|
Regulator Clock
A pendulum clock is a clock that uses a pendulum, a swinging weight, as its timekeeping element. The advantage of a pendulum for timekeeping is that it is an approximate harmonic oscillator: It swings back and forth in a precise time interval dependent on its length, and resists swinging at other rates. From its invention in 1656 by Christiaan Huygens, inspired by Galileo Galilei, until the 1930s, the pendulum clock was the world's most precise timekeeper, accounting for its widespread use. Throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, pendulum clocks in homes, factories, offices, and railroad stations served as primary time standards for scheduling daily life, work shifts, and public transportation. Their greater accuracy allowed for the faster pace of life which was necessary for the Industrial Revolution. The home pendulum clock was replaced by less-expensive synchronous electric clocks in the 1930s and 1940s. Pendulum clocks are now kept mostly for their decorative and antique val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the father of observational astronomy, modern-era classical physics, the scientific method, and modern science. Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of the pendulum and "hydrostatic balances". He was one of the earliest Renaissance developers of the thermoscope and the inventor of various sector (instrument), military compasses. With an improved telescope he built, he observed the stars of the Milky Way, the phases of Venus, the Galilean moons, four largest satellites of Jupiter, Saturn's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahasuerus Fromanteel
Ahasuerus Fromanteel (circa 25 February 1607 – circa 31 January 1693) was a clockmaker, the first maker of pendulum clocks in Britain. Life and work Fromanteel was baptised in Norwich on 25 February 1607. He was the first of five children born to Leah and Mordecai Fromanteel, a wood turner. The Fromanteels were a highly respected Flanders family of the sixteenth century. Following Spanish conquest, members of the family fled across the sea to East Anglia, establishing themselves in Colchester, Norwich, and London.Anita McConnell, "Fromanteel, Ahasuerus (bap. 1607, d. 1693)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004, online reference Ahasuerus Fromanteel was apprenticed for seven years to a blacksmith, before settling in London in 1629. He began as a crafter of steeple clocks in East Smithfield, near the Tower of London, becoming a member of Worshipful Company of Blacksmiths in 1631. He made lantern clocks with balance wheel escapement, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horological
Chronometry or horology () is the science studying the measurement of time and timekeeping. Chronometry enables the establishment of standard measurements of time, which have applications in a broad range of social and scientific areas. ''Horology'' usually refers specifically to the study of mechanical timekeeping devices, while ''chronometry'' is broader in scope, also including biological behaviours with respect to time (biochronometry), as well as the dating of geological material (geochronometry). Horology is commonly used specifically with reference to the mechanical instruments created to keep time: clocks, watches, clockwork, sundials, hourglasses, clepsydras, timers, time recorders, marine chronometers, and atomic clocks are all examples of instruments used to measure time. People interested in horology are called ''horologists''. That term is used both by people who deal professionally with timekeeping apparatuses, as well as enthusiasts and scholars of horology. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandfather Clock
A grandfather clock (also a longcase clock, tall-case clock, grandfather's clock, hall clock or floor clock) is a tall, freestanding, weight-driven pendulum clock, with the pendulum held inside the tower or waist of the case. Clocks of this style are commonly 1.8–2.4 metres (6–8 feet) tall with an enclosed pendulum and weights, suspended by either cables or chains, which have to be occasionally calibrated to keep the proper time. The case often features elaborately carved ornamentation on the hood (or bonnet), which surrounds and frames the dial, or clock face. The English clockmaker William Clement is credited with developing the form in 1670. Pendulum clocks were the world's most accurate timekeeping technology until the early 20th century. Further, longcase clocks, due to their superior accuracy, served as time standards for households and businesses. Today, they are kept mainly for their decorative and antique value, having been superseded by analog clock, analog and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seconds Pendulum
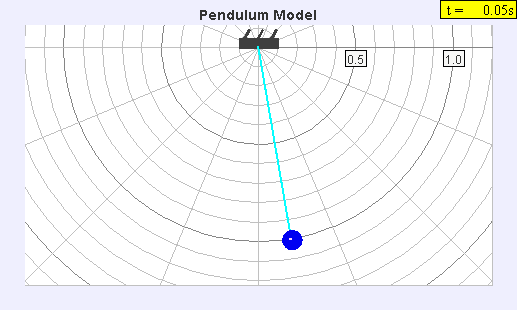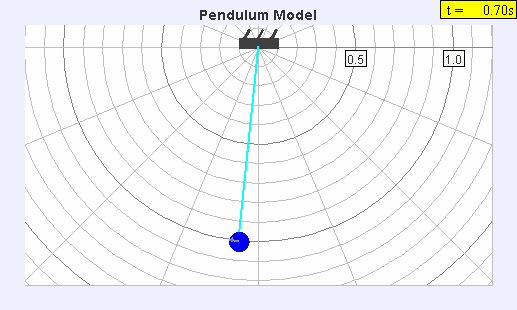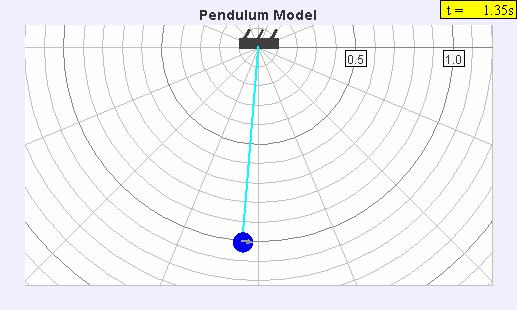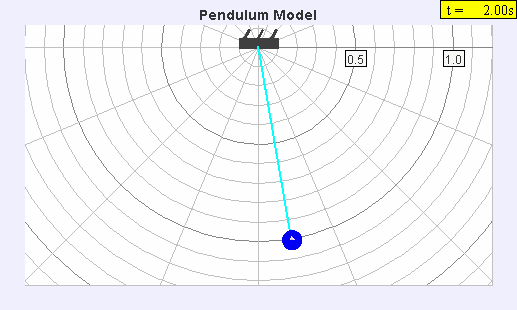
A seconds pendulum is a pendulum whose period is precisely two seconds; one second for a swing in one direction and one second for the return swing, a frequency of 0.5 Hz. Principles A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force combined with the pendulum's mass causes it to oscillate about the equilibrium position, swinging back and forth. The time for one complete cycle, a left swing and a right swing, is called the period. The period depends on the length of the pendulum, and also to a slight degree on its weight distribution (the moment of inertia about its own center of mass) and the amplitude (width) of the pendulum's swing. For a simple gravity pendulum — a point mass on a weightless string of length \ell swingin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath who was active as a physicist ("natural philosopher"), astronomer, geologist, meteorologist, and architect. He is credited as one of the first scientists to investigate living things at microscopic scale in 1665, using a compound microscope that he designed. Hooke was an impoverished scientific inquirer in young adulthood who went on to become one of the most important scientists of his time. After the Great Fire of London in 1666, Hooke (as a surveyor and architect) attained wealth and esteem by performing more than half of the Boundary (real estate), property line surveys and assisting with the city's rapid reconstruction. Often vilified by writers in the centuries after his death, his reputation was restored at the end of the twentieth century and he has been called "England's Leonardo da Vinci, Leonardo [da Vinci]". Hooke was a Fellow of the Royal Society and from 1662, he was its first Curator of Experimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
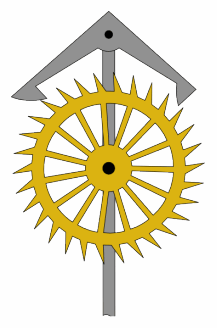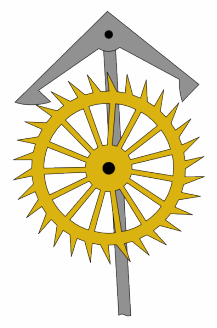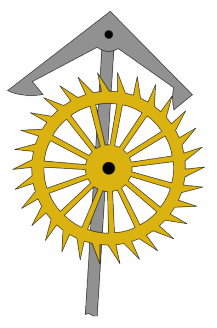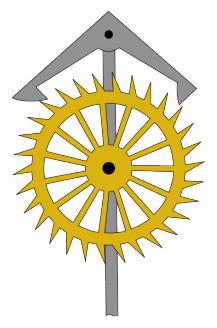
Anchor Escapement
In horology, the anchor escapement is a type of escapement used in pendulum clocks. The escapement is a mechanism in a mechanical clock that maintains the swing of the pendulum by giving it a small push each swing, and allows the clock's wheels to advance a fixed amount with each swing, moving the clock's hands forward. The anchor escapement was so named because one of its principal parts is shaped vaguely like a ship's anchor. The anchor escapement was invented by clockmaker William Clement, who popularized the anchor in his invention of the longcase or grandfather clock around 1680. Clement's invention was a substantial improvement on Robert Hooke's constant force escapement of 1671. The oldest known anchor clock is Wadham College Clock, a tower clock built at Wadham College, Oxford, in 1670, probably by clockmaker Joseph Knibb. The anchor became the standard escapement used in almost all pendulum clocks. A more accurate variation without recoil called the deadbeat escapem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isochronous (horology)
A balance spring, or hairspring, is a spring attached to the balance wheel in mechanical timepieces. It causes the balance wheel to oscillate with a resonant frequency when the timepiece is running, which controls the speed at which the wheels of the timepiece turn, thus the rate of movement of the hands. A regulator lever is often fitted, which can be used to alter the free length of the spring and thereby adjust the rate of the timepiece. The balance spring is an essential adjunct to the balance wheel, causing it to oscillate back and forth. The balance spring and balance wheel together form a harmonic oscillator, which oscillates with a precise period or "beat" resisting external disturbances and is responsible for timekeeping accuracy. The addition of the balance spring to the balance wheel around 1657 by Robert Hooke and Christiaan Huygens greatly increased the accuracy of portable timepieces, transforming early pocketwatches from expensive novelties to useful timekeepers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movement (clockwork)
In horology, a movement, also known as a caliber or calibre (British English), is the mechanism of a watch or Clock, timepiece, as opposed to the ''case'', which encloses and protects the movement, and the ''clock face, face'', which displays the time. The term originated with mechanical timepieces, whose clockwork movements are made of many moving parts. The movement of a digital watch is more commonly known as a module. In modern mass-produced clocks and watches, the same movement is often inserted into many different styles of case. When buying a quality pocketwatch from the mid-19th to the mid-20th century, for example, the customer would select a movement and case individually. Mechanical movements get dirty and the lubricants dry up, so they must periodically be disassembled, cleaned, and lubricated. One source recommends servicing intervals of: 3–5 years for watches, 15–20 years for grandfather clocks, 10–15 years for wall or mantel clocks, 15–20 years for anniv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
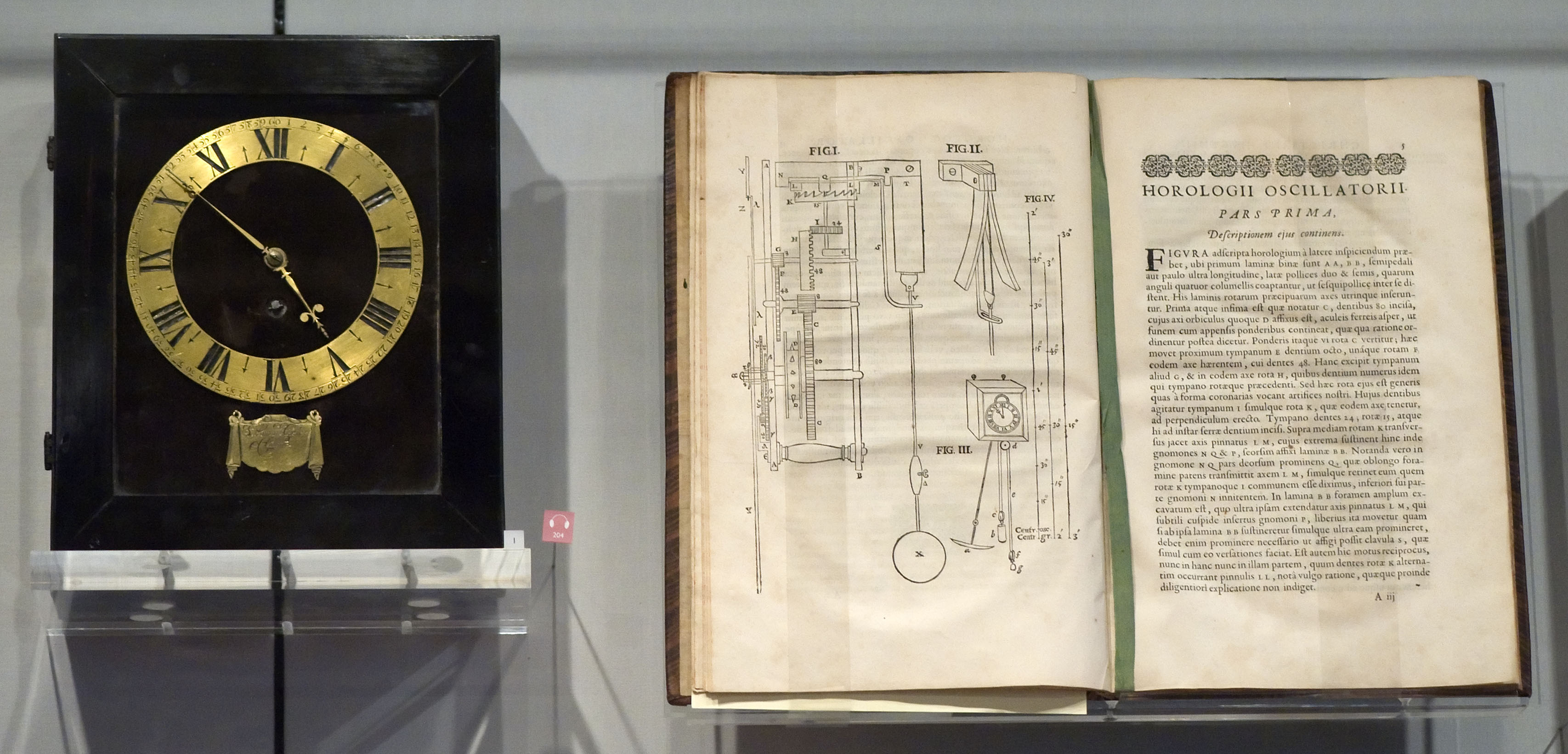
Horologium Oscillatorium
(English language, English: ''The Pendulum Clock: or Geometrical Demonstrations Concerning the Motion of Pendula as Applied to Clocks'') is a book published by Dutch mathematician and physicist Christiaan Huygens in 1673 and his major work on pendulum, pendula and horology. It is regarded as one of the three most important works on mechanics in the 17th century, the other two being Galileo Galilei, Galileo’s ''Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations Relating to Two New Sciences'' (1638) and Isaac Newton, Newton’s (1687). Much more than a mere description of clocks, Huygens's is the first modern treatise in which a physical problem (the Acceleration, accelerated motion of a falling body) is Mathematical model, idealized by a set of Parameter, parameters then analyzed mathematically and constitutes one of the seminal works of applied mathematics.Bruce, I. (2007). Christian Huygens: Horologium Oscillatorium'. Translated and annotated by Ian Bruce. The book is also known fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verge Escapement
The verge (or crown wheel) escapement is the earliest known type of mechanical escapement, the mechanism in a mechanical clock that controls its rate by allowing the gear train to advance at regular intervals or 'ticks'. Verge escapements were used from the late 13th century until the mid 19th century in clocks and pocketwatches. The name verge comes from the Latin ''virga'', meaning stick or rod. Its invention is important in the history of technology, because it made possible the development of all-mechanical clocks. This caused a shift from measuring time by Continuous function, continuous processes, such as the flow of liquid in water clocks, to repetitive, oscillatory processes, such as the swing of pendulums, which had the potential to be more accurate., p.31 Oscillating timekeepers keep time for all modern clocks. Verge and foliot clocks The verge escapement dates from 13th-century Europe, where its invention led to the development of the first all-mechanical clocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |