|
Refsum Disease
Refsum disease is an autosomal recessive neurological disease that results in the over-accumulation of phytanic acid in cells and tissues. It is one of several disorders named after Norwegian neurologist Sigvald Bernhard Refsum (1907–1991). Refsum disease typically begins to show symptoms during adolescence, although symptoms may first appear anywhere between infancy and old age. Refsum disease is definitively diagnosed by lab tests showing above average serum levels of phytanic acid, or through genetic testing. Signs and symptoms Individuals with Refsum disease present with neurologic damage, cerebellar degeneration, and peripheral neuropathy. Most cases are symmetric (affecting the left and right sides of the body equally) and feature both motor and sensory nerve deficits with similar time of onset and rate of disease progression. Onset is most commonly in childhood or adolescence with a progressive course, although periods of stagnation or remission do occur. Rarely, sympto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytanic Acid
Phytanic acid (or 3,7,11,15-tetramethyl hexadecanoic acid) is a branched-chain fatty acid that humans can obtain through the consumption of dairy products, ruminant animal fats, and certain fish. Western diets are estimated to provide 50–100 mg of phytanic acid per day. In a study conducted in Oxford, individuals who consumed meat had, on average, a 6.7-fold higher geometric mean plasma phytanic acid concentration than did vegans. Human pathology Unlike most fatty acids, phytanic acid cannot be metabolized by β-oxidation. Instead, it undergoes α-oxidation in the peroxisome, where it is converted into pristanic acid by the removal of one carbon. Pristanic acid can undergo several rounds of β-oxidation in the peroxisome to form medium chain fatty acids that can be converted to carbon dioxide and water in mitochondria. Individuals with adult Refsum disease, an autosomal recessive neurological disorder caused by mutations in the '' PHYH'' gene, have impaired α-oxidation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellar Ataxia
Cerebellar ataxia is a form of ataxia originating in the cerebellum. Non-progressive congenital ataxia (NPCA) is a classical presentation of cerebral ataxias. Cerebellar ataxia can occur as a result of many diseases and may present with symptoms of an inability to coordinate balance, gait, extremity and eye movements. Lesions to the cerebellum can cause dyssynergia, dysmetria, dysdiadochokinesia, dysarthria and ataxia of stance and gait. Deficits are observed with movements on the same side of the body as the lesion (ipsilateral). Clinicians often use visual observation of people performing motor tasks in order to look for signs of ataxia. Signs and symptoms Damage to the cerebellum causes impairment in motor skills and can cause nystagmus. Almost a third of people with isolated, late onset cerebellar ataxia go on to develop multiple system atrophy. The cerebellum's role has been observed as not purely motor. It is combined with intellect, emotion and planning. Cerebellar de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second is called recessive. This state of having Heterozygosity, two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or Heredity, inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizomelic Chondrodysplasia Punctata
Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata is a rare developmental brain disorder characterized by abnormally short arms and legs (''rhizomelia''), seizures, recurrent respiratory tract infections and congenital cataracts. The cause is a genetic mutation that results in low levels of plasmalogens, which are a type of lipid found in cell membranes throughout the body, but whose function is not known. Signs and symptoms Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata has the following symptoms: * Bilateral shortening of the femur, resulting in short legs * Post-natal growth problems (deficiency) * Cataracts * Intellectual disability * Possible seizures * Possible infections of respiratory tract Genetics This condition is a consequence of mutations in the '' PEX7'' gene, the '' GNPAT'' gene (which is located on chromosome 1) or the '' AGPS'' gene. The condition is acquired in an autosomal recessive manner. Pathophysiology The mechanism of rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata in the case of type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and Signal_transduction, transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and produce physiological responses, such as a change in the electrophysiology, electrical activity of a cell. For example, GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, inhibits electrical activity of neurons by binding to GABAA receptor, GABA receptors. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand (biochemistry), ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Cell surface receptors, also known as transmembrane receptors, include ligand-gated ion channels, G prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
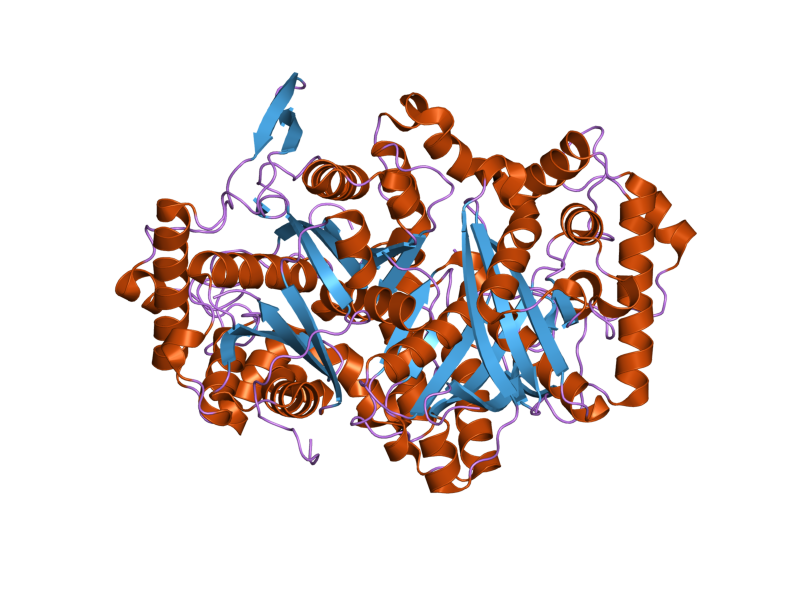
Peroxin-7
Peroxin-7 is a receptor associated with Refsum's disease and rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata type 1. See also * Peroxin Peroxins (or peroxisomal/peroxisome biogenesis factors) represent several protein families found in peroxisomes. Deficiencies are associated with several peroxisomal disorders. Peroxins serve several functions including the recognition of c ... External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Refsum Disease GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on Rhizomelic Chondrodysplasia Punctata Type 1 * {{biochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytanoyl-CoA Hydroxylase
In enzymology, a phytanoyl-CoA dioxygenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :phytanoyl-CoA + 2-oxoglutarate + O2 \rightleftharpoons 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA + succinate + CO2 The three substrates of this enzyme are phytanoyl-CoA, 2-oxoglutarate (2OG), and O2, whereas its three products are 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA, succinate, and CO2. This enzyme belongs to the family of iron(II)-dependent oxygenases, which typically incorporate one atom of dioxygen into the substrate and one atom into the succinate carboxylate group. The mechanism is complex, but is believed to involve ordered binding of 2-oxoglutarate to the iron(II) containing enzyme followed by substrate. Binding of substrate causes displacement of a water molecule from the iron(II) cofactor, leaving a vacant coordination position to which dioxygen binds. A rearrangement occurs to form a high energy iron-oxygen species (which is generally thought to be an iron(IV)=O species) that performs the actual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-oxidation
Enzymatic steps of alpha oxidation, 250px Alpha oxidation (α-oxidation) is a process by which certain branched-chain fatty acids are broken down by removal of a single carbon from the carboxyl end. In humans, alpha-oxidation is used in peroxisomes to break down dietary phytanic acid, which cannot undergo beta-oxidation due to its β-methyl branch, into pristanic acid. Pristanic acid can then acquire CoA and subsequently become beta oxidized, yielding propionyl-CoA. Pathway Alpha-oxidation of phytanic acid is believed to take place entirely within peroxisomes. #Phytanic acid is first attached to CoA to form phytanoyl-CoA. #Phytanoyl-CoA is oxidized by phytanoyl-CoA dioxygenase, in a process using Fe2+ and O2, to yield 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA. #2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA is cleaved by 2-hydroxyphytanoyl-CoA lyase in a TPP-dependent reaction to form pristanal and formyl-CoA (in turn later broken down into formate and eventually CO2). #Pristanal is oxidized by aldehyde dehydrogenase t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peroxisomal Disorder
Peroxisomal disorders represent a class of medical conditions caused by defects in peroxisome functions. This may be due to defects in single enzymes important for peroxisome function or in peroxins, proteins encoded by ''PEX'' genes that are critical for normal peroxisome assembly and biogenesis. Peroxisome biogenesis disorders Peroxisome biogenesis disorders (PBDs) include the Zellweger syndrome spectrum (PBD-ZSD) and rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata type 1 (RCDP1). PBD-ZSD represents a continuum of disorders including infantile Refsum disease, neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, and Zellweger syndrome. Collectively, PBDs are autosomal recessive developmental brain disorders that also result in skeletal and craniofacial dysmorphism, liver dysfunction, progressive sensorineural hearing loss, and retinopathy. PBD-ZSD is most commonly caused by mutations in the ''PEX1'', ''PEX6'', ''PEX10'', ''PEX12'', and ''PEX26'' genes. This results in the over-accumulation of very long chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA), most typically a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine, is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine. Catechol can be either a free molecule or a substituent of a larger molecule, where it represents a 1,2-dihydroxybenzene group. Catecholamines are derived from the amino acid tyrosine, which is derived from dietary sources as well as synthesis from phenylalanine. Catecholamines are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins in circulation. Included among catecholamines are epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and dopamine. Release of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla of the adrenal glands is part of the fight-or-flight response. Tyrosine is created from phenylalanine by hydroxylation by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Tyrosine is also ingested directly from dietary prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, chest pain, or decreased level of consciousness. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacarpal Bones
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones ( wrist bones), which articulate with the forearm. The metacarpal bones are homologous to the metatarsal bones in the foot. Structure The metacarpals form a transverse arch to which the rigid row of distal carpal bones are fixed. The peripheral metacarpals (those of the thumb and little finger) form the sides of the cup of the palmar gutter and as they are brought together they deepen this concavity. The index metacarpal is the most firmly fixed, while the thumb metacarpal articulates with the trapezium and acts independently from the others. The middle metacarpals are tightly united to the carpus by intrinsic interlocking bone elements at their bases. The ring metacarpal is somewhat more mobile while the fifth metacarpal is semi-independent.Tubiana ''et al'' 1998, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |