|
Reuse Of Excreta
Reuse of human excreta is the safe, beneficial use of treated human waste, human excreta after applying suitable treatment steps and risk management approaches that are customized for the intended reuse application. Beneficial uses of the treated excreta may focus on using the plant nutrition, plant-available nutrients (mainly nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium) that are contained in the treated excreta. They may also make use of the organic matter and energy contained in the excreta. To a lesser extent, reuse of the excreta's water content might also take place, although this is better known as reclaimed water, water reclamation from municipal wastewater. The intended reuse applications for the nutrient content may include: soil conditioner or fertilizer in agriculture or horticulture, horticultural activities. Other reuse applications, which focus more on the organic matter content of the excreta, include use #Solid fuel, heat, electricity, as a fuel source or as an energy source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvest Of Peppers At A SOIL Experimental Garden
Harvesting is the process of collecting plants, animals, or fish (as well as fungi) as food, especially the process of gathering mature crops, and "the harvest" also refers to the collected crops. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulse (legume), pulses for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechanization, harvesting is the most manual labour, labor-intensive activity of the growing season. On large mechanized farms, harvesting uses farm machinery, such as the combine harvester. Automation has increased the efficiency of both the seeding and harvesting processes. Specialized harvesting equipment, using conveyor belts for gentle gripping and mass transport, replaces the manual task of removing each seedling by hand. The term "harvesting" in general usage may include immediate postharvest handling, including cleaning, sorting, packing, and cooling. The completion of harvesting marks the end of the growing season, or the growing c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicator Organism
Indicator organisms are used as a proxy to monitor conditions in a particular environment, ecosystem, area, habitat, or consumer product. Certain bacteria, fungi and helminth eggs are being used for various purposes. Types Indicator bacteria Certain bacteria can be used as indicator organisms in particular situations, such as when present in bodies of water. Indicator bacteria themselves may not be pathogenic but their presence in waste may indicate the presence of other pathogens. Similar to how there are various types of indicator organisms, there are also various types of indicator bacteria. The most common indicators are total coliforms, fecal coliforms, ''E. coli'', and enterococci. The presence of bacteria commonly found in human feces, termed coliform bacteria (e.g. '' E. coli''), in surface water is a common indicator of faecal contamination. The means by which pathogens found in fecal matter can enter recreational bodies of water include, but are not limited to, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuse
Reuse is the action or practice of using an item, whether for its original purpose (conventional reuse) or to fulfill a different function (creative reuse or repurposing). It should be distinguished from recycling, which is the breaking down of used items to make raw materials for the manufacture of new products. Reuse—by taking, but not reprocessing, previously used items—helps save time, money, energy and resources. In broader economic terms, it can make quality products available to people and organizations with limited means, while generating jobs and business activity that contribute to the economy. Examples Reuse centers and virtual exchange Reuse centers (also known as a "swap shop" or a "take-it-or-leave-it") facilitate the transaction and redistribution of unwanted, yet perfectly usable, materials and equipment from one entity to another. The entities that benefit from either side of this service (as donors, sellers, recipients, or buyers) can be businesses, nonprof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how biomass is defined, e.g., only from plants, from plants and algae, from plants and animals. The vast majority of biomass used for bioenergy does come from plants and fecal matter. Bioenergy is a type of renewable energy that the bioenergy industry claims has the potential to assist with climate change mitigation. Uses in different contexts Ecology * Biomass (ecology), the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. This can be the biomass of particular species or the biomass of a particular community or habitat. Energy * Biomass (energy), biomass used for energy production or in other words: biological mass used as a renewable energy source (usually produced through agriculture, forestry or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
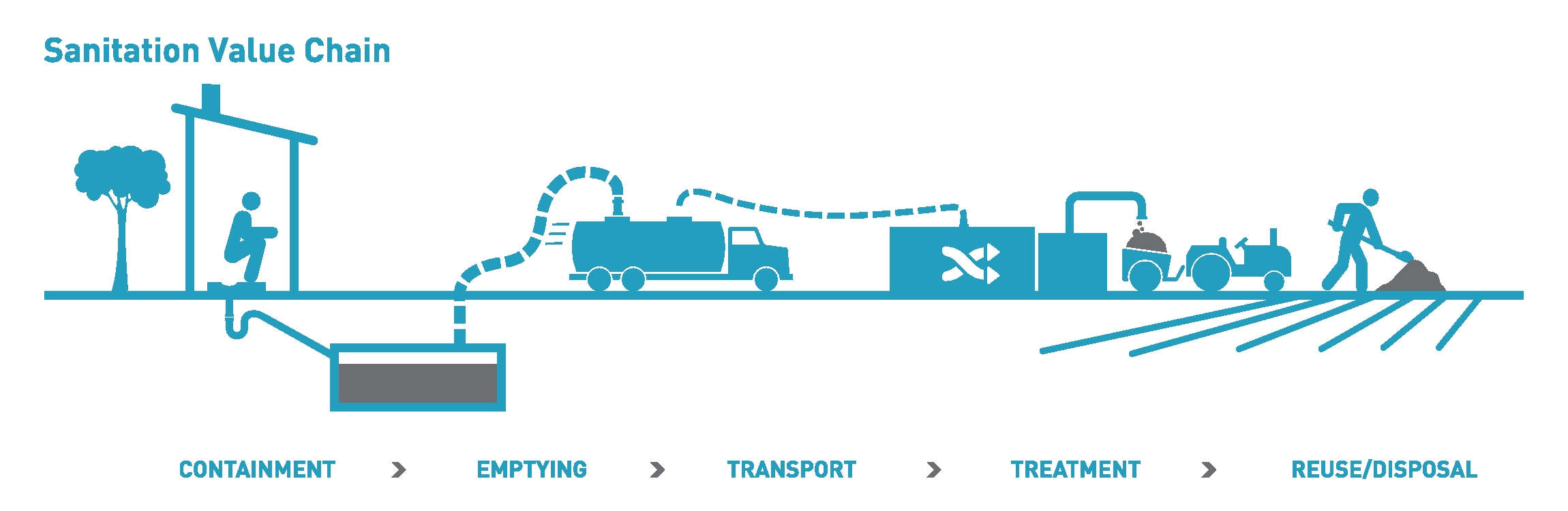
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions . Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total sanita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Economy
A circular economy (also referred to as circularity or CE) is a model of resource Production (economics), production and Resource consumption, consumption in any economy that involves sharing, leasing, Reuse, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling existing materials and products for as long as possible. The concept aims to tackle global challenges such as climate change, biodiversity loss, waste, and pollution by emphasizing the design-based implementation of the three base principles of the model. The main three principles required for the transformation to a circular economy are: designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. CE is defined in contradistinction to the traditional linear economy. The idea and concepts of a circular economy have been studied extensively in academia, business, and government over the past ten years. It has been gaining popularity because it can help to minimize Greenhouse gas emis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing Country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The terms low-and middle-income country (LMIC) and newly emerging economy (NEE) are often used interchangeably but they refer only to the economy of the countries. The World Bank classifies the world's economies into four groups, based on gross national income per capita: high-, upper-middle-, lower-middle-, and low-income countries. Least developed countries, landlocked developing countries, and small island developing states are all sub-groupings of developing countries. Countries on the other end of the spectrum are usually referred to as high-income countries or developed countries. There are controversies over the terms' use, as some feel that it perpetuates an outdated concept of "us" and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sewage Sludge
Sewage sludge is the residual, semi-solid material that is produced as a by-product during sewage treatment of industrial or municipal wastewater. The term "septage" also refers to sludge from simple wastewater treatment but is connected to simple on-site sanitation systems, such as septic tanks. After treatment, and dependent upon the quality of sludge produced (for example with regards to heavy metal content), sewage sludge is most commonly either disposed of in landfills, dumped in the ocean or applied to land for its fertilizing properties, as pioneered by the product Milorganite. The term " Biosolids" is often used as an alternative to the term sewage sludge in the United States, particularly in conjunction with reuse of sewage sludge as fertilizer after sewage sludge treatment. Biosolids can be defined as organic wastewater solids that can be reused after stabilization processes such as anaerobic digestion and composting. Opponents of sewage sludge reuse reject this t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from residences and from commercial, institutional and public facilities that exist in the locality. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a creativecommons:by/4.0/, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License Sub-types of sewage are greywater (from sinks, bathtubs, showers, dishwashers, and clothes washers) and blackwater (waste), blackwater (the water used to flush toilets, combined with the human waste that it flushes away). Sewage also contains soaps and detergents. Food waste may be present from dishwashing, and food quantities may be increased where garbage disposal units are used. In regions where toilet paper is used rather than bidets, that paper is also added to the sewage. Sewage contains macro-pollu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinking Water Quality Standards
Drinking water quality standards describes the quality parameters set for drinking water. Water may contain many harmful constituents, yet there are no universally recognized and accepted international standards for drinking water. Even where standards do exist, the permitted concentration of individual constituents may vary by up to ten times from one set of standards to another. Many countries specify standards to be applied in their own country. In Europe, this includes the European Drinking Water Directive and in the United States, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) establishes standards as required by the Safe Drinking Water Act. China adopted its own drinking water standard GB3838-2002 (Type II) enacted by Ministry of Environmental Protection in 2002. For countries without a legislative or administrative framework for such standards, the World Health Organization publishes guidelines on the standards that should be achieved. Where drinking water qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater Pollution
Groundwater pollution (also called groundwater contamination) occurs when pollutants are released to the ground and make their way into groundwater. This type of water pollution can also occur naturally due to the presence of a minor and unwanted constituent, contaminant, or impurity in the groundwater, in which case it is more likely referred to as contamination rather than pollution. Groundwater pollution can occur from on-site sanitation systems, landfill leachate, effluent from wastewater treatment plants, leaking sewers, petrol filling stations, hydraulic fracturing (fracking) or from over application of fertilizers in agriculture. Pollution (or contamination) can also occur from naturally occurring contaminants, such as arsenic contamination of groundwater, arsenic or fluoride. Using polluted groundwater causes hazards to public health through poisoning or the spread of disease (Waterborne diseases, water-borne diseases). The pollutant often produces a contaminant Plume (f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |