|
Rhenium Diboride
Rhenium diboride (ReB2) is a synthetic high-hardness material that was first synthesized in 1962. The compound is formed from a mixture of rhenium, noted for its resistance to high pressure, and boron, which forms short, strong covalent bonds with rhenium. It has regained popularity in recent times in hopes of finding a material that possesses hardness comparable to that of diamond. Unlike other high-hardness synthetic materials, such as the c-BN, rhenium diboride can be synthesized at ambient pressure, potentially simplifying a mass production. However, the high cost of rhenium and commercial availability of alternatives such as polycrystalline c-BN, make a prospect of large-scale applications less likely. Synthesis ReB2 can be synthesized by at least three different methods at standard atmospheric pressure: solid-state metathesis, melting in an electric arc, and direct heating of the elements. In the metathesis reaction, rhenium trichloride and magnesium diboride ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagonal
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°. Regular hexagon A regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral and equiangular. In other words, a hexagon is said to be regular if the edges are all equal in length, and each of its internal angle is equal to 120°. The Schläfli symbol denotes this polygon as \ . However, the regular hexagon can also be considered as the cutting off the vertices of an equilateral triangle, which can also be denoted as \mathrm\ . A regular hexagon is bicentric, meaning that it is both cyclic (has a circumscribed circle) and tangential (has an inscribed circle). The common length of the sides equals the radius of the circumscribed circle or circumcircle, which equals \tfrac times the apothem (radius of the inscribed circle). Measurement The longest diagonal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Diboride
Magnesium diboride is the inorganic compound of magnesium and boron with the formula MgB2. It is a dark gray, water-insoluble solid. The compound becomes superconducting at 39 K (−234 °C), which has attracted attention. In terms of its composition, MgB2 differs strikingly from most low-temperature superconductors, which feature mainly transition metals. Its superconducting mechanism is primarily described by BCS theory. Superconductivity Magnesium diboride's superconducting properties were discovered in 2001. Its critical temperature (''T''c) of is the highest amongst conventional superconductors. Among conventional ( phonon-mediated) superconductors, it is unusual. Its electronic structure is such that there exist two types of electrons at the Fermi level with widely differing behaviours, one of them ( sigma-bonding) being much more strongly superconducting than the other ( pi-bonding). This is at odds with usual theories of phonon-mediated superconductivity which ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spark Plasma Sintering
Spark plasma sintering (SPS), also known as field assisted sintering technique (FAST) or pulsed electric current sintering (PECS), or plasma pressure compaction (P2C) is a sintering technique. The main characteristic of SPS is that the pulsed or unpulsed DC or AC current directly passes through the graphite die, as well as the powder compact, in case of conductive samples. Joule heating has been found to play a dominant role in the densification of powder compacts, which results in achieving near theoretical density at lower sintering temperature compared to conventional sintering techniques. The heat generation is internal, in contrast to the conventional hot pressing, where the heat is provided by external heating elements. This facilitates a very high heating or cooling rate (up to 1000 K/min), hence the sintering process generally is very fast (within a few minutes). The general speed of the process ensures it has the potential of densifying powders with nanosize or nanostruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Fraction (chemistry)
In chemistry, the mass fraction of a substance within a mixture is the ratio w_i (alternatively denoted Y_i) of the mass m_i of that substance to the total mass m_\text of the mixture. Expressed as a formula, the mass fraction is: : w_i = \frac . Because the individual masses of the ingredients of a mixture sum to m_\text, their mass fractions sum to unity: : \sum_^ w_i = 1. Mass fraction can also be expressed, with a denominator of 100, as percentage by mass (in commercial contexts often called ''percentage by weight'', abbreviated ''wt.%'' or ''% w/w''; see mass versus weight). It is one way of expressing the composition of a mixture in a dimensionless size; mole fraction (percentage by moles, mol%) and volume fraction ( percentage by volume, vol%) are others. When the prevalences of interest are those of individual chemical elements, rather than of compounds or other substances, the term ''mass fraction'' can also refer to the ratio of the mass of an element to the tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders, as well as numerous industrial applications. With a Vickers hardness of >30 GPa, it is one of the hardest known materials, behind cubic boron nitride and diamond. History Boron carbide was discovered in the 19th century as a by-product of reactions involving metal borides, but its chemical formula was unknown. It was not until the 1930s that the chemical composition was estimated as B4C. Controversy remained as to whether or not the material had this exact 4:1 stoichiometry, as, in practice the material is always slightly carbon-deficient with regard to this formula, and X-ray crystallography shows that its structure is highly complex, with a mixture of C-B-C chains and B12 icosahedra. These features argued against a very simple exact B4C empirical formula. Because of the B12 structural unit, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
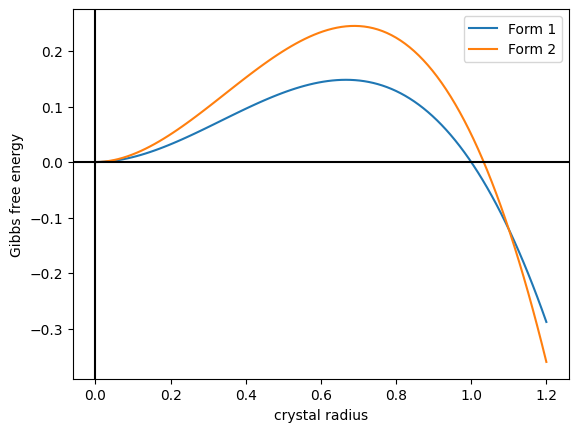
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In crystallography, polymorphism is the phenomenon where a compound or element can crystallize into more than one crystal structure. The preceding definition has evolved over many years and is still under discussion today. Discussion of the defining characteristics of polymorphism involves distinguishing among types of transitions and structural changes occurring in polymorphism versus those in other phenomena. Overview Phase transitions (phase changes) that help describe polymorphism include polymorphic transitions as well as melting and vaporization transitions. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." Additionally, Walter McCrone described the phases in polymorphic matter as "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." McCrone also def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indentation Size Effect
The indentation size effect (ISE) is the observation that hardness tends to increase as the indent size decreases at small scales. When an indent (any small mark, but usually made with a special tool) is created during material testing, the hardness of the material is not constant. At the small scale, materials will actually be harder than at the macro-scale. For the conventional indentation size effect, the smaller the indentation, the larger the difference in hardness. The effect has been seen through nanoindentation and microindentation measurements at varying depths. Dislocations increase material hardness by increasing flow stress through dislocation blocking mechanisms. Materials contain statistically stored dislocations (SSD) which are created by homogeneous strain and are dependent upon the material and processing conditions. Geometrically necessary dislocations (GND) on the other hand are formed, in addition to the dislocations statistically present, to maintain continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zirconium Diboride
Zirconium diboride (ZrB2) is a highly covalent refractory ceramic material with a hexagonal crystal structure. ZrB2 is an ultra-high temperature ceramic (UHTC) with a melting point of 3246 °C. This along with its relatively low density of ~6.09 g/cm3 (measured density may be higher due to hafnium impurities) and good high temperature strength makes it a candidate for high temperature aerospace applications such as hypersonic flight or rocket propulsion systems. It is an unusual ceramic, having relatively high thermal and electrical conductivities, properties it shares with isostructural titanium diboride and hafnium diboride. ZrB2 parts are usually hot pressed (pressure applied to the heated powder) and then machined to shape. Sintering of ZrB2 is hindered by the material's covalent nature and presence of surface oxides which increase grain coarsening before densification during sintering. Pressureless sintering of ZrB2 is possible with sintering additives suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Diboride
Titanium diboride (TiB2) is an extremely hard ceramic which has excellent heat conductivity, oxidation stability and wear resistance. TiB2 is also a reasonable electrical conductor,J. Schmidt et al. "Preparation of titanium diboride TiB2 by spark plasma sintering at slow heating rate" Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 8 (2007) 37free download/ref> so it can be used as a cathode material in aluminium smelting and can be shaped by electrical discharge machining. Physical properties TiB2 shares some properties with boron carbide and titanium carbide, but many of its properties are superior to those of B4C & TiC: Exceptional hardness at extreme temperature *2nd hardest material at 3000°C (diamond) *3rd hardest material at 2800°C (cBN) *4th hardest material at 2100°C ( B4C) *5th hardest material at 1000°C ( B6O) Advantages over other borides *Highest boride elastic modulus *Highest boride fracture toughness *Highest boride compressive strength *3rd highest boride melting point (3230 °C) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A wide bandgap semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal since 1893 for use as an abrasive. Grains of silicon carbide can be bonded together by sintering to form very hard ceramics that are widely used in applications requiring high endurance, such as car brakes, car clutches and ceramic plates in bulletproof vests. Large single crystals of silicon carbide can be grown by the Lely method and they can be cut into gems known as synthetic moissanite. Electronic applications of silicon carbide such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and Cat's whisker detector, detectors in early radios were first demonstrated around 1907. SiC is used in semiconductor electronics devices that operate at high temperatures or high voltages, or both. Natural occurrence Naturally occurring moissanite is found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: ) is a carbide containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into shapes through sintering for use in industrial machinery, engineering facilities, molding blocks, cutting tools, chisels, abrasives, armor-piercing bullets and jewelry. Tungsten carbide is approximately three times as stiff as steel, with a Young's modulus of approximately 530–700 GPa, and is twice as dense as steel. It is comparable with corundum (α- ) in hardness, approaching that of a diamond, and can be polished and finished only with abrasives of superior hardness such as cubic boron nitride and diamond. Tungsten carbide tools can be operated at cutting speeds much higher than high-speed steel (a special steel blend for cutting tools). Tungsten carbide powder was first synthesized by H. Moissan in 1893, and the industrial production of the cemented form starte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Hardness Test
The Vickers hardness test was developed in 1921 by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell scale, Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the indenter, and the indenter can be used for all materials irrespective of hardness. The basic principle, as with all common measures of hardness, is to observe a material's ability to resist plastic deformation from a standard source. The Vickers test can be used for all metals and has one of the widest scales among hardness tests. The unit of hardness given by the test is known as the Vickers Pyramid Number (HV) or Diamond Pyramid Hardness (DPH). The hardness number can be converted into units of pascal (unit), pascals, but should not be confused with pressure, which uses the same units. The hardness number is determined by the load over the surface area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |