|
Regalianus
P. C. Regalianus (died 260/261), known in English as Regalian, was Roman usurper for a few months in 260 and/or 261, during the Crisis of the Third Century, a period of intense political instability in the Roman Empire. Regalian was acclaimed emperor by the troops along the Danube river, a region of the empire that frequently experienced barbarian raids, probably in the hope that he might be able to secure the frontier. Accounts by surviving literary sources concerning Regalian are brief and few in number, and are mostly considered unreliable. The ''Historia Augusta'' relates that he was of Dacian descent, and a descendant of the Dacian king Decebalus, but this is mostly rejected in modern scholarship. Regalianus was married to Sulpicia Dryantilla, a woman from a prestigious senatorial family, which instead points to Regalian also being of high-ranking Roman descent. Regalian's acclamation as emperor was in the wake of a previous usurpation attempt by Ingenuus, also proclaimed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Cassius Regallianus
Gaius Cassius RegallianusThis name is written "Regallianus" on the external side of table I of the military diploma, while on the internal side of the table II it is written as "Regalianus". was a Roman senator active around AD 200. He was appointed consul suffectus in 202 as the colleague of Titus Murenius Severus. Both Regallianus and his colleague were unknown to historians until the publication in 2001 of a military diploma. This discovery, and especially Regallianus' existence, attracted attention, for previously the only known occurrence of the ''cognomen'' "Regal(l)ianus" is that of a usurper, Regalianus, who in 260 revolted against the emperor Gallienus, in the area of the Danube. He is known only by the coins he had struck and a passage in the unreliable ''Historia Augusta''. The coins minted from the usurper bear his name as P C REGALIANVS, whose ''nomen'' is usually expanded as ''Cornelius'', although other possibilities are not excluded. The presence, in the early 3rd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulpicia Dryantilla
Sulpicia Dryantilla (died 260/261) was the wife of Regalianus, Roman usurper against Gallienus. Regalianus gave her the title of Augusta to legitimize his claim. Virtually nothing is known of her except that she was the daughter of Claudia Ammiana Dryantilla and Sulpicius Pollio, an accomplished senator and officer under Caracalla. She most likely died in 260/261 along with her husband, when he was killed by a coalition of his own people and the Rhoxolani The Roxolani or Rhoxolāni ( , ; ) were a Sarmatians, Sarmatian people documented between the 2nd century BC and the 4th century AD, first east of the Borysthenes (Dnieper) on the coast of Lake Maeotis (Sea of Azov), and later near the borders o .... Most, but not all, of Regalianus' coins have the formula ''AUGG''. (implying two rulers, rather than ''AUG''., which implies one) as part of their reverse legend. The plural ''AUGG''. was likely intentional, but the intended meaning is not clear. It is more likely that it refers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
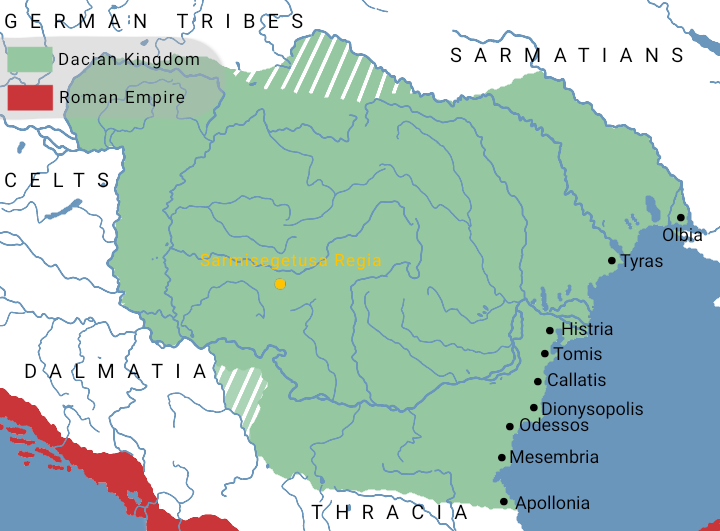
Decebalus
Decebalus (; ), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacians, Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invasion in the reign of Domitian, securing a period of independence during which Decebalus consolidated his rule. When Trajan came to power, his armies invaded Dacia to weaken its threat to the Roman border territories of Moesia. Decebalus was defeated in 102 AD, and his own sister was abducted within this timeframe and forcibly wed into Roman nobility, causing some historians to infer that she was the ancestress of the usurper, Regalianus, who claimed to be a kinsman of Decebalus. He remained in power as a client king, but continued to assert his independence, leading to a final and overwhelming Roman invasion north of the Danube in 105 AD. Trajan reduced the Dacian capital Sarmizegetusa Regia, Sarmizegetusa to ruins in 106 AD, abso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoninianus
The ''antoninianus'' or pre-reform radiate was a coin A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ... used during the Roman Empire thought to have been valued at 2 ''Denarius, denarii''. It was initially silver, but was slowly debasement, debased to bronze with a minimal silver content. The coin was introduced by Caracalla in early 215 AD. It was silver, similar to the ''denarius'', except that it was slightly larger and featured the Roman emperor, emperor wearing a radiate crown, indicating it was a double denomination. ''Antoniniani'' depicting women (usually the Roman emperor, emperor's wife) featured the bust resting upon a crescent moon. Even at its introduction, the silver content of the ''antoninianus'' was only equal to 1.5 ''denarii''. This created infla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallienus
Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus (; – September 268) was Roman emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260 and alone from 260 to 268. He ruled during the Crisis of the Third Century that nearly caused the collapse of the empire. He won numerous military victories against usurpers and Germanic tribes, but was unable to prevent the secession of important provinces. His 15-year reign was the longest in half a century. Born into a wealthy and traditional senatorial family, Gallienus was the son of Valerian and Mariniana. Valerian became Emperor in September 253 and had the Roman Senate elevate Gallienus to the rank of ''Augustus''. Valerian divided the empire between him and his son, with Valerian ruling the east and his son the west. Gallienus defeated the usurper Ingenuus in 258 and destroyed an Alemanni army at Mediolanum in 259. The defeat and capture of Valerian at Edessa in 260 by the Sasanian Empire threw the Roman Empire into the chaos of civil war. Contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnuntum
Carnuntum ( according to Ptolemy) was a Roman legionary fortress () and headquarters of the Roman navy, Pannonian fleet from 50 AD. After the 1st century, it was capital of the Pannonia Superior province. It also became a large city of approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Its impressive remains are situated on the Danube in Lower Austria halfway between Vienna and Bratislava in the Carnuntum Archaeological Park extending over an area of 10 km2 near today's villages of Petronell-Carnuntum and Bad Deutsch-Altenburg. History Military history Carnuntum first occurs in history during the reign of Augustus (6 AD), when Tiberius made it his base of operations as a Roman fort () in the campaigns against Maroboduus (Marbod). Legio XV Significant Romanisation happened when the town was selected as the garrison of the Legio XV Apollinaris, Legio XV before 14 AD. A few years later, it became the centre of the Roman fortifications along the Danube from Vindobona (now Vienna) to Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Usurper
Roman usurpers were individuals or groups of individuals who obtained or tried to obtain power by force and without legitimate legal authority. Usurpation was endemic during the Roman imperial era, especially from the crisis of the third century onwards, when political instability became the rule. Instability The first dynasty of the Roman Empire, the Julio-Claudian dynasty (27 BC – 68 AD), justified the imperial throne with familial ties through adoption. However, conflicts within the family led to the demise of the line. Nero committed suicide in 68 as an enemy of the people, resulting in a brief civil war. The Flavian dynasty started with Vespasian, only to end with the assassination of his second son, Domitian. Throughout most of the 2nd century, the empire enjoyed relative stability under the rule of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, but the next century would be characterised by endemic political instability, one of the factors that eventually contributed to the fall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurelius Victor
Sextus Aurelius Victor ( 320 – 390) was a historian and politician of the Roman Empire. Victor was the author of a now-lost monumental history of imperial Rome covering the period from Augustus to Constantius II. Under the emperor Julian (361-363), Victor served as governor of Pannonia Secunda in 361; in 389 he became praefectus urbi (urban prefect), senior imperial official in Rome. His surviving work, entitled ''De Caesaribus'' is a brief epitome of his history, and was originally titled in the two surviving manuscripts . The work was published in 361. Aurelius was born to a poor family in North Africa to an uneducated father. He was educated, first at Carthage and then at Rome. He apparently composed his history getween 358 and 360. Following the publication his reputation grew enough that Julian erected a bronze status of him in Naissus. Aurelius survived the death of the pagan Julian into the reign of the fiercely anti-pagan Theodosius I (347–395). It appears he b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' as a term is both controversial and imprecise. Spoken Latin existed for a long time and in many places. Scholars have differed in opinion as to the extent of the differences, and whether Vulgar Latin was in some sense a different language. This was developed as a theory in the nineteenth century by François Just Marie Raynouard, Raynouard. At its extreme, the theory suggested that the written register formed an elite language distinct from common speech, but this is now rejected. The current consensus is that the written and spoken languages formed a continuity much as they do in modern languages, with speech tending to evolve faster than the written language, and the written, formalised language exerting pressure back on speech. ''Vulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius (praenomen)
Publius (), feminine Publia, is a Latin ''praenomen'', or given name, personal name. It was used by both patrician and plebeian families, and was very common at all periods of Roman history. It gave rise to the patronymic ''Publilia gens, gens Publilia'', and perhaps also ''Publicia gens, gens Publicia''. The name was regularly abbreviated P.''Dictionary of Greek & Roman Biography & Mythology''''Realencyclopädie der Classischen Altertumswissenschaft''Mika Kajava, ''Roman Female Praenomina: Studies in the Nomenclature of Roman Women'' (1994) Throughout Roman history, Publius was one of the most frequently-used praenomina, typically occupying fourth or fifth place, behind ''Lucius (praenomen), Lucius'', ''Gaius (praenomen), Gaius'', and ''Marcus (praenomen), Marcus'', and occurring with about the same frequency as ''Quintus (praenomen), Quintus''. The feminine form Publia was also quite common, and is found in numerous inscriptions as late as the 3rd century, and perhaps beyond. Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffect Consul
The consuls were the highest elected public officials of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC). Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum''an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspiredafter that of the censor, which was reserved for former consuls. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated each month holding '' fasces'' (taking turns leading) when both were in Rome. A consul's ''imperium'' (military power) extended over Rome and all its provinces. Having two consuls created a check on the power of any one individual, in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symbolic representatives of Rome's republican heritage and hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaically
In language, an archaism is a word, a sense of a word, or a style of speech or writing that belongs to a historical epoch beyond living memory, but that has survived in a few practical settings or affairs. Lexical archaisms are single archaic words or expressions used regularly in an affair (e.g. religion or law) or freely; literary archaism is the survival of archaic language in a traditional literary text such as a nursery rhyme or the deliberate use of a style characteristic of an earlier age—for example, in his 1960 novel '' The Sot-Weed Factor'', John Barth writes in an 18th-century style. Archaic words or expressions may have distinctive emotional connotations—some can be humorous (''forsooth''), some highly formal (''What say you?''), and some solemn (''With thee do I plight my troth''). The word ''archaism'' is from the , ''archaïkós'', 'old-fashioned, antiquated', ultimately , ''archaîos'', 'from the beginning, ancient'. A distinction between archaic and obsole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |