|
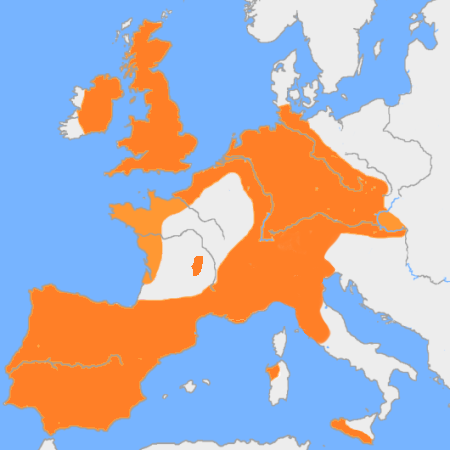
Rhône Culture
The Rhône culture was an archaeological culture of the Early Bronze Age (-1500 BC) located in eastern France and western Switzerland, centred along the Rhône river. The culture developed from the local Bell Beaker culture, possibly with further migrations from central Europe. According to Sergent (1995) the Rhône culture represents a southern variant of the Unetice culture. Rhône culture metalwork and pottery are particularly similar to those of the Straubing group in Bavaria. Artefacts and characteristics The Thun-Renzenbühl axe (), found near Thun and attributed to the Rhône culture, is one of the earliest examples of the use of damascening technique in the world. The gold inlay decoration on the axe may also have a numerical, astronomical meaning. Gallery File:Rhodanian knife-MGR Lyon-IMG 9738.jpg File:Poignard et hache en bronze - Solliès Pont - Var.jpg File:Vollgriffdolch von Döttingen.jpg File:Età del bronzo arcaica, pugnali, 2200-1600 ac ca..JPG File:Rhon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascening
Damascening is the art of inlaying different metals into one another—typically, gold or silver into a darkly oxidized steel background—to produce intricate patterns similar to niello. The English term comes from a perceived resemblance to the rich tapestry patterns of damask silk. The term is also used to describe the use of inlaid copper interconnects in integrated circuits. As its name suggests, damascene gets its name from Damascus, Syria and the ancient artisans that created and exported this craft. Background The technique, while also being used on firearms, has a long history in Japan, where it was used to decorate katana fittings, particularly tsuba. Known as zougan (象嵌) in Japanese, it has developed its own subset of terms to describe the particular patterns, although "shippou-zougan" is an enamelling technique which most Westerners would consider closer to champlevé. Damascened-inlay jewelry, especially of Japanese origin, is sometimes referred to as shakudo f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Cultures Of Europe
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloids (such as arsenic or silicon). These additions produce a range of alloys some of which are harder than copper alone or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period during which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age, which started about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures Of Europe
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Bronze Age
The Nordic Bronze Age (also Northern Bronze Age, or Scandinavian Bronze Age) is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from . The Nordic Bronze Age culture emerged about 1750 BC as a continuation of the Late Neolithic Dagger period, which is rooted in the Battle Axe culture (the Swedish-Norwegian Corded Ware variant), the Single Grave Culture (the north German and Danish Corded Ware varaiant) and Bell Beaker culture, as well as from influence that came from Central Europe. This influence most likely came from people similar to those of the Únětice culture, since they brought customs that were derived from Únětice or from local interpretations of the Únětice culture located in North Western Germany. The metallurgical influences from Central Europe are especially noticeable. The Bronze Age in Scandinavia can be said to begin shortly after 2000 BC with the introduction and use of bronze tools, followed by a more systematic adoption of bronze metalworking technology from 175 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wietenberg Culture
The Wietenberg culture was a Bronze Age Europe, Middle Bronze Age archeological culture in central Romania (Prehistory of Transylvania, Transylvania) that roughly dates to 2200–1600/1500 BCE. Representing a local variant of Usatove culture, it was contemporary with the Ottomány culture and Unetice culture and was replaced by the Noua-Sabatinovka-Coslogeni complex, Noua culture. Its name was coined after the eponymic Wietenberg Hill near Sighișoara. People of this culture traded with the Mycenaeans. Burial sites contain bronze battle axes and maces with stone heads. Pottery consists of amphorae with spiral and meandric ornament. By 1964, about 200 settlements of this culture were discovered. Gallery File:Wietenberg culture axes at National Museum of Transylvanian History 2007.jpg, Battle axes from Valea Chioarului, Maramureș County (National Museum of Transylvanian History in Cluj) File:Wientenberg gold bracelet 2.jpg, Gold bracelet (from pre-WWI book plate) File:Wiete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottomány Culture
The Ottomány culture, also known as Otomani culture in Romania or Otomani-Füzesabony culture in Hungary, was an early Bronze Age culture (–1400 BC) in Central Europe named after the eponymous site near the village of Ottomány (), today part of Sălacea, located in modern-day Bihor County, Romania. The Middle Bronze Age period of the Ottomány culture in eastern Hungary and western Romania ( to 1400 BC) is also known as the Gyulavarsánd culture. Territorial extent The Ottomány culture was located in eastern Hungary, eastern Slovakia, Crișana in western Romania, western Ukraine - Transcarpatia (Zakarpattia Oblast - within a stretch of the Carpathian Mountains) and southeast Poland (stretch of Carpathian Mountains and nearby areas). Thus, people of the Ottomány culture secured a middle stretch of what will be later known as the Amber Road, and indeed, amber is often found in Ottomány sites. The expansion of the Ottomány culture is associated with the end of the Hatvan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenean Bronze
The Pyrenean Bronze (also known as Northeastern Bronze) is a regional European Bronze Age culture, known from archaeological facies, that spread through the Spanish provinces of Girona, Barcelona, Lleida and the eastern half of Huesca; also it spread through the French departments of the Pyrenees-Orientales and Aude. From the Bell Beaker culture (2750-2300 BC), two regional styles appeared in Catalonia, one being the Pyrenean and the other the Salomó (from which the North-East Group was derived). These two styles coexisted at the same time in the provinces of Barcelona and the south of Lleida. From 1650 A.C. the Pyrenean ceramic style gave way to carinated cups, to pots with smooth or digitated cords, as well as to vessels with button appendages on the handle. Few settlements are known: Lo Lladre (Llo, Pyrenees-Orientales), Collet de Brics (Ardèvol, Lleida), Institut A. Pous (Manlleu, Barcelona), Roques del Sarró (Lleida), Cedre (Santa Coloma, Andorra). Advanced bronze met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polada Culture
The Polada culture (22nd to 16th centuries BCE) is the name for a culture of the ancient Bronze Age which spread primarily in the territory of modern-day Lombardy, Veneto and Trentino, characterized by settlements on pile-dwellings. The name derives from the small Polada peat bog (''Stagno della Polada'') in Lombardy, between Lonato del Garda, Menasasso, and Desenzano del Garda. The first findings attributed to this culture were discovered in the years between 1870 and 1875 as a result of intense activities of reclamation in that bog, and were collected by Giovanni Rambotti. The dating of carbon-14 on the finds place them between c. 1380 BCE and c. 1270 BCE. Other major sites are found in the area between Mantua, the Lake Garda and the Lake of Pusiano. It was succeeded in the Middle Bronze Age by the facies of the pile dwellings and of the dammed settlements and the Terramare culture. Chronology The Polada culture is usually assigned to the period from 2200 to 1500 BCE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armorican Tumulus Culture
The Armorican Tumulus culture is a Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age culture, located in the western part of the Armorican peninsula of France. It is known through more than a thousand burial sites covered by a tumulus or otherwise. The culture is renowned for some exceptionally richly endowed burials of chieftains of the time, which are contemporary with the elite of the Wessex culture, in England, and the Únětice culture, in Central Europe. The extensive documentation of this funerary archaeology has been supplemented by the discovery of various types of habitat (dry stone houses, open air habitats, monumental enclosures, etc.) Overview The Armorican Tumuli refer to individual burials of the Bronze Age that can be covered by a tumulus in the western part of the Armorican peninsula of France, in a region commonly called Lower Brittany. Not all the tumuli of Brittany belong to the Armorican Tumulus culture. Older tumuli in the area date from the Neolithic Europe, Neolithi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Britain
Bronze Age Britain is an era of British history that spanned from until . Lasting for approximately 1,700 years, it was preceded by the era of Neolithic Britain and was in turn followed by the period of Iron Age Britain. Being categorised as the Bronze Age, it was marked by the use of copper and then bronze by the prehistoric Britons, who used such metals to fashion tools. Great Britain in the Bronze Age also saw the widespread adoption of agriculture. During the British Bronze Age, large megalithic monuments similar to those from the Late Neolithic continued to be constructed or modified, including such sites as Avebury, Stonehenge, Silbury Hill and Must Farm. That has been described as a time "when elaborate ceremonial practices emerged among some communities of subsistence agriculturalists of western Europe". History Early Bronze Age (EBA), c. 2500–1500 BC There is no clear consensus on the date for the beginning of the Bronze Age in Great Britain and Ireland. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Cross
A sun cross, solar cross, or wheel cross is a solar symbol consisting of an equilateral cross inside a circle. The design is frequently found in the symbolism of prehistoric cultures, particularly during the Neolithic to Bronze Age periods of European prehistory. The symbol's ubiquity and apparent importance in prehistoric religion have given rise to its interpretation as a solar symbol, whence the modern English term "sun cross" (a calque of ). The symbol means ''village'' in Ancient Egyptian ( Gardiner symbol O49). One of the most famous examples of prehistoric rock carvings in Northern Europe is the sun cross with cup marks at Madsebakke, near Allinge on Bornholm Island, Denmark. These petroglyphs date back to the Bronze Age (c. 1800–500 BCE) and are among the best-preserved in Scandinavia. The big wheel sun cross, carved directly into granite bedrock, is a striking circular motif with radial arms – often interpreted as a solar symbol representing the movement of the sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |