|
Reaction Center
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex of several proteins, biological pigments, and other co-factors that together execute the primary energy conversion reactions of photosynthesis. Molecular excitations, either originating directly from sunlight or transferred as excitation energy via light-harvesting antenna systems, give rise to electron transfer reactions along the path of a series of protein-bound co-factors. These co-factors are light-absorbing molecules (also named chromophores or pigments) such as chlorophyll and pheophytin, as well as quinones. The energy of the photon is used to excite an electron of a pigment. The free energy created is then used, via a chain of nearby electron acceptors, for a transfer of hydrogen atoms (as protons and electrons) from H2O or hydrogen sulfide towards carbon dioxide, eventually producing glucose. These electron transfer steps ultimately result in the conversion of the energy of photons to chemical energy. Transforming light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. It is used by plants to make cellulose, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world, for use in cell walls, and by all living Organism, organisms to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used by the cell as energy. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as amylose and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form is -glucose, while its Stereoisomerism, stereoisomer L-glucose, -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). NADPH is the reduced form, whereas NADP is the oxidized form. NADP is used by all forms of cellular life. NADP is essential for life because it is needed for cellular respiration. NADP differs from NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate group. ADP-ribosyl cyclase allows for synthesis from nicotinamide in the salvage pathway, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferredoxin
Ferredoxins (from Latin ''ferrum'': iron + redox, often abbreviated "fd") are iron–sulfur proteins that mediate electron transfer in a range of metabolic reactions. The term "ferredoxin" was coined by D.C. Wharton of the DuPont Co. and applied to the "iron protein" first purified in 1962 by Mortenson, Valentine, and Carnahan from the anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacterium ''Clostridium pasteurianum''. Another redox protein, isolated from spinach chloroplasts, was termed "chloroplast ferredoxin". The chloroplast ferredoxin is involved in both cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation reactions of photosynthesis. In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, ferredoxin is the last electron acceptor thus reducing the enzyme NADP+ reductase. It accepts electrons produced from sunlight-Electron excitation, excited chlorophyll and transfers them to the enzyme ferredoxin: NADP+ oxidoreductase . Ferredoxins are small proteins containing iron and sulfur atoms organized as iron–sulfur clusters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
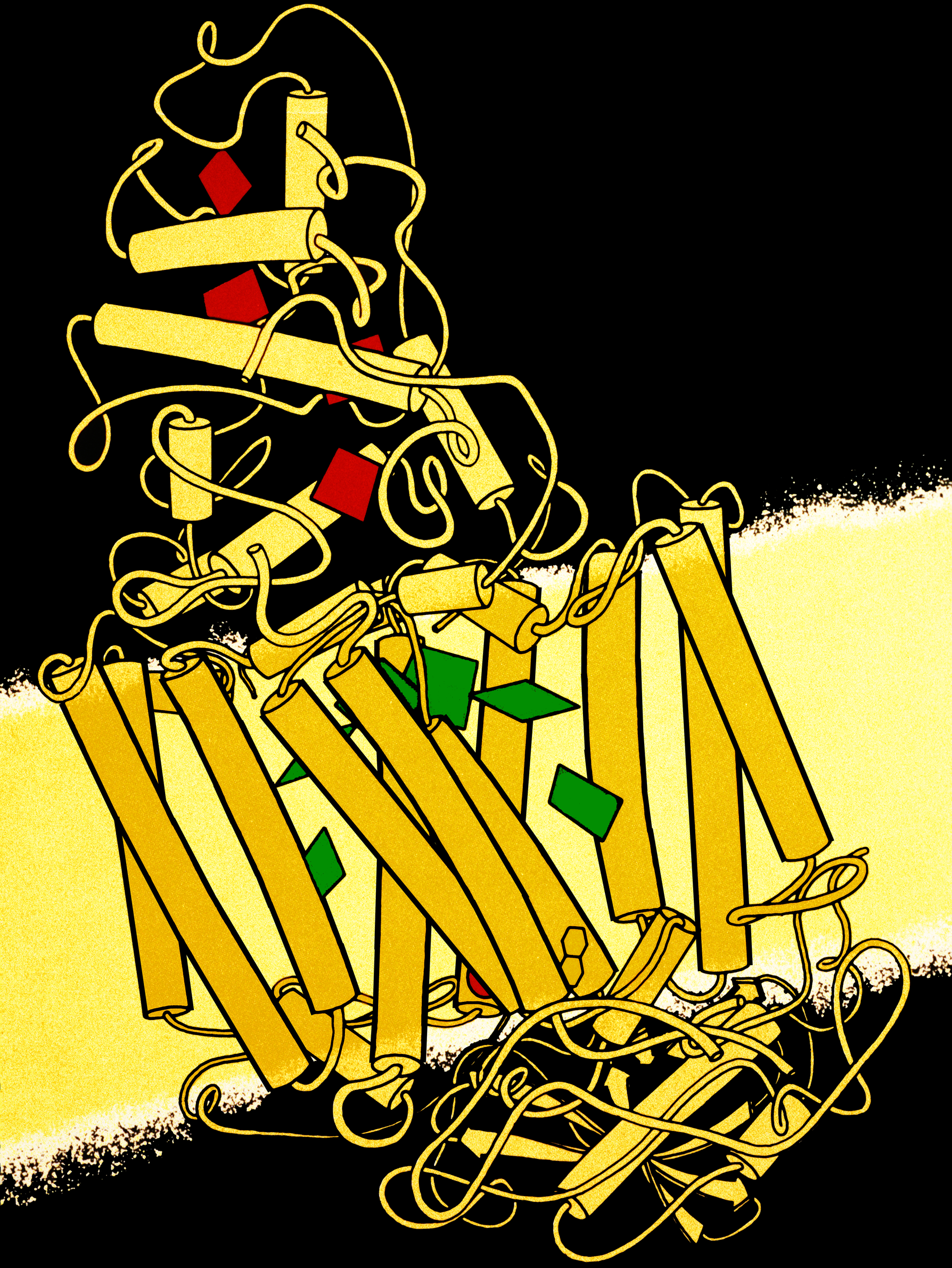
Cytochrome B6f Complex
The cytochrome ''b''6''f'' complex (plastoquinol/plastocyanin reductase or plastoquinol/plastocyanin oxidoreductase; ) is an enzyme found in the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts of plants, cyanobacteria, and green algae, that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from plastoquinol to plastocyanin: : plastoquinol + 2 oxidized plastocyanin + 2 H+ ide 1\rightleftharpoons plastoquinone + 2 reduced plastocyanin + 4 H+ ide 2 The reaction is analogous to the reaction catalyzed by cytochrome bc1 (Complex III) of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. During photosynthesis, the cytochrome b6f complex is one step along the chain that transfers electrons from Photosystem II to Photosystem I, and at the same time pumps protons into the thylakoid space, contributing to the generation of an electrochemical (energy) gradient that is later used to synthesize ATP from ADP. Enzyme structure The cytochrome b6f complex is a dimer, with each monomer composed of eight subunits. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
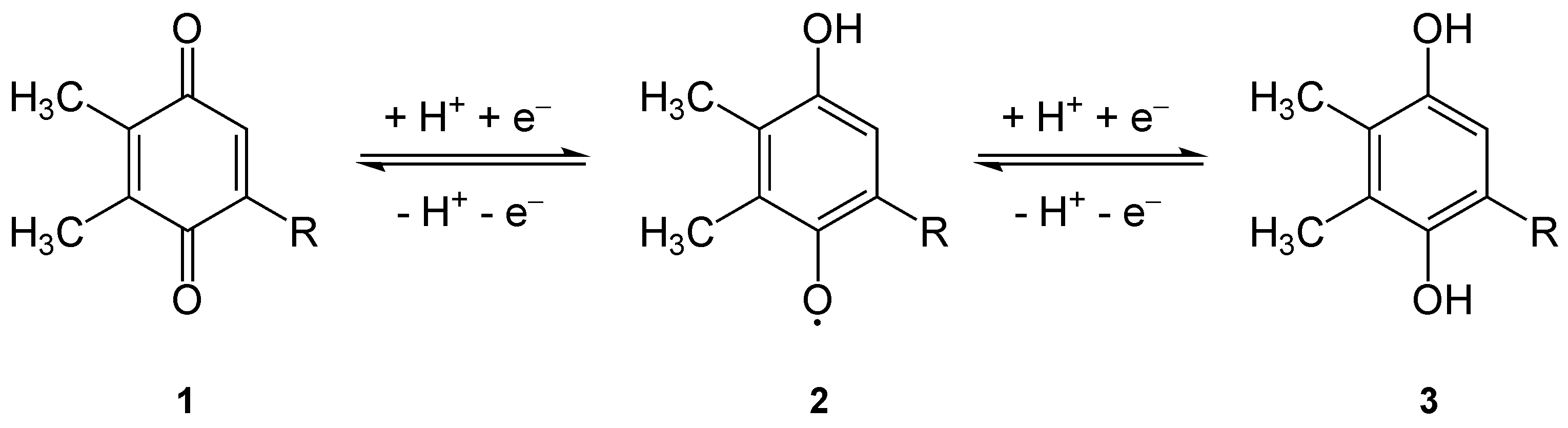
Plastoquinone
Plastoquinone (PQ) is a terpenoid-quinone ( meroterpenoid) molecule involved in the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. The most common form of plastoquinone, known as PQ-A or PQ-9, is a 2,3-dimethyl-1,4- benzoquinone molecule with a side chain of nine isoprenyl units. There are other forms of plastoquinone, such as ones with shorter side chains like PQ-3 (which has 3 isoprenyl side units instead of 9) as well as analogs such as PQ-B, PQ-C, and PQ-D, which differ in their side chains. The benzoquinone and isoprenyl units are both nonpolar, anchoring the molecule within the inner section of a lipid bilayer, where the hydrophobic tails are usually found. Plastoquinones are very structurally similar to ubiquinone, or coenzyme Q10, differing by the length of the isoprenyl side chain, replacement of the methoxy groups with methyl groups, and removal of the methyl group in the 2 position on the quinone. Like ubiquinone, it can come in severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds benzene.html" ;"title="uch as benzene">uch as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds", resulting in "a fully Conjugated system, conjugated cyclic diketone, dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone" (thus the name of the class). Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (''ortho''-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone. The name is derived from that of quinic acid (with the suffix "-one" indicating a ketone), since it is one of the compounds obtained upon oxidation of quinic acid. Quinic acid, like quinine is obtained from cinchona bark, called quinaquina in the indigenous languages of Peruvian tribes. Properties Quinones are oxidized derivatives of aromatic compounds an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Transport Chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are embedded within the membrane. The flow of electrons through the electron transport chain is an exergonic process. The energy from the redox reactions creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In aerobic respiration, the flow of electrons terminates with molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor. In anaerobic respiration, other electron acceptors are used, such as sulfate. In an electron transport chain, the redox reactions are driven by the difference in the Gibbs free energy of reactants and products. The free energy released when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypeptide Chain
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl group) res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodopseudomonas
''Rhodopseudomonas'' is a genus of bacteria from the family Nitrobacteraceae. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is an online database that maintains information on the naming and taxonomy of prokaryotes, following the taxonomy requirements and rulings of the International Code of Nomenclatu ... (LPSN). The phylogeny is based on whole-genome analysis. References Nitrobacteraceae Bacteria genera {{Nitrobacteraceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosystem II
Photosystem II (or water-plastoquinone oxidoreductase) is the first protein complex in the light-dependent reactions of oxygenic photosynthesis. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Within the photosystem, enzymes capture photons of light to energize electrons that are then transferred through a variety of coenzymes and cofactors to reduce plastoquinone to plastoquinol. The energized electrons are replaced by oxidizing water to form hydrogen ions and molecular oxygen. By replenishing lost electrons with electrons from the splitting of water, photosystem II provides the electrons for all of photosynthesis to occur. The hydrogen ions (protons) generated by the oxidation of water help to create a proton gradient that is used by ATP synthase to generate ATP. The energized electrons transferred to plastoquinone are ultimately used to reduce to NADPH or are used in non-cyclic electron flow. DCMU is a chemical often used in laboratory se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosystem I
Photosystem I (PSI, or plastocyanin–ferredoxin oxidoreductase) is one of two photosystems in the Light-dependent reactions, photosynthetic light reactions of algae, plants, and cyanobacteria. Photosystem I is an integral membrane protein Protein complex, complex that uses light energy to catalyze the electron transfer, transfer of electrons across the thylakoid membrane from plastocyanin to ferredoxin. Ultimately, the electrons that are transferred by Photosystem I are used to produce the moderate-energy hydrogen carrier NADPH. The photon energy absorbed by Photosystem I also produces a Chemiosmosis, proton-motive force that is used to generate adenosine triphosphate, ATP. PSI is composed of more than 110 Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors, significantly more than Photosystem II. History This photosystem is known as PSI because it was discovered before Photosystem II, although future experiments showed that Photosystem II is actually the first enzyme of the phot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |