|
Reiserfs
ReiserFS is a general-purpose, journaling file system initially designed and implemented by a team at Namesys led by Hans Reiser and licensed under GPLv2. Introduced in version 2.4.1 of the Linux kernel, it was the first journaling file system to be included in the standard kernel. ReiserFS was the default file system in Novell's SUSE Linux Enterprise until Novell decided to move to ext3 for future releases on October 12, 2006. ReiserFS version 3.6, now occasionally referred to as Reiser3, introduced a new on-disk format allowing larger filesizes. Namesys considered ReiserFS stable and feature-complete and ceased development on it to concentrate on its successor, Reiser4, though it continued to release security updates and critical bug fixes. Namesys went out of business in 2008 after Reiser's conviction for murder. The product is now maintained as open source by volunteers. The reiserfsprogs 3.6.27 were released on 25 July 2017. As of Linux 6.12, ReiserFS is supported on L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Reiser
Hans Thomas Reiser (born December 19, 1963) is an American computer programmer, entrepreneur, and convicted murderer. In April 2008, Reiser was convicted of the first-degree murder of his wife, Nina Reiser, who disappeared in September 2006. He subsequently pleaded guilty to a reduced charge of second-degree murder, as part of a settlement agreement that included disclosing the location of Nina Reiser's body, which he revealed to be in a shallow grave near the couple's home. Prior to his incarceration, Reiser created the ReiserFS computer file system, which may be used by the Linux kernel but is now removed, as well as its attempted successor, Reiser4. In 2004, he founded Namesys, a corporation meant to coordinate the development of both file systems. Childhood, education, and career Hans Thomas Reiser was born in Oakland, California to Ramon and Beverly (née Kleiber) Reiser and grew up in the same city. He dropped out of junior high school when he was 13 because of his d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reiser4
Reiser4 is a computer file system, successor to the ReiserFS file system, developed from scratch by Namesys and sponsored by DARPA as well as Linspire. Reiser4 was named after its former lead developer Hans Reiser. , the Reiser4 patch set is still being maintained, but according to Phoronix, it is unlikely to be merged into mainline Linux without corporate backing. Features Some of the goals of the Reiser4 file system are: * Atomicity (filesystem operations either complete, or they do not, and they do not corrupt due to partially occurring) * Different transaction models: journaling, write-anywhere (copy-on-write), hybrid transaction model * More efficient journaling through wandering logs * More efficient support of small files, in terms of disk space and speed through block suballocation * Liquid items (or virtual keys) – a special format of records in the storage tree, which completely resolves the problem of internal fragmentation * EOTTL (extents on the twig level) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ext3
ext3, or third extended filesystem, is a journaling file system, journaled file system that is commonly used with the Linux kernel. It used to be the default file system for many popular Linux distributions but generally has been supplanted by its successor version ext4. The main advantage of ext3 over its predecessor, ext2, is journaling file system, journaling, which improves reliability and eliminates the need to check the file system after an unclean or improper Shutdown (computing), shutdown. History Stephen Tweedie first revealed that he was working on extending ext2 in ''Journaling the Linux ext2fs Filesystem'' in a 1998 paper, and later in a February 1999 kernel mailing list posting. The filesystem was merged with the mainline Linux kernel in November 2001 from 2.4.15 onward. Advantages The speed performance of ext3 is less attractive than competing Linux filesystems, such as ext4, JFS (file system), JFS, ReiserFS, and XFS, but ext3 has a significant advantage in tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Kernel
The Linux kernel is a Free and open-source software, free and open source Unix-like kernel (operating system), kernel that is used in many computer systems worldwide. The kernel was created by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU operating system (OS) which was created to be a free software, free replacement for Unix. Since the late 1990s, it has been included in many Linux distributions, operating system distributions, many of which are called Linux. One such Linux kernel operating system is Android (operating system), Android which is used in many mobile and embedded devices. Most of the kernel code is written in C (programming language), C as supported by the GNU compiler collection (GCC) which has extensions beyond standard C. The code also contains assembly language, assembly code for architecture-specific logic such as optimizing memory use and task execution. The kernel has a Modular programming, modular design such that modules can be inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block Suballocation
Block suballocation is a feature of some computer file systems which allows large blocks or allocation units to be used while making efficient use of empty space at the end of large files, space which would otherwise be lost for other use to internal fragmentation. In file systems that don't support fragments, this feature is also called tail merging or tail packing because it is commonly done by packing the "tail", or last partial block, of multiple files into a single block. Rationale File systems have traditionally divided the disk into equally sized blocks to simplify their design and limit the worst-case fragmentation. Block sizes are typically multiples of 512 bytes due to the size of hard disk sectors. When files are allocated by some traditional file systems, only whole blocks can be allocated to individual files. But as file sizes are often not multiples of the file system block size, this design inherently results in the last blocks of files (called tails) occupyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inode
An inode (index node) is a data structure in a Unix-style file system that describes a file-system object such as a file or a directory. Each inode stores the attributes and disk block locations of the object's data. File-system object attributes may include metadata (times of last change, access, modification), as well as owner and permission data. A directory is a list of inodes with their assigned names. The list includes an entry for itself, its parent, and each of its children. Etymology There has been uncertainty on the Linux kernel mailing list about the reason for the "i" in "inode". In 2002, the question was brought to Unix pioneer Dennis Ritchie, who replied: A 1978 paper by Ritchie and Ken Thompson bolsters the notion of "index" being the etymological origin of inodes. They wrote: Additionally, Maurice J. Bach wrote that the word ''inode'' "is a contraction of the term index node and is commonly used in literature on the UNIX system". Details A file system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namesys
Namesys was a California corporation responsible for the design and implementation of the ReiserFS and Reiser4 filesystems. It has been inactive since late 2007 and, , is listed with the State of California with a status of "Suspended". Owned by Hans Reiser, Namesys was based in Oakland, California and also operated in Russia. The company also provided support for Linux systems. The future of the company fell into doubt after Reiser was found guilty of murder and announced plans to sell the company to pay for his legal defense. Their website has not been accessible since November 2007. Edward Shishkin, a Namesys employee, was quoted in a January 2008 CNET article as saying that "commercial activity of Namesys has stopped". Notes External links namesys.comat Internet Archive The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
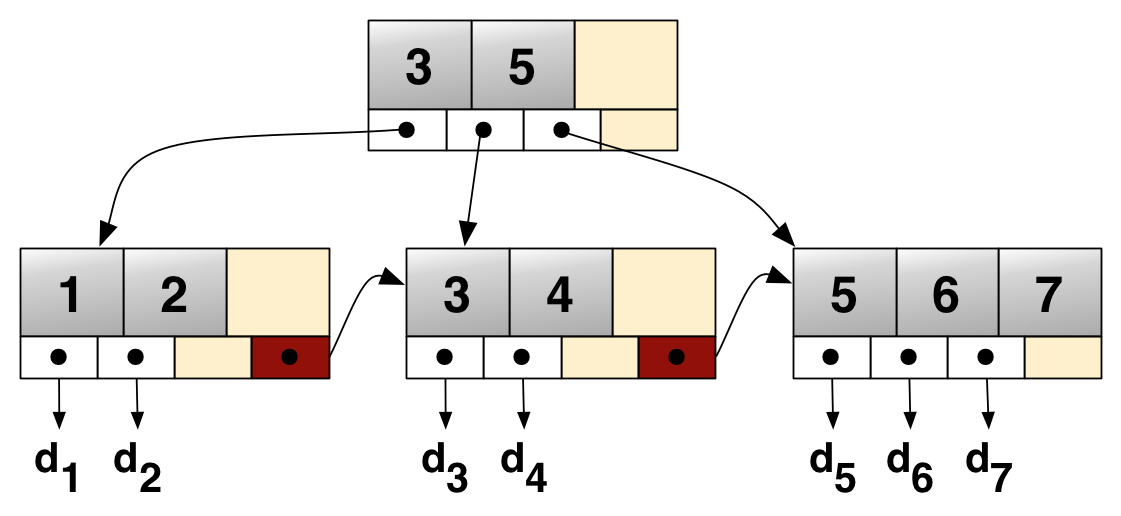
B+ Tree
A B+ tree is an m-ary tree with a variable but often large number of children per node. A B+ tree consists of a root, internal nodes and leaves. The root may be either a leaf or a node with two or more children. A B+ tree can be viewed as a B-tree in which each node contains only keys (not key–value pairs), and to which an additional level is added at the bottom with linked leaves. The primary value of a B+ tree is in storing data for efficient retrieval in a Block (data storage), block-oriented storage context—in particular, filesystems. This is primarily because unlike binary search trees, B+ trees have very high fanout (number of pointers to child nodes in a node, typically on the order of 100 or more), which reduces the number of I/O operations required to find an element in the tree. History There is no single paper introducing the B+ tree concept. Instead, the notion of maintaining all data in leaf nodes is repeatedly brought up as an interesting variant of the B- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ReactOS
ReactOS is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source operating system for i586/amd64 personal computers that is intended to be binary-code compatibility, binary-compatible with computer programs and device drivers developed for Windows Server 2003 and later versions of Microsoft Windows. ReactOS has been noted as a potential open-source drop-in replacement for Windows and has been of interest for its information on undocumented feature, undocumented Windows APIs. ReactOS has been in development since 1996. , it is still considered to be feature-incomplete Software release life cycle#Alpha, alpha software. Therefore, it is recommended by the developers to be used only for evaluation and testing purposes. However, many Windows applications are working, such as Adobe Acrobat, Adobe Reader 9.3, GIMP 2.6, and LibreOffice 5.4.Tests for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Partition Map
Apple Partition Map (APM) is a partition scheme used to define the low-level organization of data on disks formatted for use with 68k and PowerPC Macintosh computers. It was introduced with the Macintosh II. Disks using the Apple Partition Map are divided into logical blocks, with 512 bytes usually belonging to each block. The first block, ''Block 0'', contains an Apple-specific data structure called "Driver Descriptor Map" for the Macintosh Toolbox ROM to load driver updates and patches before loading from an MFS or HFS partition. Because APM allows 32 bits worth of logical blocks, the historical size of an APM formatted disk using small blocks is limited to 2 TiB. The ''Apple Partition Map'' maps out all space used (including the map) and unused (free space) on disk, unlike the minimal x86 master boot record that only accounts for used non-map partitions. This means that every block on the disk (with the exception of the first block, ''Block 0'') belongs to a partition. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SUSE Linux Enterprise
SUSE Linux Enterprise (SLE) is a Linux-based operating system developed by SUSE. It is available in two editions, suffixed with Server (SLES) for servers and mainframes, and Desktop (SLED) for workstations and desktop computers. Its major versions are released at an interval of three–four years, while minor versions (called "Service Packs") are released about every 12 months. SUSE Linux Enterprise products receive more intense testing than the upstream openSUSE community product, with the intention that only mature, stable versions of the included components will make it through to the released enterprise product. It is developed from a common code base with other SUSE Linux Enterprise products. IBM's Watson was built on IBM's POWER7 systems using SLES. Hewlett Packard Enterprise's Frontier, world's first and fastest exascale supercomputer runs on SUSE's SLES 15 (HPE Cray OS). SUSE Linux Enterprise Server SLES was developed based on SUSE Linux by a small team led by Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Lock
In operating systems, a giant lock, also known as a big-lock or kernel-lock, is a lock that may be used in the kernel to provide concurrency control required by symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) systems. A giant lock is a solitary global lock that is held whenever a thread enters kernel space and released when the thread returns to user space; a system call is the archetypal example. In this model, threads in user space can run concurrently on any available processors or processor cores, but no more than one thread can run in kernel space; any other threads that try to enter kernel space are forced to wait. In other words, the giant lock eliminates all concurrency in kernel space. By isolating the kernel from concurrency, many parts of the kernel no longer need to be modified to support SMP. However, as in giant-lock SMP systems only one processor can run the kernel code at a time, performance for applications spending significant amounts of time in the kernel is not much improv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |