|
Red Sea Rift
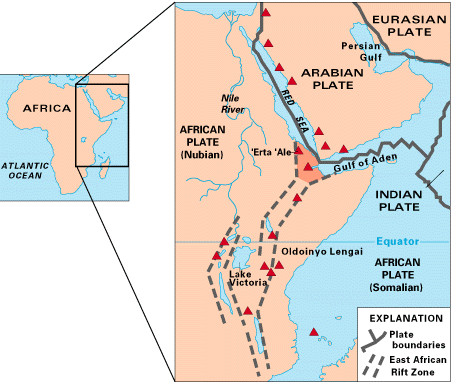
The Red Sea Rift is a mid-ocean ridge between two tectonic plates, the African plate and the Arabian plate. It extends from the Dead Sea Transform fault system, and ends at an intersection with the Aden Ridge and the East African Rift, forming the Afar triple junction in the Afar Depression of the Horn of Africa. The Red Sea Rift was formed by the divergence between the African and Arabian plates. The rift transitioned from a continental rift to an oceanic rift. Magnetic anomalies suggest that the spreading rate on either side of the Red Sea is about 1 cm/year. The African plate has a rotation rate of 0.9270 degrees/ Ma (million years), while the Arabian plate has a rotation rate of 1.1616 degrees/Ma. Spreading model A two-stage spreading model explains the tectonic evolution in this region. The first major rift motion was seen in the lower/middle Eocene, followed by major seafloor spreading in the late Eocene and early Oligocene. This was followed by a period of 30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATJ Map (color) , Quebec, Canada
{{dab ...
ATJ or atj may refer to: *''America's Toughest Jobs'', an American reality television show *Anya Taylor-Joy, an actress *''Asian Theatre Journal'' *atj, the ISO 639-3 code for Atikamekw language Atikamekw (endonym: ''Atikamekw Nehiromowin'', literally "Atikamekw native language") is a variety of the Algonquian language Cree and the language of the Atikamekw people of southwestern Quebec, Canada. It is spoken by nearly all the Atikame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate mineral, silicate rock between the Earth's crust, crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. It has a mass of and makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 46% of Earth's radius and 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly solid but, on geologic time scales, it behaves as a viscosity, viscous fluid, sometimes described as having the consistency of caramel. Partial melting of the mantle at mid-ocean ridges produces oceanic crust, and partial melting of the mantle at subduction zones produces continental crust. Structure Rheology Earth's upper mantle is divided into two major rheology, rheological layers: the rigid lithosphere comprising the uppermost mantle (the lithospheric mantle), and the more ductile asthenosphere, separated by the Lithosphere-Asthenosphere boundary, lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. Lithosphere underlying ocean crust has a thickness of around , whereas lithosphere underlying cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bab Al-Mandab
The Bab-el-Mandeb (), the Gate of Grief or the Gate of Tears, is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden and by extension the Indian Ocean. Etymology In "Bab-el-Mandeb", "Bab" means "gate" while "Mandeb" means "lamentation" or "grief". The strait derives its name from the dangers attending its navigation or, according to an Arab legend, from the numbers who were drowned by an earthquake that separated the Arabian Peninsula from the Horn of Africa. History Paleo-environmental and tectonic events in the Miocene epoch created the Danakil Isthmus, a land bridge forming a broad connection between Yemen and Ethiopia. During the last 100,000 years, eustatic sea level fluctuations have led to alternate opening and closing of the straits. According to the recent single origin hypothesis, the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb were probably witness to the earliest migrations of modern human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabal Al-Tair
Jabal al-Tair Island (or Jebel Teir, Jabal al-Tayr, Tair Island, Al-Tair Island, Jazirat at-Tair) ( ''Jazīrat Jabal aṭ-Ṭayr'', 'Bird Mountain Island') is a roughly oval volcano, volcanic island in Yemen, northwest of the constricted Bab al-Mandab passage at the mouth of the Red Sea, about halfway between mainland Yemen and Eritrea. From 1996 until an eruption in 2007, Yemen maintained two watchtowers and a small military base on the island. After 124 years of dormant volcano, dormancy, the volcano that created the island erupted on 30 September 2007. Geography The island is roughly oval, about long, across at its widest and in area. It lies nearly halfway between Yemen to the east and Eritrea about south west. It is about from the Yemeni Kamaran Island; the Saudi Arabian Farasan Islands lie to the north east. The island comprises the basaltic stratovolcano Jabal al-Tair (Tair Mountain; ''Jabal aṭ-Ṭayr'', literally, "Bird Mountain") rising from seabed some bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement
A basement is any Storey, floor of a building that is not above the grade plane. Especially in residential buildings, it often is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the Furnace (house heating), furnace, water heating, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, Garage (residential), car park, and air-conditioning system are located; so also are amenities such as the electrical system and cable television distribution point. In cities with high property prices, such as London, basements are often fitted out to a high standard and used as living space. In British English, the word ''basement'' is usually used for underground floors of, for example, department stores. The word is usually used with buildings when the space below the ground floor is habitable and with (usually) its own access. The word ''cellar'' applies to the whole underground level or to any large underground room. A ''subcellar'' or ''subbasement'' is a level that lies below the basement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Velocity
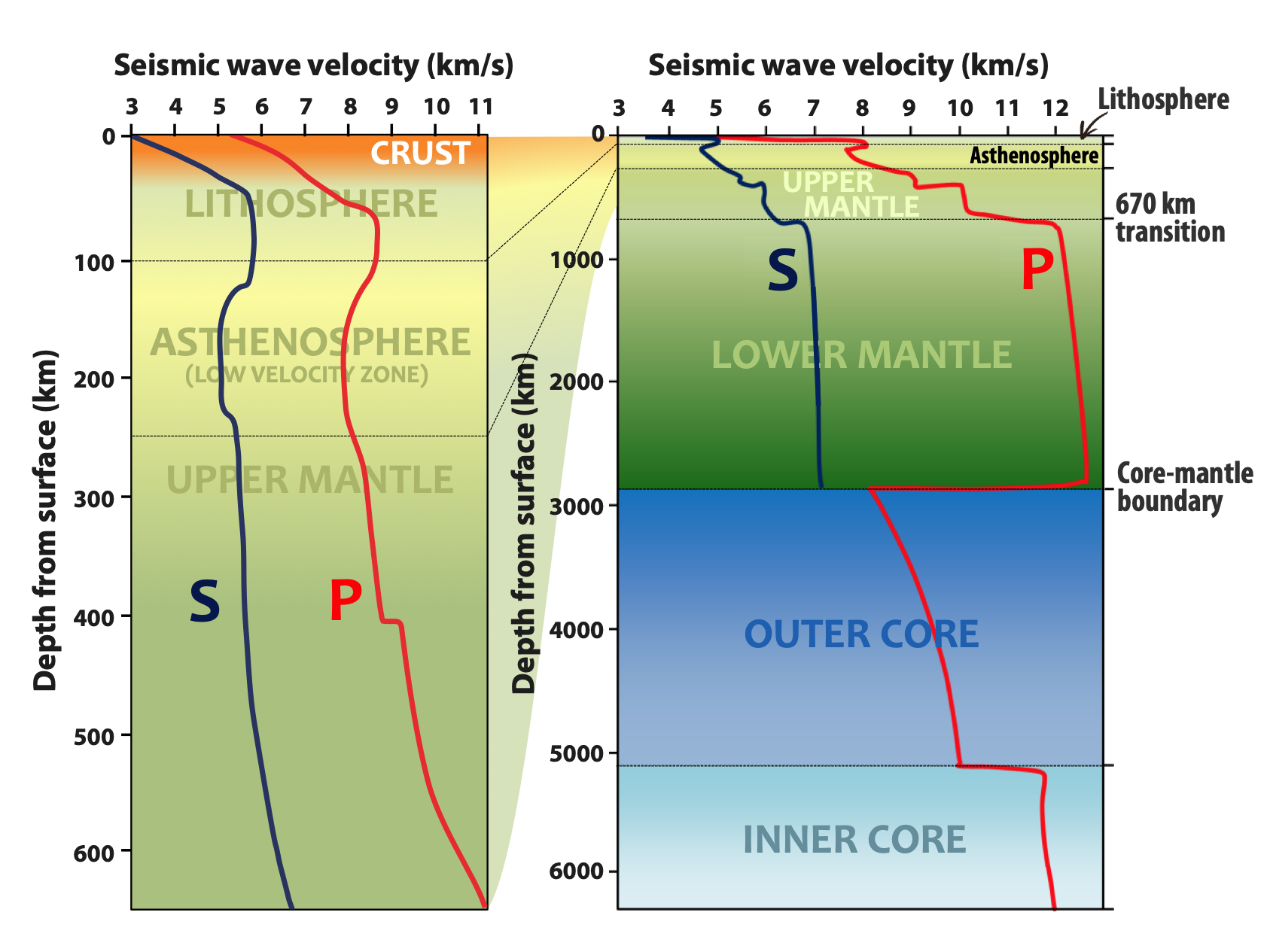
A seismic wave is a mechanical wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth or another planetary body. It can result from an earthquake (or generally, a quake), volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic energy. Seismic waves are studied by seismologists, who record the waves using seismometers, hydrophones (in water), or accelerometers. Seismic waves are distinguished from seismic noise (ambient vibration), which is persistent low-amplitude vibration arising from a variety of natural and anthropogenic sources. The propagation velocity of a seismic wave depends on density and elasticity of the medium as well as the type of wave. Velocity tends to increase with depth through Earth's crust and mantle, but drops sharply going from the mantle to Earth's outer core. Earthquakes create distinct types of waves with different velocities. When recorded by a seismic observatory, their d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Mantle (Earth)
The upper mantle of Earth is a very thick layer of rock inside the planet, which begins just beneath the crust (at about under the oceans and about under the continents) and ends at the top of the lower mantle the . Temperatures range from approximately at the upper boundary with the crust to approximately at the boundary with the lower mantle. Upper mantle material that has come up onto the surface comprises about 55% olivine, 35% pyroxene, and 5 to 10% of calcium oxide and aluminum oxide minerals such as plagioclase, spinel, or garnet, depending upon depth. Seismic structure The density profile through Earth is determined by the velocity of seismic waves. Density increases progressively in each layer, largely due to compression of the rock at increased depths. Abrupt changes in density occur where the material composition changes. The upper mantle begins just beneath the crust and ends at the top of the lower mantle. The upper mantle causes the tectonic plates to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vine–Matthews–Morley Hypothesis
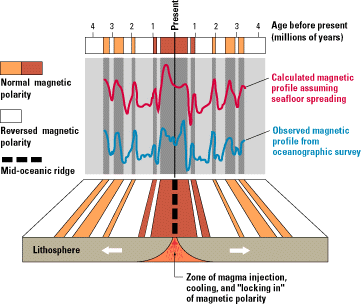
The Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis, also known as the Morley–Vine–Matthews hypothesis, was the first key scientific test of the seafloor spreading theory of continental drift and plate tectonics. Its key impact was that it allowed the rates of plate motions at mid-ocean ridges to be computed. It states that the Earth's oceanic crust acts as a recorder of reversals in the geomagnetic field direction as seafloor spreading takes place. History Harry Hess proposed the seafloor spreading hypothesis in 1960 (published in 1962); the term "spreading of the seafloor" was introduced by geophysicist Robert S. Dietz in 1961. According to Hess, seafloor was created at mid-oceanic ridges by the convection of the Earth's mantle, pushing and spreading the older crust away from the ridge. Geophysicist Frederick John Vine and the Canadian geologist Lawrence W. Morley independently realized that if Hess's seafloor spreading theory was correct, then the rocks surrounding the mid-ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dike (geology)
In geology, a dike or dyke is a sheet of rock that is formed in a fracture of a pre-existing rock body. Dikes can be either magmatic or sedimentary in origin. Magmatic dikes form when magma flows into a crack then solidifies as a sheet intrusion, either cutting across layers of rock or through a contiguous mass of rock. Clastic dikes are formed when sediment fills a pre-existing crack.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak Magmatic dikes A magmatic dike is a sheet of igneous rock that cuts across older rock beds. It is formed when magma fills a fracture in the older beds and then cools and solidifies. The dike rock is usually more resistant to weathering than the surrounding rock, so that erosion exposes the dike as a natural wall or ridge. It is from these natural walls that dikes get their name. Dikes preserve a record of the fissures through which most mafic magma (fluid magma low in silica) reaches the surface. They are studied by geologists for the clues they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delamination
Delamination is a mode of failure where a material fractures into layers. A variety of materials, including Lamination, laminate Composite material, composites and concrete, can fail by delamination. Processing can create layers in materials, such as steel formed by Rolling (metalworking), rolling and plastics and metals from 3D printing which can fail from layer separation. Also, surface coatings, such as paints and films, can delaminate from the coated substrate. In Lamination, laminated composites, the adhesion between layers often fails first, causing the layers to separate. For example, in Fibre-reinforced plastic, fiber-reinforced plastics, sheets of high strength reinforcement (e.g., Carbon fibers, carbon fiber, fiberglass) are bound together by a much weaker polymer matrix (e.g., epoxy). In particular, loads applied perpendicular to the high strength layers, and shear loads can cause the polymer matrix to fracture or the fiber reinforcement to debond from the polymer. Del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pure Shear
In mechanics and geology, pure shear is a three-dimensional homogeneous flattening of a body. It is an example of irrotational strain in which body is elongated in one direction while being shortened perpendicularly. For soft materials, such as rubber, a strain state of pure shear is often used for characterizing hyperelastic and fracture mechanical behaviour. Pure shear is differentiated from simple shear in that pure shear involves no rigid body rotation. The deformation gradient for pure shear is given by: F = \begin1&\gamma&0 \\\gamma&1&0\\0&0&1\end Note that this gives a Green-Lagrange strain of: E = \frac\begin\gamma^2&2\gamma&0\\2\gamma&\gamma^2&0\\0&0&0\end Here there is no rotation occurring, which can be seen from the equal off-diagonal components of the strain tensor. The linear approximation to the Green-Lagrange strain shows that the small strain tensor is: \epsilon = \frac\begin0&2\gamma&0\\2\gamma&0&0\\0&0&0\end which has only shearing components. See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic Uplift
Tectonic uplift is the orogeny, geologic uplift of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface that is attributed to plate tectonics. While Isostasy, isostatic response is important, an increase in the mean elevation of a region can only occur in response to tectonic processes of Thrust tectonics, crustal thickening (such as Mountain formation, mountain building events), changes in the density distribution of the crust and underlying Mantle (geology), mantle, and flexural support due to the bending of rigid lithosphere. Tectonic uplift results in denudation (processes that wear away the earth's surface) by raising buried rocks closer to the surface. This process can redistribute large loads from an elevated region to a topographically lower area as well – thus promoting an isostatic response in the region of denudation (which can cause local bedrock uplift). The timing, magnitude, and rate of denudation can be estimated by geologists using pressure-temperature studies. Crustal thickening C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |