|
Raimondo Feletti
Raimondo Feletti (1851-1927) was an Italian physician and zoologist. Feletti worked at a clinic in Catania where a street is named for him "Via Raimondo Feletti".With Giovanni Batista Grassi he published several works on malarial parasites in birds. They described, and introduced the names '' Haemamoeba vivax'' (1890) and '' H. malariae'' (1889) for, two of the malaria parasites, soon revising the genus to ''Plasmodium''. In 1889 Grassi and Feletti, as an honor to Laveran Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran (18 June 1845 – 18 May 1922) was a French physician who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1907 for his discoveries of parasitic protozoans as causative agents of infectious diseases such as malaria ..., proposed the genus name ''Laverania'' . It is now a subgenus of ''Plasmodium''. Works *With Grassi, B., 1889, 1890. Sui parassiti della malaria. ''Rif. Med.'' 6 : 62-64. (The 1889 paper was a preprint of the 1890 paper according to Hemming, 1954). *With Grass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, underlying diseases and their treatment—the '' science'' of medicine—and also a decent competence in its applied practice—the art or '' craft'' of medicine. Both the role of the physician and the meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoologist
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. The term is derived from Ancient Greek , ('animal'), and , ('knowledge', 'study'). Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and made use of this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. The Greek physician Galen studied human anatomy and was one of the greatest surgeons of the ancient world, but after the fall of the Western Roman Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catania
Catania (, , Sicilian and ) is the second largest municipality in Sicily, after Palermo. Despite its reputation as the second city of the island, Catania is the largest Sicilian conurbation, among the largest in Italy, as evidenced also by the presence of important road and rail transport infrastructures as well as by the main airport in Sicily, fifth in Italy. It is located on Sicily's east coast, at the base of the active volcano, Mount Etna, and it faces the Ionian Sea. It is the capital of the 58-municipality region known as the Metropolitan City of Catania, which is the seventh-largest metropolitan city in Italy. The population of the city proper is 311,584, while the population of the Metropolitan City of Catania is 1,107,702. Catania was founded in the 8th century BC by Chalcidian Greeks. The city has weathered multiple geologic catastrophes: it was almost completely destroyed by a catastrophic earthquake in 1169. A major eruption and lava flow from nearby Mount Etna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Batista Grassi
Giovanni Battista Grassi (27 March 1854 – 4 May 1925) was an Italian physician and zoologist, best known for his pioneering works on parasitology, especially on malariology. He was Professor of Comparative Zoology at the University of Catania from 1883, and Professor of Comparative Anatomy at Sapienza University of Rome from 1895 until his death. His scientific contributions covered embryological development of honey bees, on helminth parasites, the vine parasite phylloxera, on migrations and metamorphosis in eels, and on termites. He was the first to describe and establish the Life cycle (biology), life cycle of the human Plasmodium, malarial parasite, ''Plasmodium falciparum'', and discovered that only female Anopheles, anopheline mosquitoes are capable of transmitting the disease. His works in malaria remain a lasting Nobel Prize controversies, controversy in the history of Nobel Prizes, because a British army surgeon Ronald Ross, who discovered the transmission of Plasmodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the '' Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected '' Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
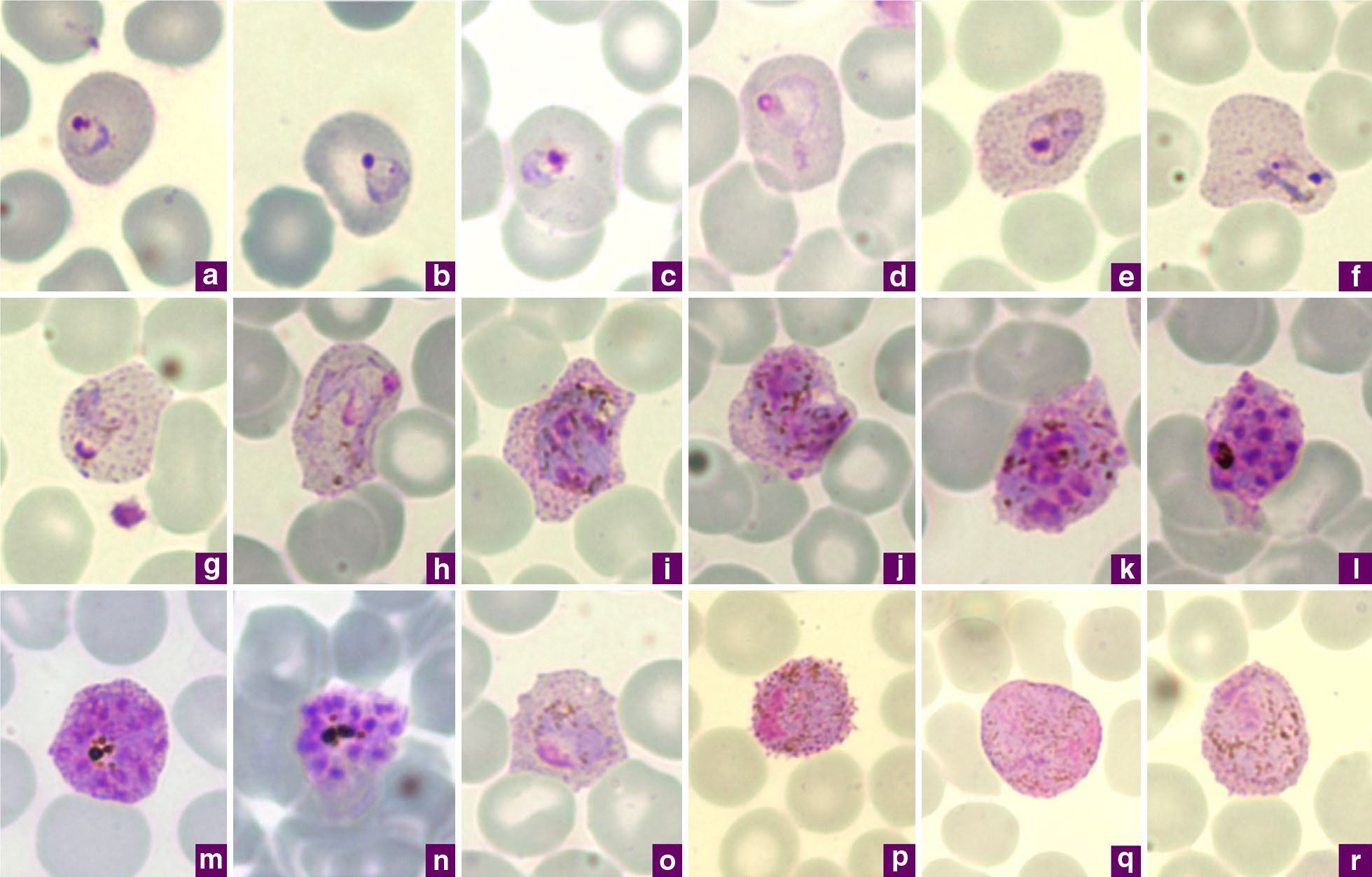
Plasmodium Vivax
''Plasmodium vivax'' is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than '' Plasmodium falciparum'', the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, ''P. vivax'' malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly (a pathologically enlarged spleen). ''P. vivax'' is carried by the female '' Anopheles'' mosquito; the males do not bite. Health Epidemiology ''Plasmodium vivax'' is found mainly in Asia, Latin America, and in some parts of Africa. ''P. vivax'' is believed to have originated in Asia, but recent studies have shown that wild chimpanzees and gorillas throughout central Africa are endemically infected with parasites that are closely related to human ''P. vivax.'' These findings indicate that human P. vivax is of African origin. ''Plasmodium vivax'' accounts for 65% of malaria cases in Asia and South America. Unlike ''Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium Malariae
''Plasmodium malariae'' is a parasitic protozoan that causes malaria in humans. It is one of several species of ''Plasmodium'' parasites that infect other organisms as pathogens, also including ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and ''Plasmodium vivax'', responsible for most malarial infection. Found worldwide, it causes a so-called "benign malaria", not nearly as dangerous as that produced by ''P. falciparum'' or ''P. vivax''. The signs include fevers that recur at approximately three-day intervals – a ''quartan fever'' or ''quartan malaria'' – longer than the two-day (tertian) intervals of the other malarial parasites. History Malaria has been recognized since the Greek and Roman civilizations over 2,000 years ago, with different patterns of fever described by the early Greeks. In 1880, Alphonse Laveran discovered that the causative agent of malaria is a parasite. Detailed work of Golgi in 1886 demonstrated that in some patients there was a relationship between the 72-hour life cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium
''Plasmodium'' is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of ''Plasmodium'' species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue (often the liver) before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect ( mosquitoes in majority cases), continuing the life cycle. ''Plasmodium'' is a member of the phylum Apicomplexa, a large group of parasitic eukaryotes. Within Apicomplexa, ''Plasmodium'' is in the order Haemosporida and family Plasmodiidae. Over 200 species of ''Plasmodium'' have been described, many of which have been subdivided into 14 subgenera based on parasite morphology and host range. Evolutionary relationships among different ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran
Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran (18 June 1845 – 18 May 1922) was a French physician who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1907 for his discoveries of parasitic protozoans as causative agents of infectious diseases such as malaria and trypanosomiasis. Following his father, Louis Théodore Laveran, he took up military medicine as his profession. He obtained his medical degree from University of Strasbourg in 1867. At the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, he joined the French Army. At the age of 29 he became Chair of Military Diseases and Epidemics at the École de Val-de-Grâce. At the end of his tenure in 1878 he worked in Algeria, where he made his major achievements. He discovered that the protozoan parasite ''Plasmodium'' was responsible for malaria, and that ''Trypanosoma'' caused trypanosomiasis or African sleeping sickness. In 1894 he returned to France to serve in various military health services. In 1896 he joined Pasteur Institute as Chief of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Francis Hemming
Arthur Francis Hemming, CMG, CBE (9 February 1893 – 22 February 1964) was an English entomologist who specialised in Lepidoptera. He was mostly known, both professionally and socially, by his middle-name as Francis Hemming. Hemming was a British civil servant and amateur lepidopterist. An expert in biological nomenclature, he served from 1937 to 1958 as Secretary to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature and was founder and editor of the ''Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature''. Over his lifetime he published more than 1,000 scientific papers on Lepidoptera. His manuscripts and other papers are deposited in the Natural History Museum in London and at the Bodleian Library, Oxford. Biography Hemming was educated at Rugby School, and Corpus Christi College, Oxford. During World War I he was severely wounded in 1916, and in 1918 he joined the British Civil Service. He was private secretary to several ministers and was appointed CMG and CBE for his services, espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |