|
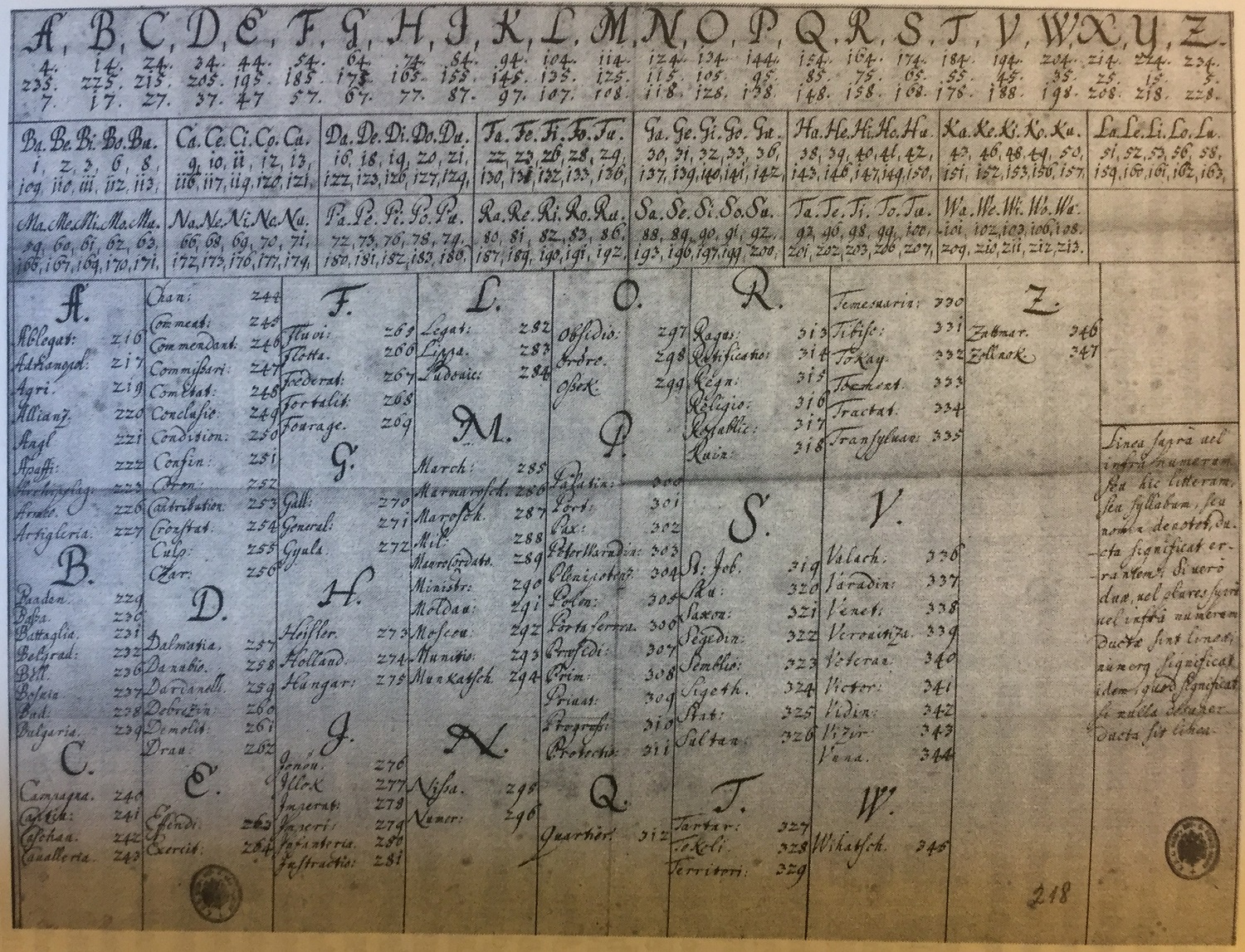
Rasterschlüssel 44
Rasterschlüssel 44 (abbr. RS 44) was a manual cipher system, used by the German Wehrmacht during the Second World War. The cipher was designed by the astronomer and sometime cryptographer Walter Fricke while working as a conscript in Section IIb, of Group 2 of OKW/Chi and introduced in March 1944 and the Allied forces codebreakers had considerable difficulties in breaking it. Cryptanalysis, if successful, generally required a 40 letter crib (known plaintext) and some two weeks, making the tactical information outdated before it could be exploited. The combination of strength and ease of use made RS 44 an ideal hand cipher. Design The cipher is a transposition based grille cipher, consisting of a grid with 25 columns and 24 rows. Each row contains 10 randomly placed white cells (to be filled with text) and 15 black cells. The columns are labeled with shuffled digraphs and numbers and the rows with digraphs. The key sheet also contains two letter substitution alphabets to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cipher
In cryptography, a cipher (or cypher) is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption—a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is ''encipherment''. To encipher or encode is to convert information into cipher or code. In common parlance, "cipher" is synonymous with " code", as they are both a set of steps that encrypt a message; however, the concepts are distinct in cryptography, especially classical cryptography. Codes generally substitute different length strings of characters in the output, while ciphers generally substitute the same number of characters as are input. There are exceptions and some cipher systems may use slightly more, or fewer, characters when output versus the number that were input. Codes operated by substituting according to a large codebook which linked a random string of characters or numbers to a word or phrase. For example, "UQJHSE" could be the code for "Proceed to the follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposition Cipher
In cryptography, a transposition cipher is a method of encryption which scrambles the positions of characters (''transposition'') without changing the characters themselves. Transposition ciphers reorder units of plaintext (typically characters or groups of characters) according to a regular system to produce a ciphertext which is a permutation of the plaintext. They differ from substitution ciphers, which do not change the position of units of plaintext but instead change the units themselves. Despite the difference between transposition and substitution operations, they are often combined, as in historical ciphers like the ADFGVX cipher or complex high-quality encryption methods like the modern Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). General principle Plaintexts can be rearranged into a ciphertext using a key, scrambling the order of characters like the shuffled pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. The resulting message is hard to decipher without the key because there are many ways the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Telecommunications In Germany
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Cryptography
Cryptography, the use of codes and ciphers to protect secrets, began thousands of years ago. Until recent decades, it has been the story of what might be called classical cryptography — that is, of methods of encryption that use pen and paper, or perhaps simple mechanical aids. In the early 20th century, the invention of complex mechanical and electromechanical machines, such as the Enigma rotor machine, provided more sophisticated and efficient means of encryption; and the subsequent introduction of electronics and computing has allowed elaborate schemes of still greater complexity, most of which are entirely unsuited to pen and paper. The development of cryptography has been paralleled by the development of cryptanalysis — the "breaking" of codes and ciphers. The discovery and application, early on, of frequency analysis to the reading of encrypted communications has, on occasion, altered the course of history. Thus the Zimmermann Telegram triggered the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Ciphers
Classical may refer to: European antiquity *Classical antiquity, a period of history from roughly the 7th or 8th century B.C.E. to the 5th century C.E. centered on the Mediterranean Sea *Classical architecture, architecture derived from Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity *Classical mythology, the body of myths from the ancient Greeks and Romans *Classical tradition, the reception of classical Greco-Roman antiquity by later cultures * Classics, study of the language and culture of classical antiquity, particularly its literature *Classicism, a high regard for classical antiquity in the arts Music and arts *Classical ballet, the most formal of the ballet styles * Classical music, a variety of Western musical styles from the 9th century to the present * Classical guitar, a common type of acoustic guitar *Classical Hollywood cinema, a visual and sound style in the American film industry between 1927 and 1963 * Classical Indian dance, various codified art forms whose t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anagram
An anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once. For example, the word ''anagram'' itself can be rearranged into ''nag a ram'', also the word ''binary'' into ''brainy'' and the word ''adobe'' into ''abode''. The original word or phrase is known as the ''subject'' of the anagram. Any word or phrase that exactly reproduces the letters in another order is an anagram. Someone who creates anagrams may be called an "anagrammatist", and the goal of a serious or skilled anagrammatist is to produce anagrams that reflect or comment on their subject. Examples Anagrams may be created as a commentary on the subject. They may be a parody, a criticism or satire. For example: * "New York Times" = " monkeys write" * " Church of Scientology" = "rich-chosen goofy cult" * "McDonald's restaurants" = " Uncle Sam's standard rot" * " coronavirus" = "carnivorous" * "She Sells Sanctuary" = " Santa; shy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can decipher a ciphertext back to plaintext and access the original information. Encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor. For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random encryption key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but, for a well-designed encryption scheme, considerable computational resources and skills are required. An authorized recipient can easily decrypt the message with the key provided by the originator to recipients but not to unauthorized users. Historically, various forms of encryption have been used to aid in cryptography. Early encryption techniques were often used in milit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substitution Cipher
In cryptography, a substitution cipher is a method of encrypting in which units of plaintext are replaced with the ciphertext, in a defined manner, with the help of a key; the "units" may be single letters (the most common), pairs of letters, triplets of letters, mixtures of the above, and so forth. The receiver deciphers the text by performing the inverse substitution process to extract the original message. Substitution ciphers can be compared with transposition ciphers. In a transposition cipher, the units of the plaintext are rearranged in a different and usually quite complex order, but the units themselves are left unchanged. By contrast, in a substitution cipher, the units of the plaintext are retained in the same sequence in the ciphertext, but the units themselves are altered. There are a number of different types of substitution cipher. If the cipher operates on single letters, it is termed a simple substitution cipher; a cipher that operates on larger groups of lett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digraph (computing)
In computer programming, digraphs and trigraphs are sequences of two and three characters, respectively, that appear in source code and, according to a programming language's specification, should be treated as if they were single characters. Various reasons exist for using digraphs and trigraphs: keyboards may not have keys to cover the entire character set of the language, input of special characters may be difficult, text editors may reserve some characters for special use and so on. Trigraphs might also be used for some EBCDIC code pages that lack characters such as . History The basic character set of the C programming language is a subset of the ASCII character set that includes nine characters which lie outside the ISO 646 invariant character set. This can pose a problem for writing source code when the encoding (and possibly keyboard) being used does not support any of these nine characters. The ANSI C committee invented trigraphs as a way of entering source code usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grille (cryptography)
In the history of cryptography, a grille cipher was a technique for encrypting a plaintext by writing it onto a sheet of paper through a pierced sheet (of paper or cardboard or similar). The earliest known description is due to the polymath Girolamo Cardano in 1550. His proposal was for a rectangular stencil allowing single letters, syllables, or words to be written, then later read, through its various apertures. The written fragments of the plaintext could be further disguised by filling the gaps between the fragments with anodyne words or letters. This variant is also an example of steganography, as are many of the grille ciphers. Cardan grille and variations The Cardan grille was invented as a method of secret writing. The word ''cryptography'' became the more familiar term for secret communications from the middle of the 17th century. Earlier, the word ''steganography'' was common. The other general term for secret writing was ''cypher'' - also spelt ''cipher''. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crib (cryptanalysis)
The known-plaintext attack (KPA) is an attack model for cryptanalysis where the attacker has access to both the plaintext (called a crib), and its encrypted version (ciphertext). These can be used to reveal further secret information such as secret keys and code books. The term "crib" originated at Bletchley Park, the British World War II decryption operation, where it was defined as: History The usage "crib" was adapted from a slang term referring to cheating (e.g., "I cribbed my answer from your test paper"). A "crib" originally was a literal or interlinear translation of a foreign-language text—usually a Latin or Greek text—that students might be assigned to translate from the original language. The idea behind a crib is that cryptologists were looking at incomprehensible ciphertext, but if they had a clue about some word or phrase that might be expected to be in the ciphertext, they would have a "wedge," a test to break into it. If their otherwise random attacks on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and audacious moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi régime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and defense spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military power. In the early part of the Second World War, the ''Wehrmacht'' employed combined arms tactics (close- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)