|
Renal Cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, is a group of cancers that starts in the kidney. Symptoms may include blood in the urine, a lump in the abdomen, or back pain. Fever, weight loss, and tiredness may also occur. Complications can include spread to the lungs or brain. The main types of kidney cancer are renal cell cancer (RCC), transitional cell cancer (TCC), and Wilms' tumor. RCC makes up approximately 80% of kidney cancers, and TCC accounts for most of the rest. Risk factors for RCC and TCC include smoking, certain pain medications, previous bladder cancer, being overweight, high blood pressure, certain chemicals, and a family history. Risk factors for Wilms' tumor include a family history and certain genetic disorders such as WAGR syndrome. Diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical imaging. It is confirmed by tissue biopsy. Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. Kidney c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherapies that reduce or suppress are classified as '' suppression immunotherapies''. Immunotherapy is under preliminary research for its potential to treat various forms of cancer. Cell-based immunotherapies are effective for some cancers. Immune effector cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes work together to defend the body against cancer by targeting abnormal antigens expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Vaccine-induced immunity to COVID-19 relies mostly on an immunomodulatory T-cell response. Therapies such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), interferons, imiquimod and cellular membrane fractions from bacteria are licensed for medical use. Others in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five-year Survival Rate
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year survival rate. There are absolute and relative survival rates, but the latter are more useful and commonly used. __TOC__ Relative and absolute rates Five-year relative survival rates are more commonly cited in cancer statistics. Five-year absolute survival rates may sometimes also be cited. * Five-year ''absolute'' survival rates describe the percentage of patients alive five years after the disease is diagnosed. * Five-year ''relative'' survival rates describe the percentage of patients with a disease alive five years after the disease is diagnosed, divided by the percentage of the general population of corresponding sex and age alive after five years. Typically, cancer five-year relative survival rates are well below 100%, reflecting exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAGR Syndrome
WAGR syndrome (also known as WAGR complex, Wilms tumour-aniridia syndrome, aniridia-Wilms tumour syndrome) is a rare genetic syndrome in which affected children are predisposed to develop Wilms' tumour (a tumour of the kidneys), aniridia (absence of the coloured part of the eye, the iris), genitourinary anomalies, and mental retardation. The "G" is sometimes instead given as " gonadoblastoma", since the genitourinary anomalies can include tumours of the gonads (testes or ovaries). Some WAGR syndrome patients show severe childhood obesity and hyperphagia, and are categorised as WAGRO (adding obesity) which may be associated with the coinciding loss of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) a gene that is also on chromosome 11. The condition, first described by Miller et al. in 1964 in its association with other congenital malformations, results from a deletion on chromosome 11 resulting in the loss of several genes. As such, it is one of the best studied examples of a condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilms' Tumor
Wilms' tumor or Wilms tumor, also known as nephroblastoma, is a cancer of the kidneys that typically occurs in children (rarely in adults), and occurs most commonly as a renal tumor in child patients. It is named after Max Wilms, the German surgeon (1867–1918) who first described it. Approximately 650 cases are diagnosed in the U.S. annually. The majority of cases occur in children with no associated genetic syndromes; however, a minority of children with Wilms' tumor have a congenital abnormality. It is highly responsive to treatment, with about 90 percent of children being cured. Signs and symptoms Typical signs and symptoms of Wilms' tumor include the following: * a painless, palpable abdominal mass * loss of appetite * abdominal pain * fever * nausea and vomiting * blood in the urine (in about 20% of cases) * high blood pressure in some cases (especially if synchronous or metachronous bilateral kidney involvement) * Rarely as varicoceleErginel B, Vural S, Akın M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Cell Cancer
Transitional cell carcinoma is a type of cancer that arises from the transitional epithelium, a tissue lining the inner surface of these hollow organs. It typically occurs in the urothelium of the urinary system; in that case, it is also called urothelial carcinoma. It is the most common type of bladder cancer and cancer of the ureter, urethra, and urachus. Symptoms of urothelial carcinoma in the bladder include hematuria (blood in the urine). Diagnosis includes urine analysis and imaging of the urinary tract (cystoscopy). It accounts for 95% of bladder cancer cases and bladder cancer is in the top 10 most common malignancy disease in the world and is associated with approximately 200,000 deaths per year in the United States alone. It is the second most common type of kidney cancer, but accounts for only five to 10 percent of all primary renal malignant tumors. Men and older people have a higher rate of urothelial carcinomas. Other risk factors include smoking and exposure to aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Cell Cancer
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90–95% of cases. It is more common in men (with a male-to-female ratio of up to 2:1). It is most commonly diagnosed in the elderly (especially in people over 75 years of age). Initial treatment is most commonly either partial or complete removal of the affected kidney(s). Where the cancer has not metastasised (spread to other organs) or burrowed deeper into the tissues of the kidney, the five-year survival rate is 65–90%, but this is lowered considerably when the cancer has spread. The body is remarkably good at hiding the symptoms and as a result people with RCC often have advanced disease by the time it is discovered. The initial symptoms of RCC often include blood in the urine (occurring in 40% of affected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
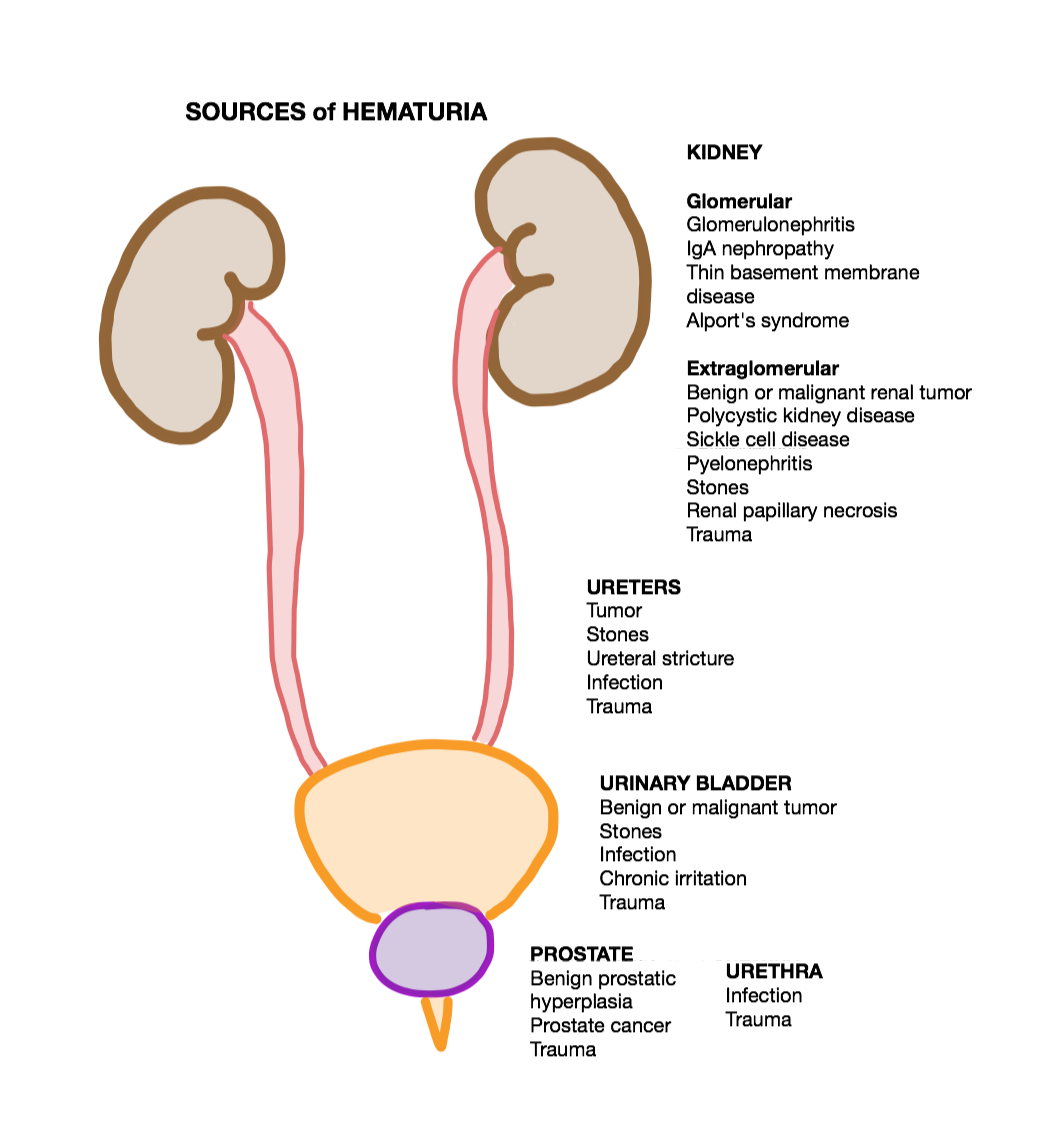
Blood In The Urine
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. "Gross hematuria" occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and some foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dipst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal artery, renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the urinary bladder, bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, Acid-base homeostasis, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |