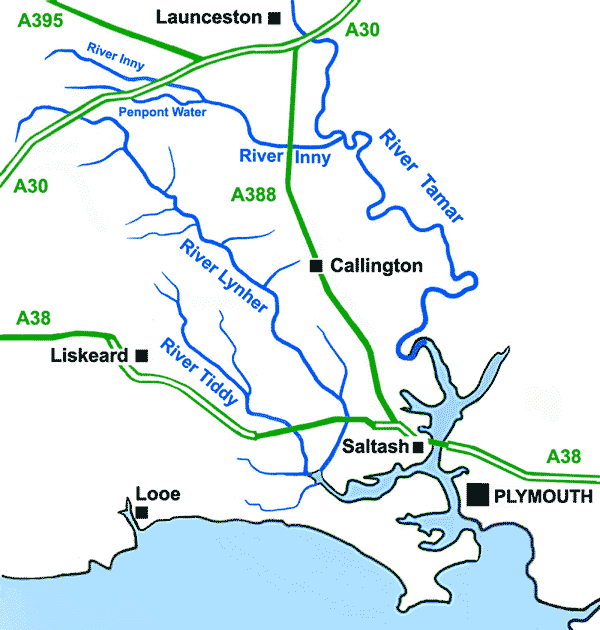
|
River Inny, Cornwall
The River Inny () is a small river in East Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. A tributary of the River Tamar, the Inny is about long from its source near Davidstow on the eastern flank of Bodmin Moor to its confluence with the Tamar at Inny Foot near Dunterton. The Inny's catchment is 108 square kilometres. The Inny's main tributary, Penpont Water, joins it at Two Bridges. Cornwall Rivers Project website; River Inny; retrieved April 2010 The course of River Inny is initially east-southeast. From Two Bridges it runs southeast before running due east for the last few miles to its confluence with the Tamar. River Inny supports , g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymallus Thymallus
''Thymallus thymallus'', the grayling or European grayling, is a species of freshwater fish in the salmon family (biology), family Salmonidae. It is the only species of the genus ''Thymallus'' (the graylings) native to Europe, where it is widespread from the United Kingdom and France to the Ural Mountains in Russia, and Balkans on the south-east, but does not occur in the southern parts of the continent. It was introduced to Morocco in 1948, but it does not appear to have become established there. Description The grayling grows to a maximum recorded length of and a maximum recorded weight of . Of typical ''Thymallus'' appearance, the grayling proper is distinguished from the similar Arctic grayling (''T. arcticus arcticus'') by the presence of 5–8 dorsal fin, dorsal and 3–4 anal fin, anal spines, which are absent in the other species; ''T. thymallus'' also has a smaller number of soft rays in these fins. Individuals of the species have been recorded as reaching an age of 14 y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivers Of Cornwall
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sediment or alluvium carried by rivers shapes the landscape aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Snipe
The common snipe (''Gallinago gallinago'') is a small, stocky wader native to the Old World. Distribution and habitat The breeding habitats are marshes, bogs, tundra and wet meadows throughout the Palearctic. In the north, the distribution limit extends from Iceland over the north of the British Isles and northern Fennoscandia, where it occurs at around 70°N, as well as through European Russia and Siberia. Here it is mostly on the northern edge of the Taiga zone at 71°N, but reaches 74°N on the east coast of the Taymyr Peninsula. In the east it extends to Anadyr, Kamchatka, Bering Island and the Kuril Islands, The southern boundary of the distribution area in Europe runs through northern Portugal, central France, northern Italy, Bulgaria, and Ukraine, with populations in the west being only very scattered. In Asia, the distribution extends south to northern Turkestan, locally to Afghanistan and the Middle East, through the Altai and further to Manchuria and Ussuri. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Curlew
The Eurasian curlew or common curlew (''Numenius arquata'') is a very large wader in the family Scolopacidae. It is one of the most widespread of the curlews, breeding across temperate Europe and Asia. In Europe, this species is often referred to just as the "curlew", and in Scotland known as the "whaup" in Scots. Taxonomy The Eurasian curlew was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under the binomial name ''Scolopax arquata''. It is now placed with eight other curlews in the genus '' Numenius'' that was introduced by the French ornithologist Mathurin Jacques Brisson in 1760. The genus name ''Numenius'' is from Ancient Greek νουμήνιος, ''noumēnios'', a bird mentioned by Hesychius. It is associated with the curlew because it appears to be derived from ''neos'', "new" and ''mene'' "moon", referring to the crescent-shaped bill. The species name ''arquata'' is the Medieval Latin name for this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-throated Dipper
The white-throated dipper (''Cinclus cinclus''), also known as the European dipper or just dipper, is an aquatic passerine bird found in Europe, Middle East, Central Asia and the Indian Subcontinent. The species is divided into several subspecies, based primarily on colour differences, particularly of the pectoral band. Taxonomy and systematics The white-throated dipper was described in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under the binomial name ''Sturnus cinclus''. The current genus '' Cinclus'' was introduced by the German naturalist Moritz Balthasar Borkhausen in 1797. The name ''cinclus'' is from the Ancient Greek word that was used to describe small tail-wagging birds that resided near water. Of the five species now placed in the genus, a molecular genetic study has shown that the white-throated dipper is most closely related to the other Eurasian species, the brown dipper (''Cinclus pallasii''). There are 14 subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand Martin
The sand martin (''Riparia riparia''), also known as collared sand martin or common sand martin, and in the Americas as the bank swallow, is a migratory passerine bird in the swallow family Hirundinidae. It has a wide range in summer, embracing practically the whole Holarctic area, from Europe, across Asia to the Pacific Ocean, and throughout North America. It winters in eastern and southern Africa, southern Asia, and South America. Taxonomy This species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'', and originally named ''Hirundo riparia''; the description consisted of the simple "''H rundocinerea, gula abdomineque albis''" ("an ash-grey swallow, with white throat and belly") and the type locality was simply given as "Europa", subsequently refined to refer to Linnaeus's homeland of Sweden. The specific name means "of the riverbank"; it is derived from the Latin ''ripa'' "riverbank". There are three or four weakly-defined subspecies: * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Kingfisher
The common kingfisher (''Alcedo atthis''), also known as the Eurasian kingfisher and river kingfisher, is a small kingfisher with seven subspecies recognized within its wide distribution across Eurasia and North Africa. It is resident in much of its range, but migrates from areas where rivers freeze in winter. This sparrow-sized bird has the typical short-tailed, large-headed kingfisher profile; it has blue upperparts, orange underparts and a long bill. It feeds mainly on fish, caught by diving, and has special visual adaptations to enable it to see prey under water. The glossy white eggs are laid in a nest at the end of a burrow in a riverbank. Taxonomy The common kingfisher was first described by Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' in 1758 as ''Gracula atthis''. The modern binomial name derives from the Latin ', 'kingfisher' (from Greek , '), and ''Atthis'', a beautiful young woman of Lesbos, and favourite of Sappho. The genus '' Alcedo'' compri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
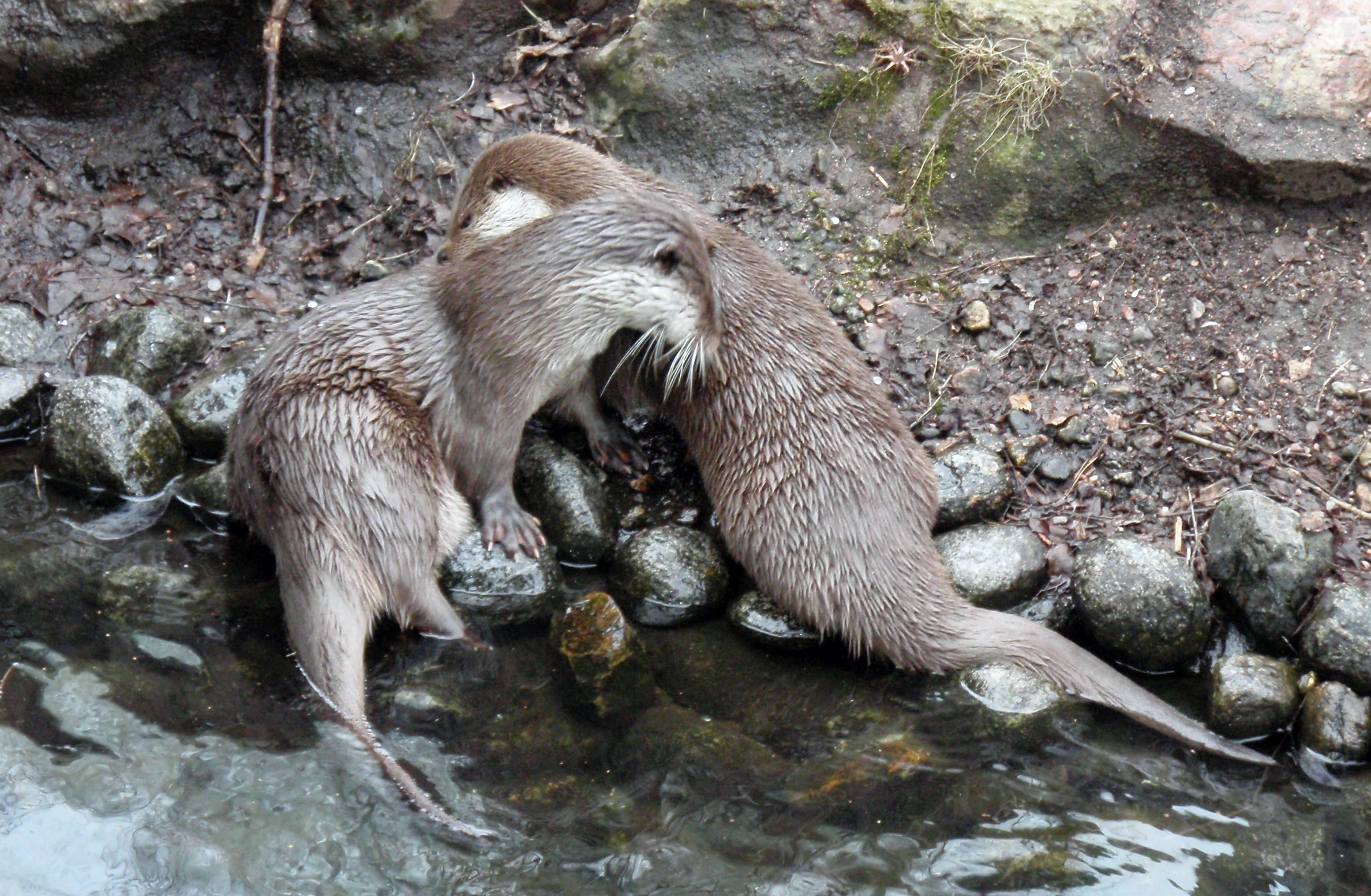
European Otter
The Eurasian otter (''Lutra lutra''), also known as the European otter, Eurasian river otter, European river otter, common otter, and Old World otter, is a semiaquatic mammal native to Eurasia and the Maghreb. The most widely distributed member of the otter subfamily (Lutrinae) of the weasel family (Mustelidae), it is found in the waterways and coasts of Europe, many parts of Asia, and parts of northern Africa. The Eurasian otter has a diet mainly of fish, and is strongly territorial. It is endangered in some parts of its range, but is recovering in others. Description The Eurasian otter is a typical species of the otter subfamily. Brown above and cream below, these long, slender creatures are well-equipped for their aquatic habits. Their bones show osteosclerosis, increasing their density to reduce buoyancy. This otter differs from the North American river otter by its shorter neck, broader visage, the greater space between the ears and its longer tail. However, the Eurasian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (''Salmo'') and North Pacific (''Oncorhynchus'') basins. ''Salmon'' is a colloquial or common name used for fish in this group, but is not a scientific name. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen, all coldwater fish of the subarctic and cooler temperate regions with some sporadic endorheic populations in Central Asia. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the shallow gravel stream bed, beds of freshwater headstreams and spend their juvenile fish, juvenile years in rivers, lakes and freshwater wetlands, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Trout
Sea trout is the common name usually applied to anadromous (sea-run) forms of brown trout (''Salmo trutta''), and is often referred to as ''Salmo trutta'' morpha ''trutta''. Other names for anadromous brown trout are bull trout, sewin (Wales), peel or peal (southwest England), mort (northwest England), finnock (Scotland), white trout (Ireland) and salmon trout (culinary). The term "sea trout" is also used to describe other anadromous salmonids, such as coho salmon (''Oncorhynchus kisutch''), coastal cutthroat trout (''Oncorhynchus clarkii clarkii''), brook trout (''Salvelinus fontinalis''), Arctic char (''Salvelinus alpinus alpinus'') and Dolly Varden (''Salvenlinus malma''). Even some non-salmonid fish species are also commonly known as sea trout, such as Northern pikeminnow (''Ptychocheilus oregonensis'') and members of the weakfish family (''Cynoscion''). Range Anadromous brown trout are widely distributed in Europe along the Atlantic and Baltic coasts, the United Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trout
Trout (: trout) is a generic common name for numerous species of carnivorous freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of which are members of the subfamily Salmoninae in the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used for some similar-shaped but non-salmonid fish, such as the spotted seatrout/speckled trout (''Cynoscion nebulosus'', which is actually a croaker). Trout are closely related to salmon and have similar migratory life cycles. Most trout are strictly potamodromous, spending their entire lives exclusively in freshwater lakes, rivers and wetlands and migrating upstream to spawn in the shallow gravel beds of smaller headwater creeks. The hatched fry and juvenile trout, known as ''alevin'' and ''parr'', will stay upstream growing for years before migrating down to larger waterbodies as maturing adults. There are some anadromous species of trout, such as the steelhead (a coastal subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |