|
Rheinardia
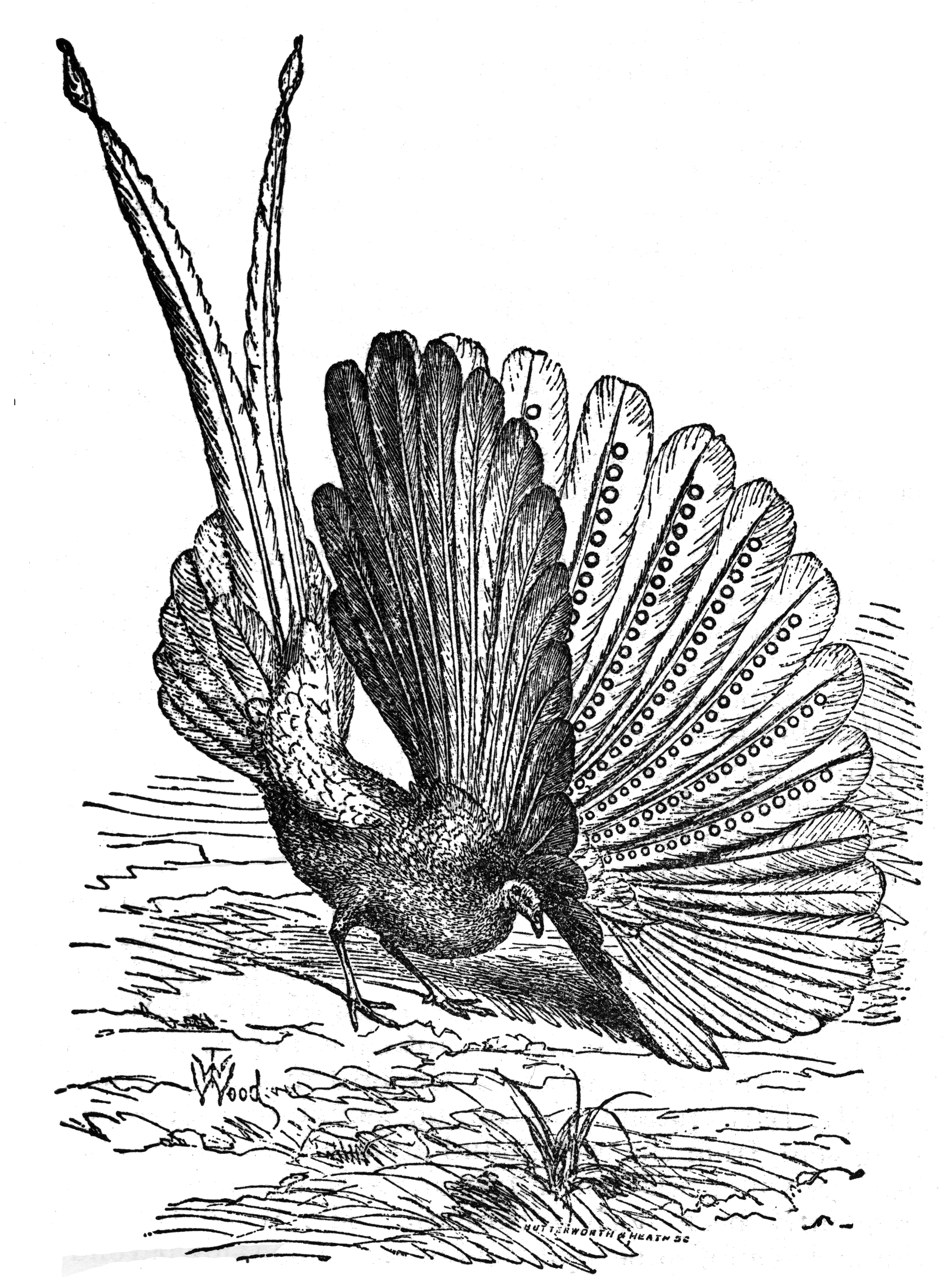
The Crested argus is a species of large peafowl-like bird in the genus ''Rheinardia'' of the pheasant family. Taxonomy Although traditionally treated as a single species with two subspecies, it has long been suspected that a species pair is involved and recent evidence, albeit using the controversial Tobias criteria, also supports treating each subspecies as a separate species. The split results in two monotypic species: The two forms differ significantly in plumage, display and vocalisations and both are threatened by human activity. Description Crested arguses have dark-brown-spotted black and buff plumage, a heavy pink bill, brown irises and blue skin around the eyes. The head has two crests; the hind crest, which extends down the occiput, is erected when alarmed and during intentional behaviors including pair bonding and courtship displays. The male has a broad and greatly elongated tail of twelve feathers. The tail covert (or "train") of the male is the longest of any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnamese Crested Argus
The Vietnamese crested argus (''Rheinardia ocellata'') is a large and spectacular peafowl-like species of bird in the pheasant family with dark-brown-spotted black and buff plumage, a heavy pink bill, brown irises and blue skin around the eyes. The head has two crests; the hind crest, which extends down the occiput, is erected when alarmed and during intentional behaviors including pair bonding and courtship displays. The male has a broad and greatly elongated tail of twelve feathers. The tail covert (or "train") of the male is the longest of any bird and is believed to contain the longest (and widest) feathers to occur in a wild bird; the Reeves's pheasant has tail feathers of similar length but which are considerably narrower. The tail coverts measure up to in length, giving the bird a total length of . Description Both sexes are similar in size, with females possessing a prominent marbled barring and more colourful dorsal plumage than the male. They possess white facial pluma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayan Crested Argus
The Malayan crested argus (''Rheinardia nigrescens'') is a large and spectacular peafowl-like species of bird in the pheasant family with dark-brown-spotted black and buff plumage, a heavy pink bill, brown irises and blue skin around the eyes. The head has two crests; the hind crest, which extends down the occiput, is erected when alarmed and during intentional behaviors including pair bonding and courtship displays. The male has a broad and greatly elongated tail of twelve feathers. The tail covert (or "train") of the male is the longest of any bird and is believed to contain the longest (and widest) feathers to occur in a wild bird; the Reeves's pheasant has tail feathers of similar length but which are considerably narrower. The tail coverts measure up to in length, giving the bird a total length of . Description The female is similar in size, with a prominent marbled barring and more colourful dorsal plumage than the male. Her conspicuous white facial plumage is like the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Argus
The great argus (''Argusianus argus''), or greater argus, is a large species of pheasant from Southeast Asia. It is known for its impressive plumage and courtship behavior. It is not to be confused with the two species of closely related crested argus, genus ''Rheinardia''. Taxonomy Carl Linnaeus gave the great argus its specific name (from which its common name and genus name are derived) because of the intricate eye-like patterns on its wings, in reference to Argus, a hundred-eyed giant in Greek mythology. There are two subspecies recognized: Nominate ''argus'' of the Malay peninsula and Sumatra, and ''A. a. grayi'' of Borneo. William Beebe considered the two races to be distinct species, but they have since been lumped. The genus ''Argusianus'' was introduced in 1849 by the English zoologist George Gray with the great argus as the type species. Double-banded argus The double-banded argus (''Argusianus bipunctatus''), known only from a portion of a single primary flight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
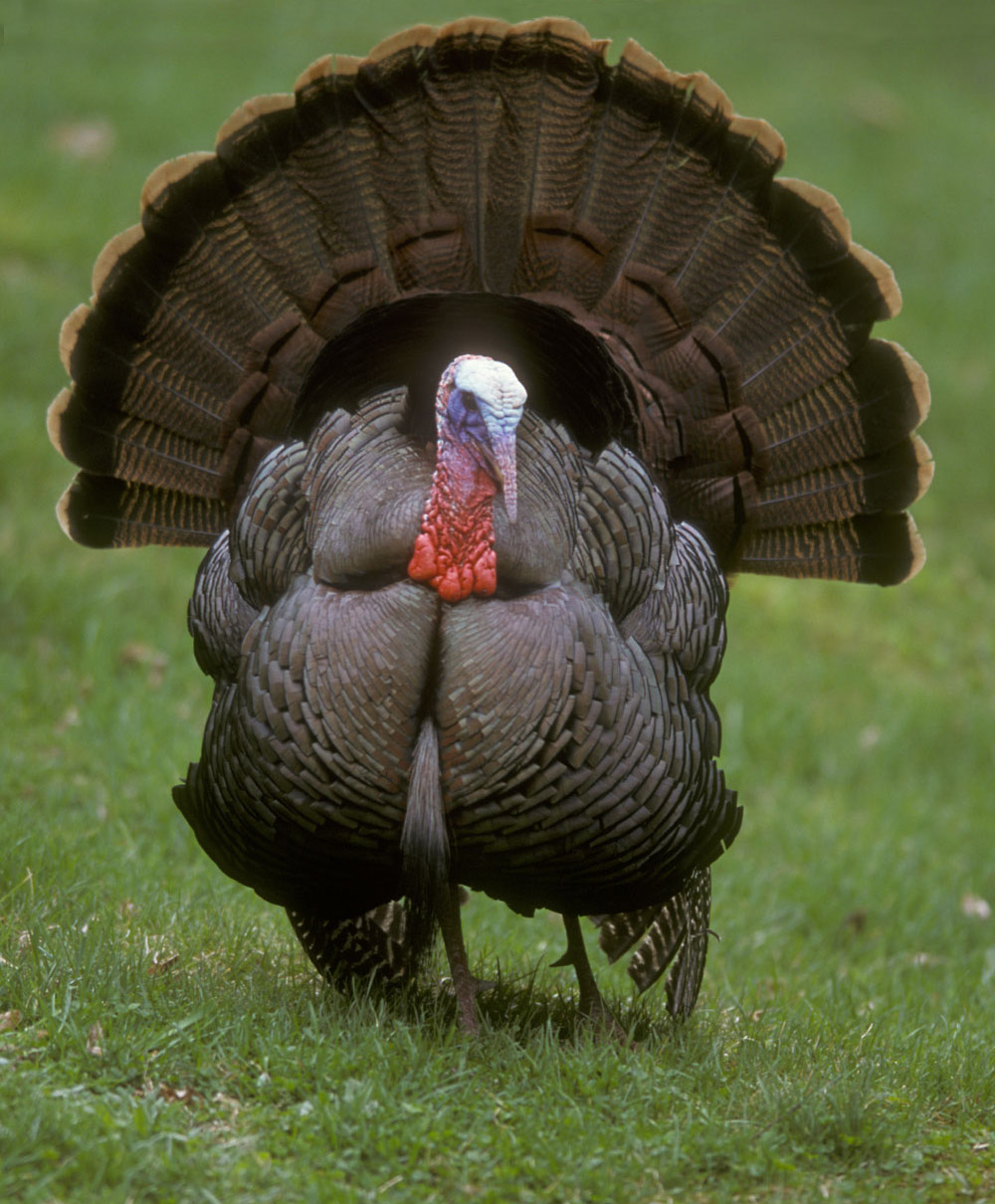
Galliformes
Galliformes is an order (biology), order of heavy-bodied ground-feeding birds that includes turkey (bird), turkeys, chickens, Old World quail, quail, and other landfowl. Gallinaceous birds, as they are called, are important in their ecosystems as seed dispersers and predators, and are often reared by humans for their meat and eggs, or hunted as game birds. The order contains about 290 species, inhabiting every continent except Antarctica, and divided into five Family (biology), families: Phasianidae (including chicken, quail, partridges, pheasants, turkeys, peafowl (peacocks) and grouse), Odontophoridae (New World quail), Numididae (guinea fowl), Cracidae (including chachalacas and curassows), and Megapodiidae (incubator birds like malleefowl and Brushturkey, brush-turkeys). They adapt to most environments except for innermost deserts and perpetual ice. Many gallinaceous species are skilled runners and escape predators by running rather than flying. Males of most species a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheasant
Pheasants ( ) are birds of several genera within the family Phasianidae in the order Galliformes. Although they can be found all over the world in introduced (and captive) populations, the pheasant genera's native range is restricted to Eurasia. The classification "pheasant" is paraphyletic, as birds referred to as pheasants are included within both the subfamilies Phasianinae and Pavoninae, and in many cases are more closely related to smaller phasianids, grouse, and turkey (formerly classified in Perdicinae, Tetraoninae, and Meleagridinae) than to other pheasants. Pheasants are characterised by strong sexual dimorphism, males being highly decorated with bright colours and adornments such as wattles. Males are usually larger than females and have longer tails. Males play no part in rearing the young. A pheasant's call or cry can be recognised by the fact it sounds like a rusty sink or valve being turned. Pheasants eat mostly seeds, grains, roots, and berries, while in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peafowl
Peafowl is a common name for two bird species of the genus '' Pavo'' and one species of the closely related genus '' Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae (the pheasants and their allies). Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female peafowl are referred to as peahens. The two Asiatic species are the blue or Indian peafowl originally from the Indian subcontinent, and the green peafowl from Southeast Asia. The third peafowl species, the Congo peafowl, is native only to the Congo Basin. Male peafowl are known for their piercing calls and their extravagant plumage. The latter is especially prominent in the Asiatic species, which have an eye-spotted "tail" or "train" of covert feathers, which they display as part of a courtship ritual. The functions of the elaborate iridescent coloration and large "train" of peacocks have been the subject of extensive scientific debate. Charles Darwin suggested that they served to attract females, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and southwest. The country has a population of approximately eight million. Its Capital city, capital and most populous city is Vientiane. The country is characterized by mountainous terrain, Buddhist temples, including the UNESCO's World Heritage Site of Luang Prabang, and French colonial architecture. The country traces its historic and cultural identity to Lan Xang, a kingdom which existed from the 13th to 18th centuries. Through its location, the kingdom was a hub for overland trade. In 1707, Lan Xang split into three kingdoms: Kingdom of Luang Phrabang, Luang Prabang, Kingdom of Vientiane, Vientiane, and Kingdom of Champasak, Champasak. In 1893, these kingdoms were unified under French protection as part of French Indochina. Laos was und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Sexual Behaviour
Animal sexual behaviour takes many different forms, including within the same species. Common mating or Reproduction, reproductively motivated systems include Monogamous pairing in animals, monogamy, Polygyny in animals, polygyny, Polyandry in nature, polyandry, Animal sexual behaviour#Polygamy, polygamy and Promiscuity#Other animals, promiscuity. Other sexual behaviour may be reproductively motivated (e.g. Sexual coercion among animals, sex apparently due to duress or coercion and situational sexual behaviour) or Non-reproductive sexual behavior in animals, non-reproductively motivated (e.g. Homosexual behavior in animals, homosexual sexual behaviour, bisexuality, bisexual sexual behaviour, cross-species sex, Paraphilia, sexual arousal from objects or places, Necrophilia in animals, sex with dead animals, etc.). When animal sexual behaviour is reproductively motivated, it is often termed ''mating'' or ''Copulation (zoology), copulation''; for most non-human mammals, mating and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |