to capture and manipulate prey by biting and crushing. The pharyngeal jaws, so-called because they are positioned within the pharynx, are used to further process the food and move it from the mouth to the stomach. Cartilaginous fishes, such as sharks and Batoidea, rays, have one set of oral jaws made mainly of cartilage. They do not have pharyngeal jaws. Generally jaws are Articulation (anatomy), articulated and oppose vertically, comprising an upper jaw and a lower jaw and can bear numerous ordered teeth. Cartilaginous fishes grow multiple sets ''(polyphyodont)'' and replace teeth as they wear by moving new teeth laterally from the medial jaw surface in a conveyor-belt fashion. Teeth are replaced multiple times also in most bony fishes, but unlike cartilaginous fishes, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |