|
Raymond Grégoire
Raymond Grégoire (31 December 1905 – 24 March 1960) was a French teacher and research physicist. He was a PhD student of Marie Curie and made his career at the Curie Laboratory (now preserved as the Curie Museum) in Paris from 1927 to 1960. Early life and education Raymond Emile Georges was born in Paris at dawn on 1 January 1906. His father was Émile, Grégoire, an accountant, and his mother was Mélanie Grégoire, née Combes, a stay-at-home wife. His father decided to register the birth for the previous day, 31 December 1905. At that time babies were delivered at home and registering a son a year earlier meant that his army service would also begin a year earlier and the boy would then subsequently enter active life a year earlier. The young Raymond knew little of his father who was working at Salle Wagram in Paris as an accountant. The latter was called up early in the First World War in 1914, and came back in 1918 having suffered gas attacks. His internal and external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Curie
Maria Salomea Skłodowska-Curie (; ; 7 November 1867 – 4 July 1934), known simply as Marie Curie ( ; ), was a Polish and naturalised-French physicist and chemist who conducted pioneering research on radioactivity. She was List of female Nobel laureates, the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, the first person Nobel Prize#Multiple laureates, to win a Nobel Prize twice, and the only person to win a Nobel Prize in two scientific fields. Her husband, Pierre Curie, was a co-winner of her first Nobel Prize, making them the Nobel Prize#Statistics, first married couple to win the Nobel Prize and launching the Nobel Prize#Family laureates, Curie family legacy of five Nobel Prizes. She was, in 1906, the first woman to become a professor at the University of Paris. She was born in Warsaw, in what was then the Congress Poland, Kingdom of Poland, part of the Russian Empire. She studied at Warsaw's clandestine Flying University and began her practical scientific training in Warsaw. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
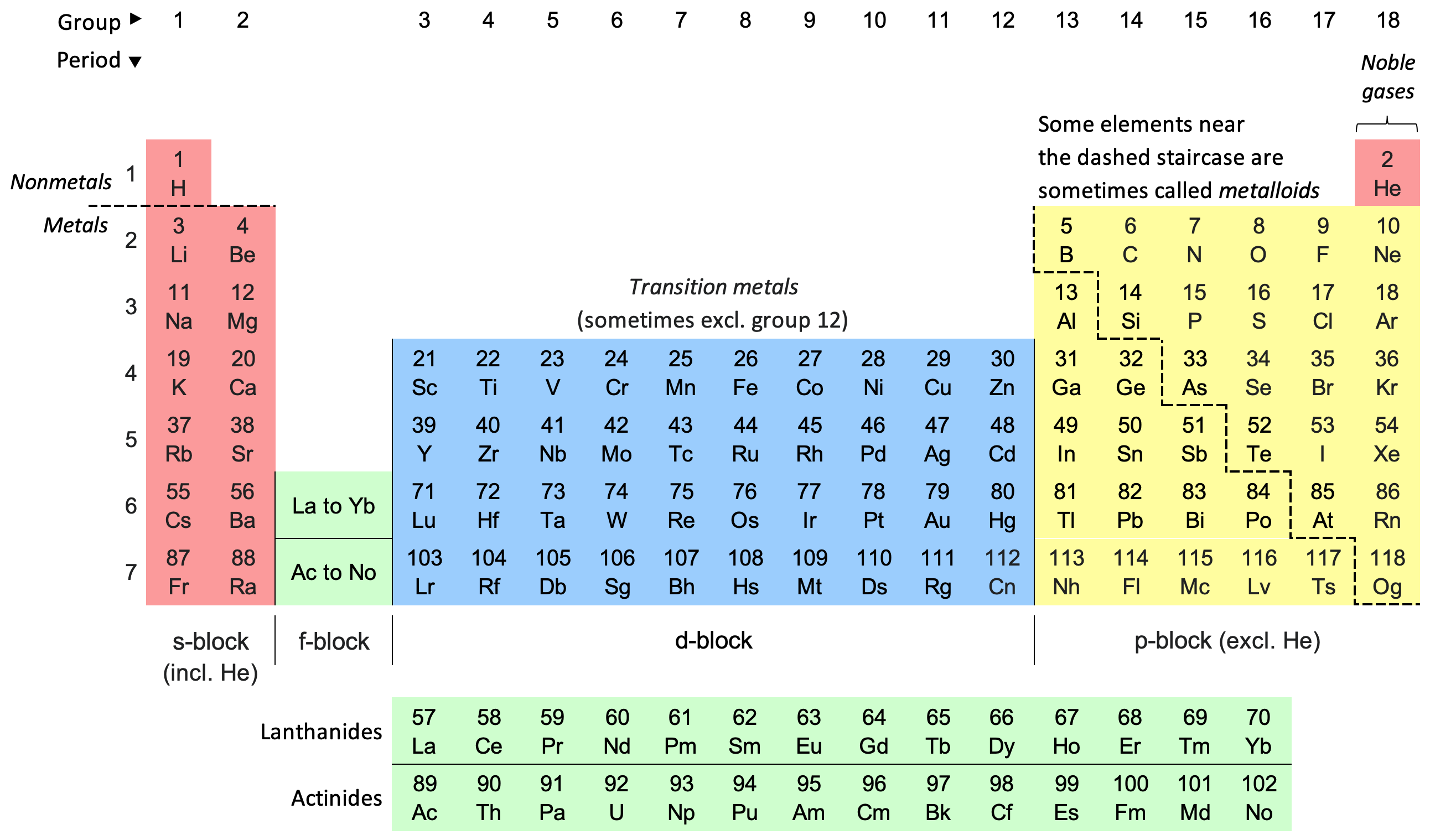
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Perrin (physicist)
Francis Perrin (17 August 1901 – 4 July 1992) was a French physicist, who worked on nuclear physics, fission and neutrinos. He was the high-commissioner Commissariat à l'énergie atomique (Atomic Energy Commission, CEA) in France and a collaborator of CERN. He was involved in the development of nuclear weapons for France and the cooperation with Israel on nuclear research. He was the son of Physics Nobel laureate Jean Perrin and the brother-in-law of Pierre Victor Auger. Physicist Francis Perrin was born in Paris and attended École Normale Supérieure in Paris. In 1928 he obtained a doctorate in mathematical sciences from the faculté des sciences of Paris, based upon a thesis on Brownian motion and became a faculty member of Collège de France. In 1933, in connection with the neutrino, Francis Perrin estimated that "the mass must be null—or at least small compared to the mass of the electron". Subsequently, he worked at the Collège de France on the fission of uran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marguerite Perey
Marguerite Catherine Perey (19 October 1909 – 13 May 1975) was a French physicist and a student of Marie Curie. In 1939, Perey discovered the element francium by purifying samples of lanthanum that contained actinium. In 1962, she was the first woman to be elected to the French Académie des Sciences, an honor denied to her mentor Curie. Perey died of cancer in 1975. Early life Perey was born in 1909 in Villemomble, France, just outside Paris where the Curie's Radium Institute was located. Although she hoped to study medicine, the death of her father left the family in financial difficulties. Perey earned a chemistry diploma from Paris' Technical School of Women's Education in 1929; while not a "degree", it did qualify her to work as a chemistry technician. In 1929 at the age of 19, Perey interviewed for a role as a personal assistant (technician) to Marie Curie at Curie's Radium Institute in Paris, France, and was hired. Marie Curie took on a mentoring role to Perey, tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Academy Of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (, ) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific method, scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, and is one of the earliest Academy of Sciences, Academies of Sciences. Currently headed by Patrick Flandrin (President of the academy), it is one of the five Academies of the . __TOC__ History The Academy of Sciences traces its origin to Colbert's plan to create a general academy. He chose a small group of scholars who met on 22 December 1666 in the King's library, near the present-day Bibliothèque nationale de France, Bibliothèque Nationale, and thereafter held twice-weekly working meetings there in the two rooms assigned to the group. The first 30 years of the academy's existence were relatively informal, since no statutes had as yet been laid down for the ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESIGELEC
ESIGELEC is a French engineering school, founded in 1901, and located in Rouen. It is part of the Grandes écoles group of French academic institutions specializing in engineering and sciences and is a university level institution with the special status Grands établissements. It is under supervision of the Ministry of Higher Education and Research and jointly managed by the chamber of commerce of Rouen, the Society of Engineers in Electrical Engineering (in , SIGELEC), and a consortium of private companies. History In 1901, Alexandre Charliat, an engineer from École Centrale Paris, decided to create a school of engineers corresponding to its own perspective on education. He named it the Practical School of Industrial Electricity () and established it at 53 rue Belliard in Paris. The school was later renamed the School of Industrial Electricity of Paris (EEIP; ). It was renamed again in 1980, becoming the 'Superior School of Electrical Engineers' (; ESIGELEC). The Ministry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panthéon
The Panthéon (, ), is a monument in the 5th arrondissement of Paris, France. It stands in the Latin Quarter, Paris, Latin Quarter (Quartier latin), atop the , in the centre of the , which was named after it. The edifice was built between 1758 and 1790, from designs by , at the behest of King Louis XV, Louis XV of France; the king intended it as a church dedicated to Genevieve, Saint Genevieve, Paris's patron saint, whose relics were to be housed in the church. Neither Soufflot nor Louis XV lived to see the church completed. By the time the construction was finished, the French Revolution had started; the National Constituent Assembly (France), National Constituent Assembly voted in 1791 to transform the Church of Saint Genevieve into a mausoleum for the remains of distinguished French citizens, modelled on the Pantheon, Rome, Pantheon in Rome which had been used in this way since the 17th century. The first was , although his remains were removed from the building a few years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frédéric Joliot-Curie
Jean Frédéric Joliot-Curie (; ; 19 March 1900 – 14 August 1958) was a French chemist and physicist who received the 1935 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with his wife, Irène Joliot-Curie, for their discovery of induced radioactivity. They were the second married couple, after his parents-in-law, to win the Nobel Prize, adding to the Curie family legacy of five Nobel Prizes. Joliot-Curie and his wife also founded the Orsay Faculty of Sciences, part of the Paris-Saclay University. Biography Early years Born in Paris, France, Frédéric Joliot was a graduate of ESPCI Paris. In 1925 he became an assistant to Marie Curie, at the Radium Institute. He fell in love with her daughter Irène Curie, and soon after their marriage in 1926 they both changed their surnames to Joliot-Curie. At the insistence of Marie, Joliot-Curie obtained a second baccalauréat, a bachelor's degree, and a doctorate in science, doing his thesis on the electrochemistry of radio-elements. Career W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irène Joliot-Curie
Irène Joliot-Curie (; ; 12 September 1897 – 17 March 1956) was a French chemist and physicist who received the 1935 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with her husband, Frédéric Joliot-Curie, for their discovery of induced radioactivity. They were the second married couple, after her parents, to win the Nobel Prize, adding to the Curie family legacy of five Nobel Prizes. This made the Curies the family with the most Nobel laureates to date. Her mother Marie Skłodowska-Curie and she also form the only mother–daughter pair to have won Nobel Prizes whilst Pierre and Irène Curie form the only father-daughter pair to have won Nobel Prizes by the same occasion, whilst there are six father-son pairs who have won Nobel Prizes by comparison. She was also one of the first three women to be a member of a French government, becoming undersecretary for Scientific Research under the Popular Front in 1936. Both children of the Joliot-Curies, Hélène and Pierre, are also scientists. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernand Holweck
Fernand Holweck (21 July 1890 – 24 December 1941) was a French physicist who made important contributions in the fields of vacuum technology, electromagnetic radiation and gravitation. He is also remembered for his personal sacrifice in the cause of the French Resistance and his aid to Allied airmen in World War II. Biography Holweck was born on 21 July 1890 to a family from the Alsace Region who had opted to remain French at the end of the Franco-Prussian war in 1870. He studied at the École supérieure de physique et de chimie industrielles de la ville de Paris (ESPCI), where he graduated top of his class in engineering physics and became personal assistant to Marie Curie. During his military service he worked under the wireless telegraphy pioneer Gustave-Auguste Ferrié at the Eiffel Tower radio station, and by 1914 he had produced his first patent, relating to thermionic tubes. During World War I, 1914–1918, he served first at the front, working on methods to detect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Alternative Energies And Atomic Energy Commission
The French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission, or CEA ( French: Commissariat à l'énergie atomique et aux énergies alternatives), is a French public government-funded research organisation in the areas of energy, defense and security, information technologies and health technologies. The CEA maintains a cross-disciplinary culture of engineers and researchers, building on the synergies between fundamental and technological research. CEA is headed by a board headed by the general administrator (currently François Jacq since 20 April 2018), advised by the high-commissioner for atomic energy (currently ). Its yearly budget amounts to €5.8 billion and its permanent staff is slightly over 21,000 persons. History CEA was created in 1945; since then, the successive high-commissioners have been Frédéric Joliot-Curie, Francis Perrin, , , Raoul Dautry, René Pellat, Bernard Bigot, Catherine Cesarsky, , and François Jacq. In December 2009, French President Ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertrand Goldschmidt
Bertrand Goldschmidt (2 November 1912 – 11 June 2002) was a French chemist. He is considered one of the fathers of the French atomic bomb, which was tested for the first time in 1960 in the nuclear test Gerboise Bleue. Biography Bertrand Goldschmidt was born in Paris on 2 November 1912 to a French mother and a Belgian father of Jewish origin. He entered the Paris School of Industrial Physics and Chemistry in 1932 and was recruited to the Radium Institute in 1933 by Marie Curie. He obtained his doctorate in 1939. During the Battle of France, Goldschmidt served in a military laboratory in Poitiers and was taken prisoner by the invading Germans. They later released him and he moved into the unoccupied zone. He taught for a short time in Montpellier, until the post-surrender Vichy government changed the status of Jews under pressure from the Germans. He then emigrated to the United States and arrived in New York City in May 1941, where he joined the Free French Forces. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |