|
Rigvedic Dialogue Hymns
The Rigveda contains a number of dialogue hymns ('s) in the form of dialogues, representing the earliest surviving sample of this genre. It can be argued to be an early precursor of Indian classical drama. They are found in the youngest part of the Rigveda ( RV 1 and RV 10), dating to roughly the 12th to 10th centuries BC, with the exception of the older River hymn ( RV 3.33), where the rivers answer in reply to Vishvamitra's prayer. *1.179 Agastya and Lopamudra (5 trishtubhs, 1 brhati) *3.33 Vishvamitra and the Rivers (12 trishtubhs, 1 anushtubh) *10.10: dialogue of Yama and Yami (12 anushtubhs) *10.51 Agni and the gods (9 trishtubhs) *10.86 Indrani, Indra, the "he-ape" Vrshakapi and his wife *10.95: dialogue of Pururavas and Urvashi (18 trishtubhs) *10.183: dialogue between the sacrificer and his wife (3 trishtubhs) See also * Gambler's Lament (a Rigvedic "monologue" hymn) References {{DEFAULTSORT:Rigvedic Dialogue Hymns Dialogue Dialogue (sometimes spelled dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Shakala Shakha, Śakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum. The ''Rigveda'' is the oldest known Vedic Sanskrit text. Its early layers are among the oldest extant texts in any Indo-European language. Most scholars believe that the sounds and texts of the ''Rigveda'' have been orally transmitted with precision since the 2nd millennium BCE, through Indian mathematics#Styles of memorisation, methods of memorisation of exceptional complexity, rigour and fidelity, though the dates are not confirmed and remain contentious till concrete evidence surfaces. Philolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
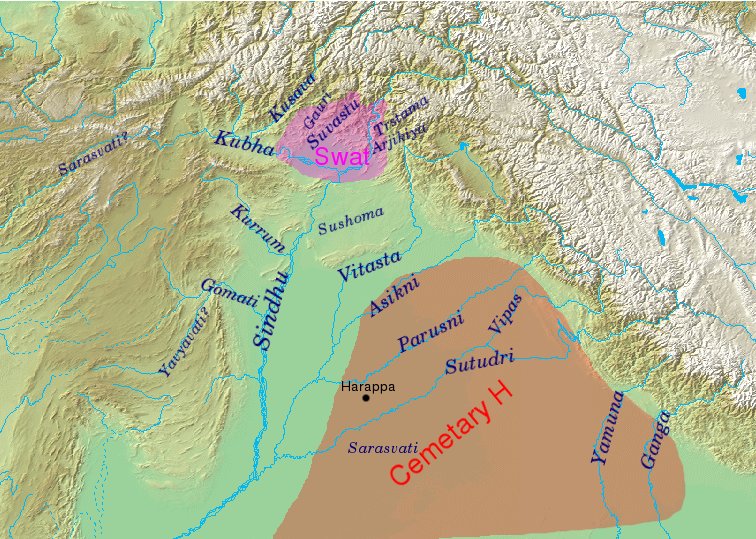
Rigvedic Rivers
The Rigveda refers to a number of rivers located in the northwestern Indian subcontinent, from Gandhara to Kurukshetra. Rigvedic geography Identification of Rigvedic hydronyms has engaged multiple historians; it is the single most important way of establishing the geography and chronology of the early Vedic period. Rivers with certain identifications stretch from eastern Afghanistan to the western Gangetic plain, clustering in the Punjab. The Rigveda mentions the ''sapta-sindhavaḥ'' (, seven rivers), along with other rivers: ''Sapta-sindhavaḥ'' is cognate with Avestan ''hapta həndu'', and is interpreted as referring to Punjab. The region's name comes from پنج, ''panj'', 'five' and آب, ''āb'', 'water' thus " five waters", a Persian calque of the Indo-Aryan ''Pancha-nada'' meaning "five rivers". The same names were often imposed on different rivers as the Vedic culture migrated eastward from around Afghanistan (where they stayed for a considerable time) to the subc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
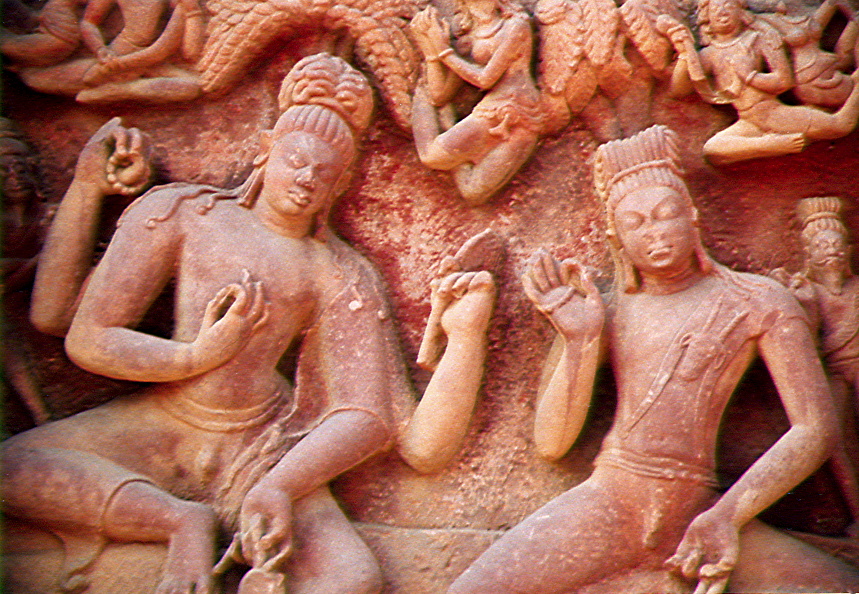
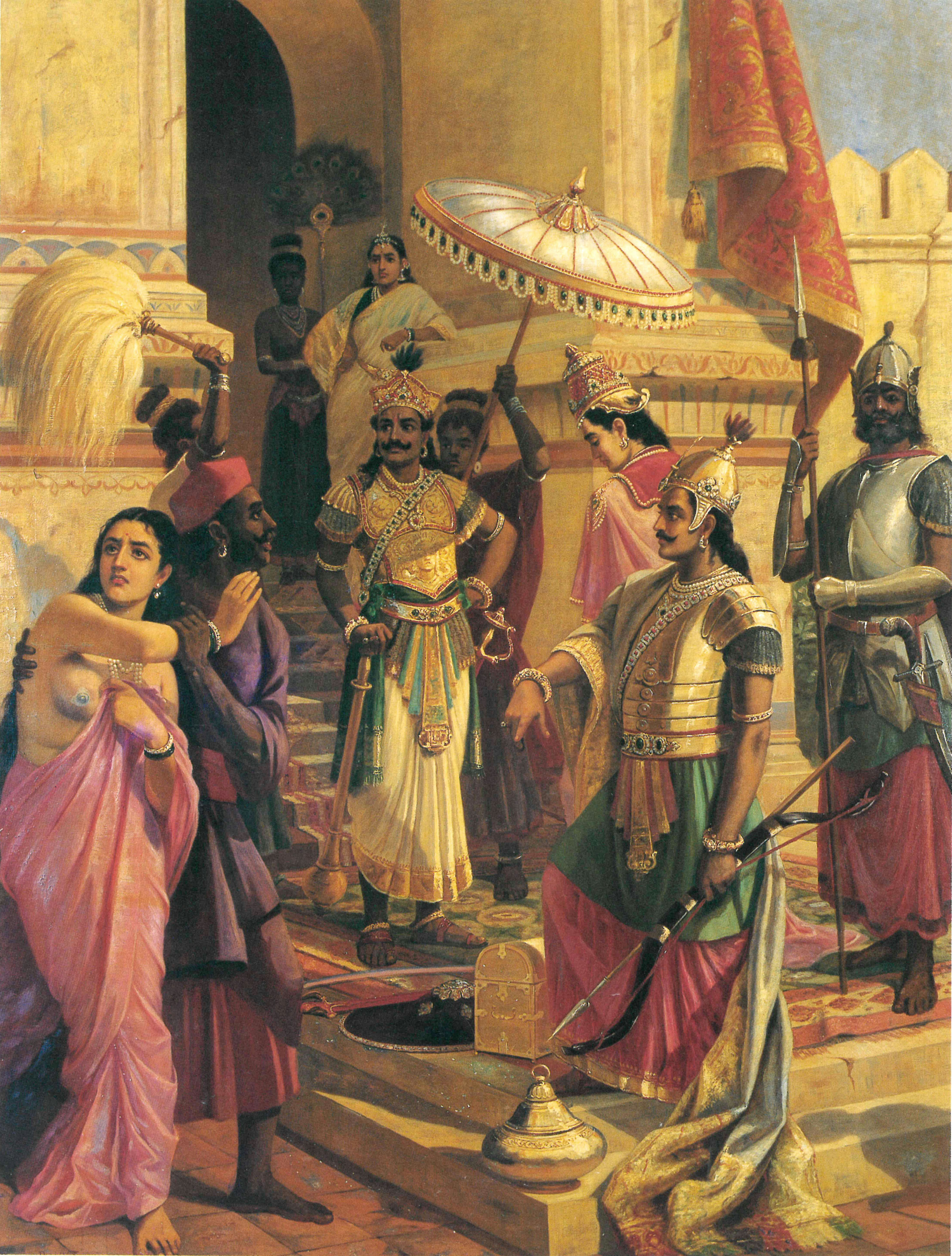
Urvashi
Urvashi (, ) is the most prominent apsara mentioned in the Hindu scriptures like the ''Vedas'', the epics ''Ramayana'' and ''Mahabharata'', as well as the ''Puranas''. She is regarded as the most beautiful of all the apsaras, and an expert dancer. Urvashi has been featured in many mythological events. She emerged out of the thigh of sage Narayana and occupies a special place in the court of Indra, the king of the gods and ruler of svarga. She is famous for her marriage with Pururavas, the first king of the legendary ''Chandravamsha'', whom she later abandoned. She also plays a significant part in the birth of Vashishtha and Agastya, two of the most revered sages in Hinduism. Urvashi's story has been an inspiration for various arts, performances and literature. The poet Kalidasa (fl. 4th -5th century CE) has adapted Urvashi and Pururavas as the main characters in his play Vikramorvashiyam. Etymology The Sanskrit name ''"Urvaśī"'' is derived from roots''uru'' and ''aś''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pururavas
Pururavas (Sanskrit: पुरूरवस्, ''Purūravas'') is a character in Hindu literature, a king who served as the first of the Lunar dynasty. According to the Vedas, he is a legendary entity associated with Surya (the sun) and Usha (the dawn), and is believed to reside in the middle region of the cosmos. The Rig Veda (X.95.18) states that he was a son of Ilā and was a pious ruler. However, the ''Mahabharata'' states that Ila was both his mother and his father. According to the ''Vishnu Purana'', his father was Budha, and he was ancestor of the tribe of Pururavas, from whom descended the Yadavas, Kauravas, and Pandavas of Mahābhārata. Legends Birth and early life Pururavas was born in Treta Yuga, as the son of Budha and Ila. Budha was the son of Chandra, the moon god, and thus Pururavas was the first Chandravamsha King. Since he was born on Mount Puru, he was called Pururavas. Reign According to the Puranas, Pururavas reigned from Pratisthana (Prayaga). He perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vrshakapi
Vrishakapi (Sanskrit: वृषाकपिः, IAST: ''Vṛṣākapi'') is a name found in vedic texts which in later texts is known as an alternative name of either Vishnu, Rudra or Surya Surya ( ; , ) is the Sun#Dalal, Dalal, p. 399 as well as the solar deity in Hinduism. He is traditionally one of the major five deities in the Smarta tradition, Smarta tradition, all of whom are considered as equivalent deities in the Panchaya .... References External links Story of Vrishakapi Creator gods Destroyer gods Hindu eschatology Hindu gods {{Hinduism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Indra
Indra (; ) is the Hindu god of weather, considered the king of the Deva (Hinduism), Devas and Svarga in Hinduism. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. [3 volumes] Indra is the most frequently mentioned deity in the ''Rigveda''. He is celebrated for his powers based on his status as a god of order, and as the one who killed the great evil, an Asura (Hinduism), asura named Vritra, who obstructed human prosperity and happiness. Indra destroys Vritra and his "deceiving forces", and thereby brings rain and sunshine as the saviour of mankind. Indra's significance diminishes in the post-Vedic Indian literature, but he still plays an important role in various mythological events. He is depicted as a powerful hero. According to the ''Vishnu Purana'', Indra is the title borne by the king of the gods, which changes every Manvantara – a cyclic period of time in Hindu cosmology. Each Manvantara has its own Indra and the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sachi
Indrani (Sanskrit: इन्द्राणी, IAST: ''Indrāṇī''), also known as Shachi (Sanskrit: शची, IAST: ''Śacī''), is the queen of the devas in Hinduism. Described as tantalisingly beautiful, proud and kind, she is the daughter of the asura Puloman and the consort of the king of the devas, Indra. According to legend, due to her heavenly beauty and sensuality, Indrani was desired by many men, many of whom tried to marry her. When Indra was away performing his penance for the slaying of Vritasura, Nahusha, a mortal king of the Lunar dynasty, was chosen as the ruler of heaven. The latter tried to seduce Shachi and make her his queen, though she cleverly executed a scheme to dethrone him and later reunite with her husband. Indrani (or Aindri) is also one of the Sapta Matrika—the seven divine mothers. She is an important goddess in Shaktism, a major sect of Hinduism. Indrani is rarely worshipped as an independent deity and is most often worshipped with I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Agni
Agni ( ) is the Deva (Hinduism), Hindu god of fire. As the Guardians of the directions#Aṣṭa-Dikpāla ("Guardians of Eight Directions"), guardian deity of the southeast direction, he is typically found in southeast corners of Hindu temples. In the Hindu cosmology, classical cosmology of Hinduism, fire (''Agni'') is one of the five inert impermanent elements (''Pancha Bhuta, Pañcabhūtá'') along with sky (''Ākāśa''), water (''Apas''), air (''Vāyu'') and earth (''Pṛthvī''), the five combining to form the empirically perceived material existence (''Prakṛti''). In the Vedas, Agni is a major and most invoked god along with Indra and Soma (deity), Soma. Agni is considered the mouth of the gods and goddesses and the medium that conveys offerings to them in a ''homa (ritual), homa'' (votive ritual). He is conceptualized in ancient Hindu texts to exist at three levels, on earth as fire, in the atmosphere as lightning, and in the sky as the sun. This triple presence accords ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yama And Yami
Yama (), also known as Kāla and Dharmarāja, is the Hindu god of death and justice, responsible for the dispensation of law and punishment of sinners in his abode, Naraka. He is often identified with Dharmadeva, the personification of ''Dharma'', though the two deities have different origins and myths. In Vedic tradition, Yama was considered the first mortal who died and espied the way to the celestial abodes; as a result, he became the ruler of the departed. His role, characteristics, and abode have been expounded in texts such as the ''Upanishads'', the ''Ramayana'', the ''Mahabharata'', and the ''Puranas''. Yama is described as the twin of the goddess Yami, and the son of the god Surya (sun) (in earlier traditions Vivasvat) and Sanjna. He judges the souls of the dead and, depending on their deeds, assigns them to the realm of the Pitris (forefathers), Naraka (hell), or to be reborn on the earth. Yama is one of the Lokapalas (guardians of the realms), appointed as the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vishvamitra
Vishvamitra (, ) is one of the most venerated rishis or sages of ancient India. Vishvamitra is one of the seven Brahmarshi. According to Hindu tradition, he is stated to have written most of the Mandala 3 of the Rigveda, including the Gayatri Mantra (3.62.10). The Puranas mention that only 24 rishis since antiquity have understood the whole meaning of —and thus wielded the whole power of — the Gayatri Mantra. Vishvamitra is supposed to have been the first, and Yajnavalkya the last. Before renouncing his kingdom and royal status, Brahmarishi Vishvamitra was a king, and thus he retained the title of Rajarshi, or 'royal sage'. Textual background Historically, Viśvāmitra Gāthina was a Rigvedic rishi who was the chief author of Mandala 3 of the Rigveda. Viśvāmitra was taught by Jamadagni Bhārgava. He was the purohita of the Bharata tribal king Sudās, until he was replaced by Vasiṣṭha. He aided the Bharatas in crossing the Vipāśa and Śutudrī rivers (mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dialogue
Dialogue (sometimes spelled dialog in American and British English spelling differences, American English) is a written or spoken conversational exchange between two or more people, and a literature, literary and theatrical form that depicts such an exchange. As a philosophy, philosophical or didactic device, it is chiefly associated in the West with the Socratic dialogue as developed by Plato, but antecedents are also found in other traditions including Indian literature. Etymology The term ''dialogue'' stems from the Greek language, Greek (, ); its roots are (, ) and (, ). The first extant author who uses the term is Plato, in whose works it is closely associated with the art of dialectic. Latin took over the word as . As genre Antiquity Dialogue as a genre in the Middle East and Asia dates back to ancient works, such as Sumerian disputations preserved in copies from the late third millennium BC, Rigvedic dialogue hymns, and the ''Mahabharata''. In the West, Plato ( BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |