|
Ribosomal Pause
Ribosomal pause refers to the queueing or stacking of ribosomes during translation of the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of mRNA transcripts. These transcripts are decoded and converted into an amino acid sequence during protein synthesis by ribosomes. Due to the pause sites of some mRNA's, there is a disturbance caused in Translation (biology), translation. Ribosomal pausing occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. A more severe pause is known as a ribosomal stall. It's been known since the 1980s that different mRNAs are translated at different rates. The main reason for these differences was thought to be the concentration of varieties of rare tRNAs limiting the rate at which some transcripts could be decoded. However, with research techniques such as ribosome profiling, it was found that at certain sites there were higher concentrations of ribosomes than average, and these pause sites were tested with specific codons. No link was found between the occupancy of spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Syn
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Dalton (unit), Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biopolymer, biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligand (biochemistry), ligands such as coenzymes and cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed Residue (chemistry)#Biochemistry, residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as Transfer RNA, transfer RNA (tRNA) and Small nuclear RNA, small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional List of RNAs, non-coding RNA. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and viruses—to generate the macromolecule, macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, ''i.e.'' observable trait. The genetic information stored in DNA represents the genotype, whereas the phenotype results from the "interpretation" of that informati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
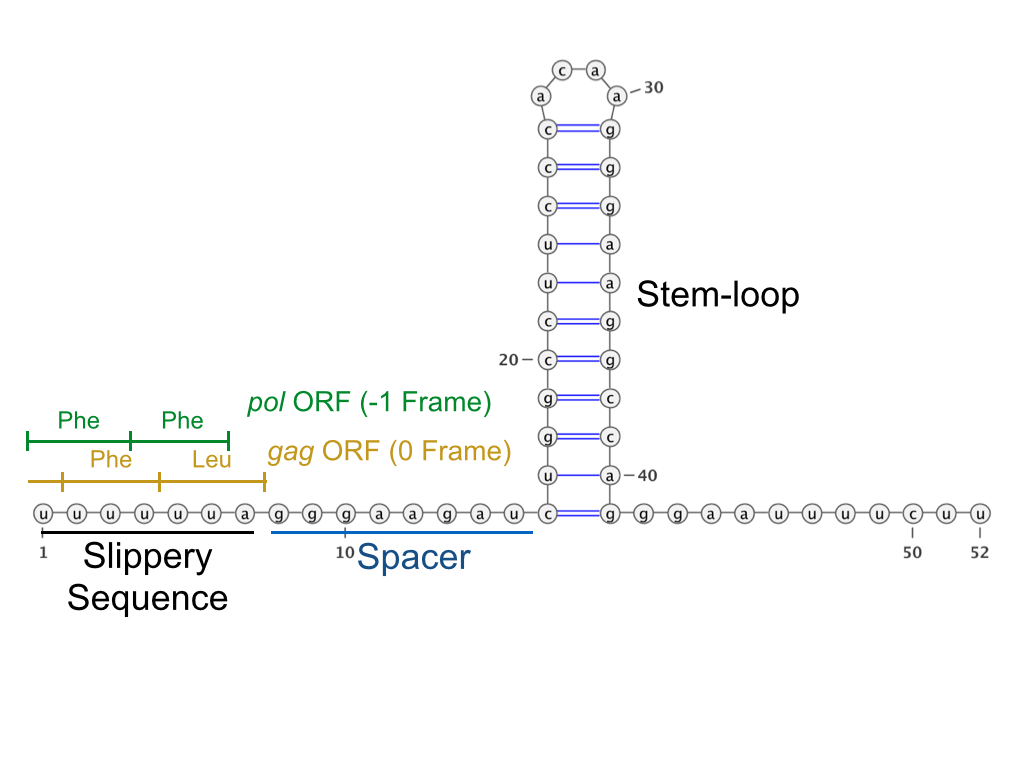
Ribosomal Frameshift
Ribosomal frameshifting, also known as translational frameshifting or translational recoding, is a biological phenomenon that occurs during translation that results in the production of multiple, unique proteins from a single mRNA. The process can be programmed by the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and is sometimes affected by the secondary, 3-dimensional mRNA structure. It has been described mainly in viruses (especially retroviruses), retrotransposons and bacterial insertion elements, and also in some cellular genes. Small molecules, proteins, and nucleic acids have also been found to stimulate levels of frameshifting. In December 2023, it was reported that ''in vitro''-transcribed (IVT) mRNAs in response to BNT162b2 (Pfizer–BioNTech) anti-COVID-19 vaccine caused ribosomal frameshifting. Process overview Proteins are translated by reading tri-nucleotides on the mRNA strand, also known as codons, from one end of the mRNA to the other (from the 5' to the 3' end) starting wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus Frameshifting Stimulation Element
In molecular biology, the coronavirus frameshifting stimulation element is a conserved stem-loop of RNA found in coronaviruses that can promote ribosomal frameshifting. Such RNA molecules interact with a downstream region to form a pseudoknot structure; the region varies according to the virus but pseudoknot formation is known to stimulate frameshifting. In the classical situation, a sequence 32 nucleotides downstream of the stem is complementary to part of the loop. In other coronaviruses, however, another stem-loop structure around 150 nucleotides downstream can interact with members of this family to form kissing stem-loops and stimulate frameshifting. Other RNA families identified in the coronavirus include the coronavirus 3′ stem-loop II-like motif (s2m), the coronavirus packaging signal and the coronavirus 3′ UTR pseudoknot. During protein synthesis, rapidly changing conditions in the cell can cause ribosomal pausing. In coronaviruses, this can affect growth rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translational Frameshift
Ribosomal frameshifting, also known as translational frameshifting or translational recoding, is a biological phenomenon that occurs during translation that results in the production of multiple, unique proteins from a single mRNA. The process can be programmed by the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and is sometimes affected by the secondary, 3-dimensional mRNA structure. It has been described mainly in viruses (especially retroviruses), retrotransposons and bacterial insertion elements, and also in some cellular genes. Small molecules, proteins, and nucleic acids have also been found to stimulate levels of frameshifting. In December 2023, it was reported that ''in vitro''-transcribed (IVT) mRNAs in response to BNT162b2 (Pfizer–BioNTech) anti-COVID-19 vaccine caused ribosomal frameshifting. Process overview Proteins are translated by reading tri-nucleotides on the mRNA strand, also known as codons, from one end of the mRNA to the other (from the 5' to the 3' end) starting wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcriptome
The transcriptome is the set of all RNA transcripts, including coding and non-coding, in an individual or a population of cells. The term can also sometimes be used to refer to all RNAs, or just mRNA, depending on the particular experiment. The term ''transcriptome'' is a portmanteau of the words ''transcript'' and ''genome''; it is associated with the process of transcript production during the biological process of transcription. The early stages of transcriptome annotations began with cDNA libraries published in the 1980s. Subsequently, the advent of high-throughput technology led to faster and more efficient ways of obtaining data about the transcriptome. Two biological techniques are used to study the transcriptome, namely DNA microarray, a hybridization-based technique and RNA-seq, a sequence-based approach. RNA-seq is the preferred method and has been the dominant transcriptomics technique since the 2010s. Single-cell transcriptomics allows tracking of transcript change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoknot
__NOTOC__ A pseudoknot is a nucleic acid secondary structure containing at least two stem-loop structures in which half of one stem is intercalated between the two halves of another stem. The pseudoknot was first recognized in the turnip yellow mosaic virus in 1982. Pseudoknots fold into knot-shaped three-dimensional conformations but are not true topological knots. These structures are categorized as cross (X) topology within the circuit topology framework, which, in contrast to knot theory, is a contact-based approach. Prediction and identification The structural configuration of pseudoknots does not lend itself well to bio-computational detection due to its context-sensitivity or "overlapping" nature. The base pairing in pseudoknots is not well nested; that is, base pairs occur that "overlap" one another in sequence position. This makes the presence of pseudoknots in RNA sequences more difficult to predict by the standard method of dynamic programming, which use a recur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome Structure Including Subunits And Binding Sites
Ribosomes () are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain via an anticodon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HBS1L
HBS1 like translational GTPase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HBS1L gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... Function This gene encodes a member of the GTP-binding elongation factor family. It is expressed in multiple tissues with the highest expression in heart and skeletal muscle. The intergenic region of this gene and the MYB gene has been identified to be a quantitative trait locus (QTL) controlling fetal hemoglobin level, and this region influences erythrocyte, platelet, and monocyte counts as well as erythrocyte volume and hemoglobin content. DNA polymorphisms at this region associate with fetal hemoglobin levels and pain crises in sickle cell disease. A single nucleotide polymorphism in exon 1 of this gene is significantly associated with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PELO
Pelo is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Brad Pelo Brad Pelo (born February 6, 1963) is an American businessman, entrepreneur, and co-founder and chief executive officer of i.TV, the company behind tvtag, a second screen app for iOS. Backed by Union Square Ventures, RRE Ventures, Rho Ventures ... (born 1963), American businessman * Dimitri Pelo (born 1985), French rugby league player * Vincent Pelo (born 1988), French rugby union player See also * PELO, a protein * Pelo Madueño (born 1968), Peruvian musician and actor * * {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |