|
Ranulph Le Meschin, Earl Of Chester
Ranulf le Meschin, 3rd Earl of Chester (1070–1129) was a Norman magnate based in northern and central England. Originating in Bessin in Normandy, Ranulf made his career in England thanks to his kinship with Hugh d'Avranches - the Earl of Chester, the patronage of kings William II Rufus and Henry I Beauclerc, and his marriage to Lucy (countess-consort of Chester), Lucy, heiress of the Bolingbroke-Spalding estates in Lincolnshire. Ranulf fought in Normandy on behalf of Henry I, and served the English king as a kind of semi-independent governor in the far north-west, in Cumberland and Westmorland, founding Wetheral Priory Gatehouse, Wetheral Priory. After the death of his cousin Richard d'Avranches, 2nd Earl of Chester, Richard d'Avranches in the White Ship Disaster of November 1120, Ranulf became earl of the county of Chester on the Anglo-Welsh marches. He held this position for the remainder of his life, and passed the title on to his son, Ranulf de Gernon. Biography Family and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
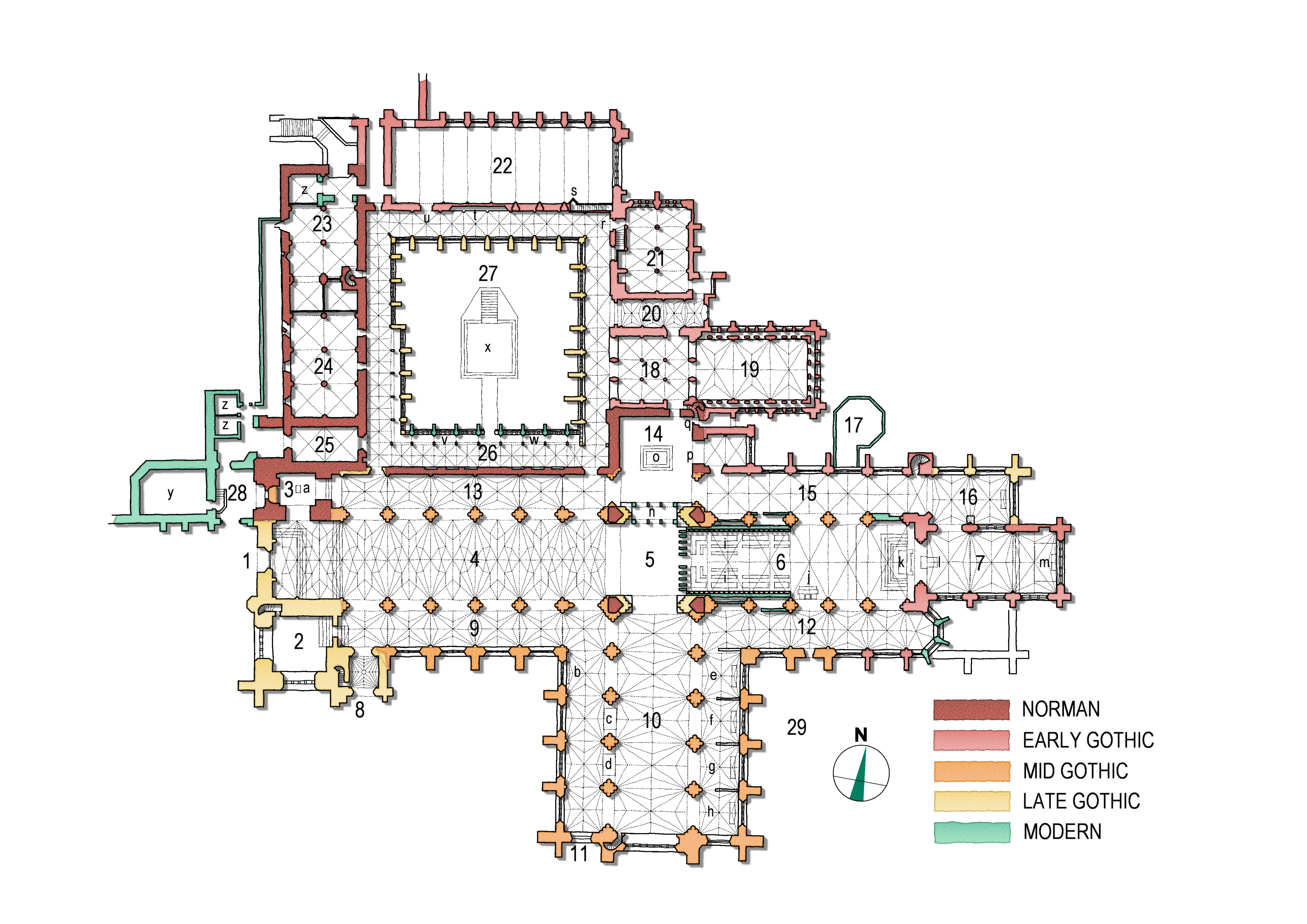
Chester Abbey
Chester Cathedral is a Church of England cathedral and the mother church of the Diocese of Chester. It is located in the city of Chester, Cheshire, England. The cathedral, formerly the abbey church of a Benedictine monastery dedicated to Saint Werburgh, is dedicated to Christ and the Blessed Virgin Mary. Since 1541, it has been the seat of the bishop of Chester. The cathedral is a Grade I listed building, and part of a heritage site that also includes the former monastic buildings to the north, which are also listed Grade I. The cathedral's construction dates from between the 10th century and the early 16th century, having been modified a number of times throughout history, a typical characteristic of English cathedrals; however, the site itself may have been used for Christian worship since Roman times. All the major styles of English medieval architecture, from Norman to Perpendicular, are represented in the present building. The cathedral and former monas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Welsh Marches
The Welsh Marches () is an imprecisely defined area along the border between England and Wales in the United Kingdom. The precise meaning of the term has varied at different periods. The English term Welsh March (in Medieval Latin ''Marchia Walliae'') was originally used in the Middle Ages to denote the marches between England and the Principality of Wales, in which Marcher lords had specific rights, exercised to some extent independently of the king of England. In modern usage, "the Marches" is often used to describe those English counties which lie along the border with Wales, particularly Shropshire and Herefordshire, and sometimes adjoining areas of Wales. However, at one time the Marches included all of the historic counties of Cheshire, Shropshire, Herefordshire, Worcestershire and Gloucestershire. Etymology The term ''March'' is from the 13th-century Middle English ''marche'' ("border region, frontier"). The term was borrowed from Old French ''marche'' ("limit, bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avranchin
Avranchin is an area in Normandy, France corresponding to the territory of the Abrincatui, a tribe of Celts from whom the city of Avranches, the main town of the Avranchin, takes its name. In 867, by the Treaty of Compiègne, Charles the Bald gave the Avranchin to Salomon, King of Brittany. In 933, it was reunited with the Duchy of Normandy by William I of Normandy. Geography Avranchin is located in the Armorican Massif south of Cotentin in the department of Manche in western or lower Normandy. The Thar river forms the northern border. The eastern border is formed by the Égrenne, a tributary of the Mayenne. To the north west lies the bay of Mont-Saint-Michel. The south west was once marked by the Couesnon river, however due to canal building in the 18th century the river now flows 4 km to the west of the region. The largest town in the area is Avranches. The village of Mortain is traditionally included as part of Avranchin. History Avranchin was once the territory of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiémois
Exmes () is a former commune in the Orne department in north-western France. On 1 January 2017, it was merged into the new commune Gouffern en Auge. 6 October 2016 It was the seat of the county of Hiémois (French: '' Comté d'Hiémois''), granted before his death in 1027 by , to his younger son, Robert, who eventually succeeded as . In 1136, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Le Goz, Viscount Of Avranches
Richard le Goz (died 1082 or after) was a Norman nobleman and supporter of William the Conqueror in the Norman conquest of England. Life Richard was the son of Thorstein le Goz, Viscount of Hiesmes, and grandson of Ansfred 'the Dane', Viscount of Hiesmes. William II, Duke of Normandy, bestowed on him the title of Viscount of Avranches sometime before 1046. Richard may also have been Lord of Creully and entrusted with the castle of Saint-James-de-Beuvron, built by William in 1067 shortly after the war against the Bretons of 1064–66. Richard provided 60 ships to support William's 1066 invasion of England but is not among those known to have been present at the Battle of Hastings. Between 1070 and 1079, Richard was involved in a ruling between Raoul Tesson and the Abbey of Fontenay. Around 1076 he was one of the judges who pronounced an award against Robert Bertram. Richard married Emma, who is believed to have been the daughter of Herluin de Conteville and Herleva (mistre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard III, Duke Of Normandy
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include " Richie", " Dick", " Dickon", " Dickie", " Rich", " Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English (the name was introduced into England by the Normans), German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Portuguese and Spanish "Ricardo" and the Italian "Riccardo" (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Normandy
The House of Normandy ( ) was a noble family originating from the Duchy of Normandy. The House of Normandy's lineage began with the Scandinavian Rollo who founded the Duchy of Normandy in 911. The House of Normandy includes members who were dukes of Normandy, counts of Rouen, as well as kings of England following the Norman conquest of England. It lasted until Stephen of the French House of Blois seized the Duchy of Normandy in 1135. The house emerged from the union between the Viking Rollo (first ruler of Normandy) and Poppa of Bayeux, a West Frankish noblewoman. William the Conqueror and his heirs down through 1135 were members of this dynasty. After that it was disputed between William's grandchildren, Matilda, whose husband Geoffrey was the founder of the House of Plantagenet, and Stephen of the House of Blois (or Blesevin dynasty). The Norman counts of Rouen were: * Rollo, 911–927 * William Longsword, 927–942 The Norman dukes of Normandy were: * Richard I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Bayeux
The Diocese of Bayeux and Lisieux (Latin: ''Dioecesis Baiocensis et Lexoviensis''; French: ''Diocèse de Bayeux et Lisieux'') is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church in France. It is coextensive with the Department of Calvados and is a suffragan to the Archdiocese of Rouen, also in Normandy. With the Concordat of 1802, the former ..., the former Diocese of Lisieux"> ..., the former Diocese of Lisieux was merged with that of pontifical brief in 1854 authorized the Bishop of Bayeux to call himself Bishop of Bayeux and Lisieux. In 2022, in the Diocese of Bayeux and Lisieux there was one priest for every 2,672 Catholics. History A local legend found in 15th-century St. Exuperius an immediate disciple of Pope Clement I">Exuperius_of_Bayeux.html" ;"title="Roman Breviary">breviaries calls Exuperius of Bayeux">St. Exuperius an immediate disciple of Pope Clement I (88 to 99 CE), and the first Bishop of Bayeux. His see would according to this therefore have been founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odo Of Bayeux
Odo of Bayeux (died 1097) was a Norman nobleman who was a bishop of Bayeux in Normandy and was made Earl of Kent in England following the Norman Conquest. He was the maternal half-brother of duke, and later king, William the Conqueror, and was, for a time, William's primary administrator in the Kingdom of England, although he was eventually tried for defrauding William's government. It is likely Odo commissioned the Bayeux Tapestry, a large tableau of the Norman Conquest, perhaps to present to his brother William. He later fell out with his brother over Odo's support for military adventures in Italy. William, on his deathbed, freed Odo. Odo died in Palermo, Sicily, on the way to crusade. Early life Odo was the son of William the Conqueror's mother Herleva and Herluin de Conteville. Count Robert of Mortain was his younger brother. There is uncertainty about his birth date. Some historians have suggested he was born around 1035. Duke William made him bishop of Bayeux in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayeux
Bayeux (, ; ) is a commune in the Calvados department in Normandy in northwestern France. Bayeux is the home of the Bayeux Tapestry, which depicts the events leading up to the Norman Conquest of England in 1066. It is also known as the first major town secured by the Allies during Operation Overlord after D-Day. Charles de Gaulle made two famous speeches in this town. Administration Bayeux is a sub-prefecture of Calvados. It is the seat of the arrondissement of Bayeux and of the canton of Bayeux. Geography Bayeux is located from the coast of the English Channel and north-west of Caen. The city, with elevations varying from above sea level – with an average of – is bisected by the River Aure. Bayeux is located at the crossroads of RN 13 and the train route Paris-Caen-Cherbourg. The city is the capital of the Bessin, which extends north-west of Calvados. Bayeux station has rail connections to Caen, Cherbourg, Granville and Paris. The river Aure flows throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranulf De Bessin
Ranulf was a masculine given name in Old French and Old Occitan, and is a masculine given name in the English language. ''Ranulf'' was introduced into England by the Norman conquest or alternatively is said to have been introduced to Scotland and northern England, by Scandinavian settlers in Early Middle Ages. (read online/ref> However, most earliest historical figures with this name originated on the continent. It is derived from the West Germanic name ''Raginulf, Raginolf''. ''Nordic Names'' : ''Raginolf'' (read online/ref> This West Germanic personal name is composed of two elements: the first, RAGN > ''ragin'', means "advice", "decision" ; the second element, ''(w)ulf / (w)olf'', means "wolf". or alternatively the Old Norse name ''Reginúlfr'' is based on the Old Norse variant forms ''reginn'' and ''úlfr''. The Old Occitan anthroponym Ranulf (''Ramnulf'', ''Rannulf'') does not contain exactly the same first element, but ''hram'', short form of Gothic ''hrabns'' "raven". Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William The Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy (as William II) from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading a Franco-Norman army to victory over the Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose. William was the son of the unmarried Duke Robert I of Normandy and his mistress Herleva. His Legitimacy (family law), illegitimate status and youth caused some difficulties for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |