|
Remember Versus Know Judgements
There is evidence suggesting that different processes are involved in remembering something versus knowing whether it is familiar.Mickley, K.R., Kensinger, E.A. (2008). Emotional valence influences the neural correlates associated with remembering and knowing. ''Cognition, affective & behavioural neuroscience, 8(2),'' 143-152. It appears that "remembering" and "knowing" represent relatively different characteristics of memory as well as reflect different ways of using memory. To remember is the conscious ''recollection'' of many vivid contextual details, such as "when" and "how" the information was learned. Remembering utilizes episodic memory and requires a deeper level of processing (e.g. undivided attention) than knowing. Errors in recollection may be due to source-monitoring errors that prevent an individual from remembering where exactly a piece of information was received. On the other hand, source monitoring may be very effective in aiding the retrieval of episodic memories. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episodic Memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at particular times and places; for example, the party on one's 7th birthday. Along with semantic memory, it comprises the category of explicit memory, one of the two major divisions of long-term memory (the other being implicit memory). The term "episodic memory" was coined by Endel Tulving in 1972, referring to the distinction between knowing and remembering: ''knowing'' is factual recollection (semantic) whereas ''remembering'' is a feeling that is located in the past (episodic). One of the main components of episodic memory is the process of recollection, which elicits the retrieval of contextual information pertaining to a specific event or experience that has occurred. Tulving seminally defined three key properties of episodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cingulate Gyrus
The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic lobe. It receives inputs from the thalamus and the neocortex, and projects to the entorhinal cortex via the cingulum (anatomy), cingulum. It is an integral part of the limbic system, which is involved with emotion formation and processing, learning, and memory. The combination of these three functions makes the cingulate gyrus highly influential in linking motivational outcomes to behavior (e.g. a certain action induced a positive emotional response, which results in learning). This role makes the cingulate cortex highly important in disorders such as Major depressive disorder, depression and schizophrenia. It also plays a role in executive function and respirator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knowledge
Knowledge is an Declarative knowledge, awareness of facts, a Knowledge by acquaintance, familiarity with individuals and situations, or a Procedural knowledge, practical skill. Knowledge of facts, also called propositional knowledge, is often characterized as Truth, true belief that is distinct from opinion or guesswork by virtue of Justification (epistemology), justification. While there is wide agreement among philosophers that propositional knowledge is a form of true belief, many controversies focus on justification. This includes questions like how to understand justification, whether it is needed at all, and whether something else besides it is needed. These controversies intensified in the latter half of the 20th century due to a series of thought experiments called ''Gettier cases'' that provoked alternative definitions. Knowledge can be produced in many ways. The main source of empirical knowledge is perception, which involves the usage of the senses to learn about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindsight Bias
Hindsight bias, also known as the knew-it-all-along phenomenon or creeping determinism, is the common tendency for people to perceive past events as having been more predictable than they were. After an event has occurred, people often believe that they could have predicted or perhaps even known with a high degree of certainty what the outcome of the event would be before it occurred. Hindsight bias may cause distortions of memories of what was known or believed before an event occurred and is a significant source of overconfidence in one’s ability to predict the outcomes of future events. Examples of hindsight bias can be seen in the writings of historians describing the outcomes of battles, in physicians’ recall of clinical trials, and in criminal or civil trials as people tend to assign responsibility on the basis of the supposed predictability of accidents. In some countries, 20/20 indicates normal visual acuity at 20 feet, from which derives the idiom " hindsight is 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tip-of-the-tongue
Tip of the tongue (also known as TOT, or lethologica) is the phenomenon of failing to retrieve a word or term from memory, combined with partial recall and the feeling that retrieval is imminent. The phenomenon's name comes from the saying, "It's on the tip of my tongue." The tip of the tongue phenomenon reveals that lexical access occurs in stages. People experiencing the tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon can often recall one or more of the target word, such as the first letter, its syllabic stress, and words similar in sound, meaning, or both sound and meaning. Individuals report a feeling of being seized by the state, feeling something like mild anguish while searching for the word, and a sense of relief when the word is found. While many aspects of the tip-of-the-tongue state remain unclear, there are two major competing explanations for its occurrence: the ''direct-access view'' and the ''inferential view''. Emotion and the strength of the emotional ties to what is trying to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
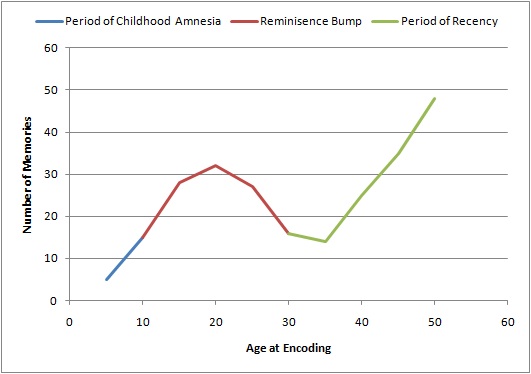
Reminiscence Bump
The reminiscence bump is the tendency for adults over forty to have increased or enhanced recollection for events that occurred during their adolescence and early adulthood. It was identified through the study of autobiographical memory and the subsequent plotting of the age of encoding of memories to form the lifespan retrieval curve. The lifespan retrieval curve is a graph that represents the number of autobiographical memories encoded at various ages during the life span. The lifespan retrieval curve contains three different parts. From birth to five years old is a period of childhood amnesia, from 15 to 25 years old is the reminiscence bump and last is a period of forgetting from the end of the reminiscence bump to present time. The reminiscence bump has been observed on the lifespan retrieval curve in multiple studies. Theorists have proposed several explanations, ranging from changes in brain biology to the type of events that typically occur during this time period. Resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
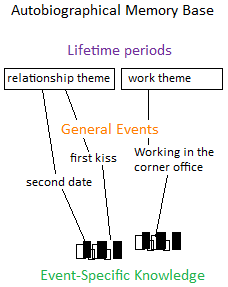
Autobiographical Memory
Autobiographical memory (AM) is a memory system consisting of episodes recollected from an individual's life, based on a combination of Episodic memory, episodic (personal experiences and specific objects, people and events experienced at particular time and place) and Semantic memory, semantic (general knowledge and facts about the world) memory. It is thus a type of explicit memory. Formation Conway and Pleydell-Pearce (2000) proposed that autobiographical memory is constructed within a self-memory system (SMS), a conceptual model composed of an autobiographical knowledge base and the working self. Autobiographical knowledge base The autobiography, autobiographical knowledge base contains knowledge of the self, used to provide information on what the self is, what the self was, and what the self can be. This information is categorized into three broad areas: lifetime periods, general events, and event-specific knowledge. ''Lifetime periods'' are composed of general knowledge a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activity in the brain that can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from brief lapses of awareness or muscle jerks to prolonged convulsions. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly, such as broken bones, or through causing accidents. The diagnosis of epilepsy typically requires at least two unprovoked seizures occurring more than 24 hours apart. In some cases, however, it may be diagnosed after a single unprovoked seizure if clinical evidence suggests a high risk of recurrence. Isolated seizures that occur without recurrence risk or are provoked by identifiable causes are not considered indicative of epilepsy. The underlying cause is often unknown, but epilepsy can result from brain injury, stroke, infections, Brain tumor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, flat or inappropriate affect. Symptoms Prodrome, develop gradually and typically begin during young adulthood and rarely resolve. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a psychiatric history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. For a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the described symptoms need to have been present for at least six months (according to the DSM-5) or one month (according to the ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially mood disorder, mood, anxiety disorder, anxiety, and substance use disorders, substance use disorders, as well as obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). About 0.3% to 0.7% of peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recollection
Recall in memory refers to the mental process of retrieving information from the past. Along with encoding and storage, it is one of the three core processes of memory. There are three main types of recall: free recall, cued recall and serial recall. Psychologists test these forms of recall as a way to study the memory processes of humansrecall. (2010). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved March 04, 2010, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/493353/recal/ref> and animals. Two main theories of the process of recall are the two-stage theory and the theory of Encoding specificity principle, encoding specificity. Theories Two-stage theory The ''two-stage theory'' states that the process of recall begins with a search and retrieval process, and then a decision or recognition process where the correct information is chosen from what has been retrieved. In this theory, recognition only involves the latter of these two stages, or processes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information among various sensory modality, modalities, including spatial sense and navigation (proprioception), the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch in the somatosensory cortex which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the postcentral gyrus, and the two-streams hypothesis#Dorsal stream, dorsal stream of the visual system. The major sensory inputs from the skin (mechanoreceptor, touch, thermoreceptor, temperature, and nociceptor, pain receptors), relay through the thalamus to the parietal lobe. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in language processing in the brain, language processing. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure – the cortical homunculus (Latin: "li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source-monitoring Error
A source-monitoring error is a type of memory errors, memory error where the source of a memory is Misattribution of memory, incorrectly attributed to some specific recollected experience. For example, individuals may learn about a current event from a friend, but later report having learned about it on the local news, thus reflecting an incorrect source attribution. This error occurs when normal perceptual and reflective processes are disrupted, either by limited Encoding (memory), encoding of source information or by disruption to the judgment processes used in source-monitoring. Depression (mood), Depression, high stress levels and damage to relevant brain areas are examples of factors that can cause such disruption and hence source-monitoring errors.Johnson, M.K., Hashtroudi, S., Lindsay, D.S. (1993). Source Monitoring. ''Psychological Bulletin'', 114(1), 3–28 Introduction One of the key ideas behind source-monitoring is that rather than receiving an actual label for a memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |