|
Rhäzüns Castle
Rhäzüns Castle () is a castle near Rhäzüns, Graubünden, Switzerland. History Rhäzüns Castle may be one of the oldest castles in Switzerland. In 960 Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto I traded a church ''in castello Beneduces et Ruzunnes'' (in the castle of Bonaduz and Rhäzüns) to the Bishop of Chur and a 976 document by Otto II, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto II confirms the trade and the existence of the castle. Over the following centuries the fortified church became a feudal castle and in 1139 Arnoldus de Ruzunne appears in the records as a Romansh people, Romansh noble, though the castle is first mentioned in 1282. During the 12th and 13th centuries the Rhäzüns family grew to become one of the most powerful noble families in the region, with Rhäzüns Castle remaining the center of their power. In 1343 they were powerful enough that a peace treaty between Disentis Abbey and Glarus was signed in the courtyard of Rhäzüns. By the 1380s they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Castle
A hill castle or mountain castle is a castle built on a natural feature that stands above the surrounding terrain. It is a term derived from the German ''Höhenburg'' used in categorising castle sites by their topographical location. Hill castles are thus distinguished from lowland castles (''Niederungsburgen''). Hill castles may be further subdivided depending on their situation into the following: * Hilltop castle (''Gipfelburg''), that stands on the summit of a hill with steep drops on all sides. A special type is the rock castle or ''Felsenburg''. * Ridge castle (''Kammburg''), that is built on the crest of a ridge. * Hillside castle (''Hangburg''), that is built on the side of a hill and thus is dominated by rising ground on one side. * Spur castle (''Spornburg''), that is built on a hill spur surrounded by steep terrain on three sides and thus only needs to be defended on the one remaining side. When in the 10th and 11th centuries castles lost their pure fortress character a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baron
Baron is a rank of nobility or title of honour, often Hereditary title, hereditary, in various European countries, either current or historical. The female equivalent is baroness. Typically, the title denotes an aristocrat who ranks higher than a lord or knight, but lower than a viscount or count. Often, barons hold their fief – their lands and income – directly from the monarch. Barons are less often the vassals of other nobles. In many kingdoms, they were entitled to wear a smaller form of a crown called a ''coronet''. The term originates from the Late Latin, Latin term , via Old French. The use of the title ''baron'' came to England via the Norman Conquest of 1066, then the Normans brought the title to Scotland and Southern Italy. It later spread to Scandinavian and Slavic lands. Etymology The word '':wikt:baron, baron'' comes from the Old French , from a Late Latin "man; servant, soldier, mercenary" (so used in Salic law; Alemannic law has in the same sense). The sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogt
An , sometimes simply advocate, (German, ), or (French, ), was a type of medieval office holder, particularly important in the Holy Roman Empire, who was delegated some of the powers and functions of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as an abbey. They typically had responsibility for the "comital" functions which defined the office of early medieval "counts", such as taxation, recruitment of militias, and maintaining law and order. This type of office could apply to specific agricultural lands, villages, castles, and even cities. In some regions, advocates came to be governors of large provinces, sometimes distinguished by terms such as . In different parts of medieval Europe, the term advocate developed different meanings, and other terms were also sometimes used to represent similar offices. For example, Anglo-Norman comital functions for larger districts were executed by vicomtes in Normandy, and sheriffs in England. In contrast, the or advocate as an offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
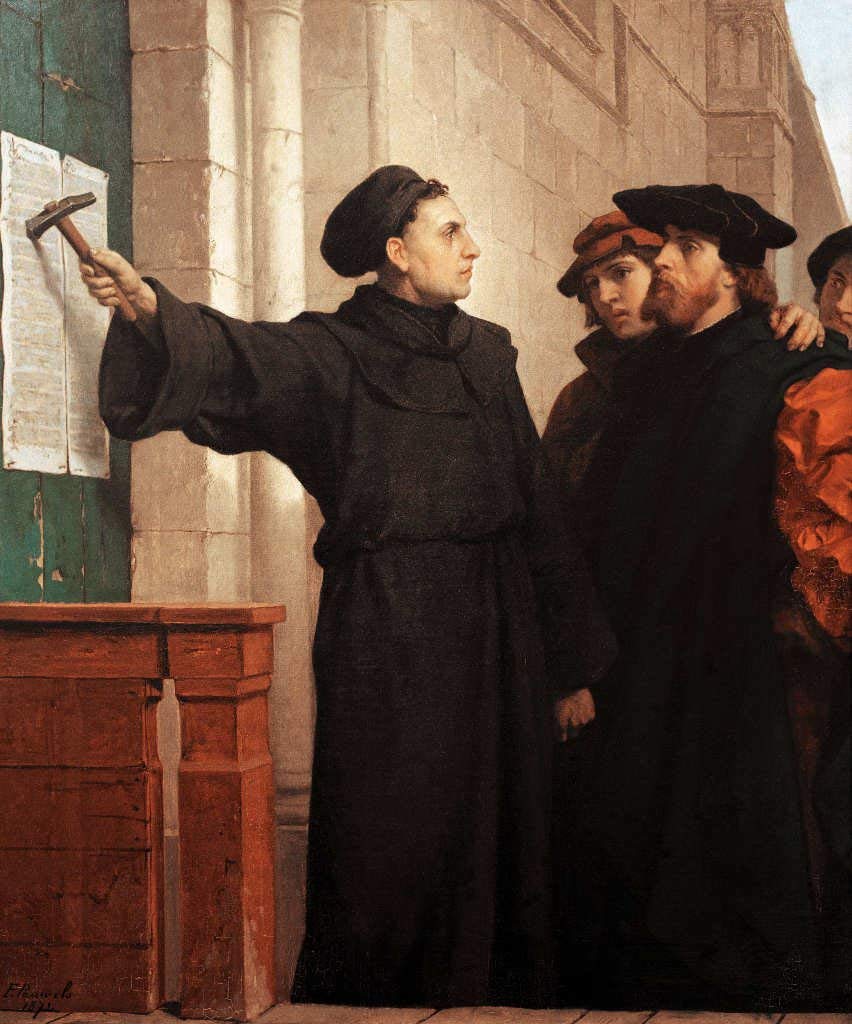
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the papacy and the authority of the Catholic Church. Towards the end of the Renaissance, the Reformation marked the beginning of Protestantism. It is considered one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe. The Reformation is usually dated from Martin Luther's publication of the '' Ninety-five Theses'' in 1517, which gave birth to Lutheranism. Prior to Martin Luther and other Protestant Reformers, there were earlier reform movements within Western Christianity. The end of the Reformation era is disputed among modern scholars. In general, the Reformers argued that justification was based on faith in Jesus alone and not both faith and good works, as in the Catholic view. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stampa Family
The Stampa are a well-known family of old Nobility of Italy, Italian nobility that rose to prominence in the 15th century. They were Grandee, Grandees of Spain, members the Order of the Golden Fleece and owned many estates throughout the Italian Peninsula, including a Soncino's Castle, Castle in Soncino, Lombardy, Soncino, a Palazzo Stampa di Soncino, Milan, Palace in Milan, and countless others in Muggiò, Melzo, Gorgonzola, Milan, Gorgonzola, Rivolta d'Adda, Ferentino and Rome. They are related to some of the most important Italian noble Nobility, houses, such as the Doria (family), Doria, House of Sforza, Sforza, House of Gonzaga, Gonzaga, House of Borromeo, Borromeo and Visconti of Milan, Visconti. Early history The Stampa trace their ancestry back to Carlo Lanfranco of the dukes of Étampes, later governor of Milan under Charlemagne, Charles the Great. His descendants settled in Milan and Gravedona ed Uniti, Gravedona, and ruled over the Val Bregaglia. The best evidence fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinterrhein (river)
The Hinterrhein (; ; ; ; ; ), or Posterior Rhine, is the right of the two initial tributaries of the Rhine (the other being the '' Vorderrhein''). It is located in the canton of Grisons (), Switzerland. One of its upper tributaries is , which is the outflow of Lago di Lei located in Lombardy, Italy. Although it is shorter in length, its volume is larger than that of the ''Vorderrhein'' at their confluence near Reichenau, after which the river is called the Alpine Rhine, which flows out into Lake Constance (). Course Flowing from the village Hinterrhein near the San Bernardino Pass through the Rheinwald valley, the river flows into a gorge called Rofla Gorge (). In this gorge, an equal-sized tributary, the Avers Rhine, adds waters from the deep Val Ferrera and the very remote alp of Avers and its side valley Valle di Lei, located on Italian territory. Below the Rofla Gorge, the valley widens into a section called Schams. The ''Hinterrhein'' then reaches Andee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergfried
''Bergfried'' (plural: ''bergfriede''; English: ''belfry''; French: ''tour-beffroi''; Italian: ''torrione''; Castilian: ''torre del homenaje'') is a tall tower that is typically found in castles of the Middle Ages in German-speaking countries and in countries under German influence. Stephen Friar in the ''Sutton Companion to Castles'' describes a bergfried as a "free-standing, fighting-tower".Friar (2003), p 36. Its defensive function is to some extent similar to that of a keep (also known as a ''donjon'') in English or French castles. However, the characteristic difference between a bergfried and a keep is that a bergfried was typically not designed for permanent habitation. Overview The living quarters of a castle with a bergfried are separate, often in a lower tower or an adjacent building called a ''palas'' (an English-style keep combines both functions of habitation and defence.) Consequently, a bergfried could be built as a tall slender tower with little internal room, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal allegiance, services or payments. The fees were often lands, land revenue or revenue-producing real property like a watermill, held in feudal land tenure: these are typically known as fiefs or fiefdoms. However, not only land but anything of value could be held in fee, including governmental office, rights of exploitation such as hunting, fishing or felling trees, monopolies in trade, money rents and tax farms. There never existed a standard feudal system, nor did there exist only one type of fief. Over the ages, depending on the region, there was a broad variety of customs using the same basic legal principles in many variations. Terminology In ancient Rome, a " benefice" (from the Latin noun , meaning "benefit") was a gift of land () f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Leagues
The Three Leagues, sometimes referred to as Raetia, was the 1471 alliance between the League of God's House, the League of the Ten Jurisdictions, and the Grey League. Its members were all Swiss Associates, associates of the Old Swiss Confederacy, and as such enjoyed positive relations with the Confederation, which eventually led to the formation of the Swiss canton of Grisons. The territory corresponds to the core territory of Raetia Curiensis (ruled by the bishops of Chur as Prince-Bishopric of Chur), the early medieval remnant of the Roman province of Raetia prima. League of God's House On 29 January 1367, the League of God's House (, , ), was founded to resist the rising power of the Bishopric of Chur and the House of Habsburg. Bishop Peter Gelyto reacted by transferring the bishopric to the Habsburgs in exchange for a pension from the ducal house. The instrument of union was signed by envoys of the cathedral chapter, the episcopal Ministerialis, the city of Chur and the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
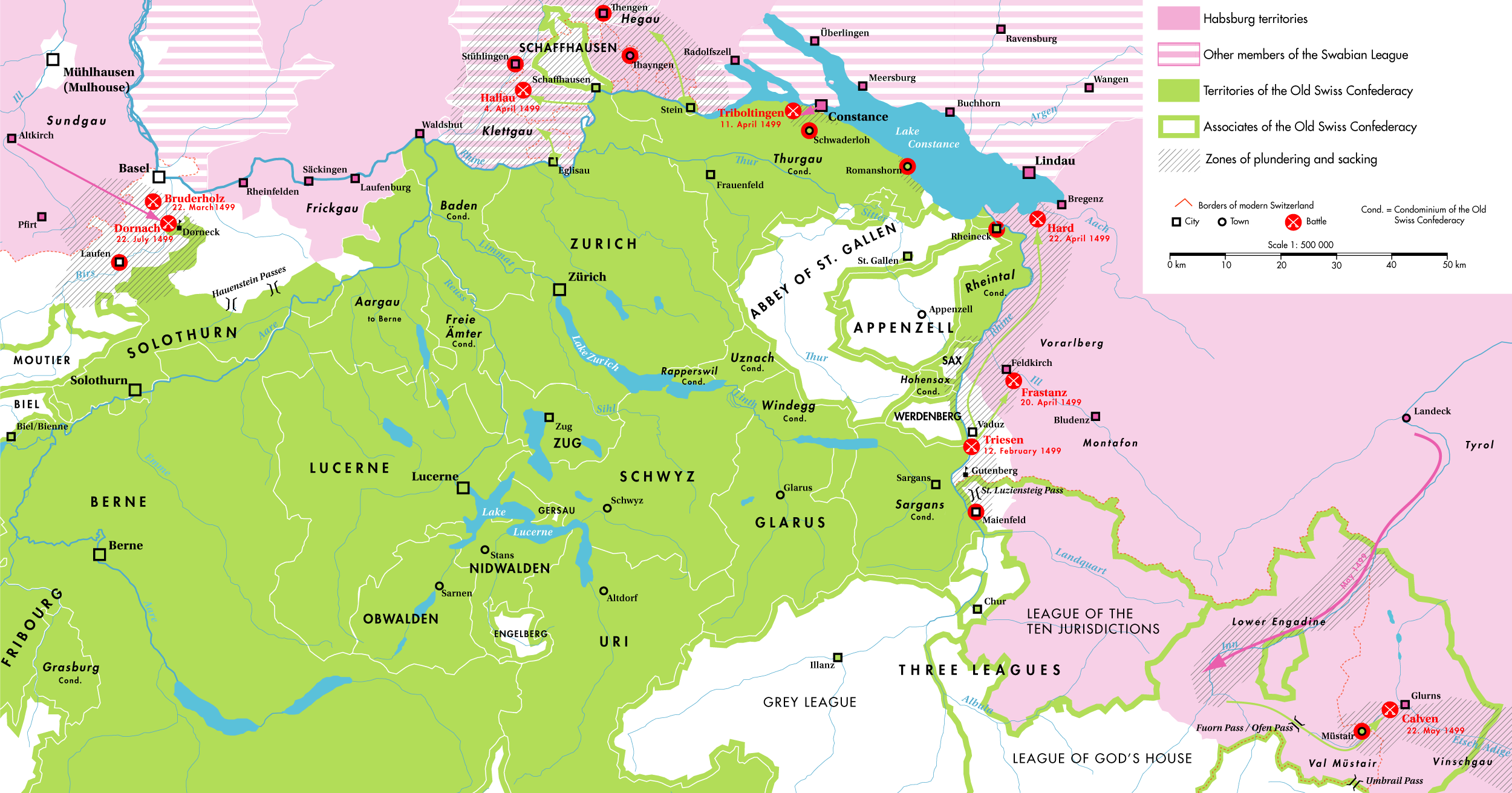
Swabian War
The Swabian War of 1499 ( (spelling depending on dialect), called or ("Swiss War") in Germany and ("War of the Engadin" in Austria) was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of Habsburg. What had begun as a local conflict over the control of the Val Müstair and the Umbrail Pass in the Grisons soon got out of hand when both parties called upon their allies for help; the Habsburgs demanding the support of the Swabian League, while the Federation of the Three Leagues of the Grisons turning to the Swiss '' Eidgenossenschaft''. Hostilities quickly spread from the Grisons through the Rhine valley to Lake Constance and even to the Sundgau in southern Alsace, the westernmost part of the Habsburg region of Further Austria.The main references used are Morard in general and Riezler for the detailed chronology in the section on the course of the war. Many battles were fought from January to July 1499, and in all but a few minor skirmishes, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts Of Werdenberg
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: Barnes & Noble, 1992. p. 73. . Especially in earlier medieval periods the term often implied not only a certain status, but also that the ''count'' had specific responsibilities or offices. The etymologically related English term "county" denoted the territories associated with some countships, but not all. The title of ''count'' is typically not used in England or English-speaking countries, and the term ''earl'' is used instead. A female holder of the title is still referred to as a ''countess'', however. Origin of the term The word ''count'' came into English from the French ', itself from Latin '—in its accusative form ''comitem''. It meant "companion" or "attendant", and as a title it indicated that someone was delegated to rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey League
The Grey League (, , or ), sometimes called ''Oberbund'', formed in 1395 in the '' Vorderrhein'' and '' Hinterrhein'' valleys, Raetia. The name Grey League is derived from the homespun grey clothes worn by the people. The league became part of the canton of Graubünden. The Grey League allied itself to the two other powers of Raetia in 1471, forming the Three Leagues. It was also an associate and ally of the Swiss Confederation and played a role in the buildup to the Thirty Years' War. Foundation In the late twelfth century, the communities in the valleys in Raetia were generally small and independent. There were very few large landholders and no central authority. For years blood feuds and battles had raged between the Lords of Belmont, Werdenberg, Rhäzüns and the Bishop of Chur as well as minor nobles. The constant warfare had seriously damaged trade and transportation in the region. To reduce the violence and encourage trade, the leaders and nobles of the valle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |