|
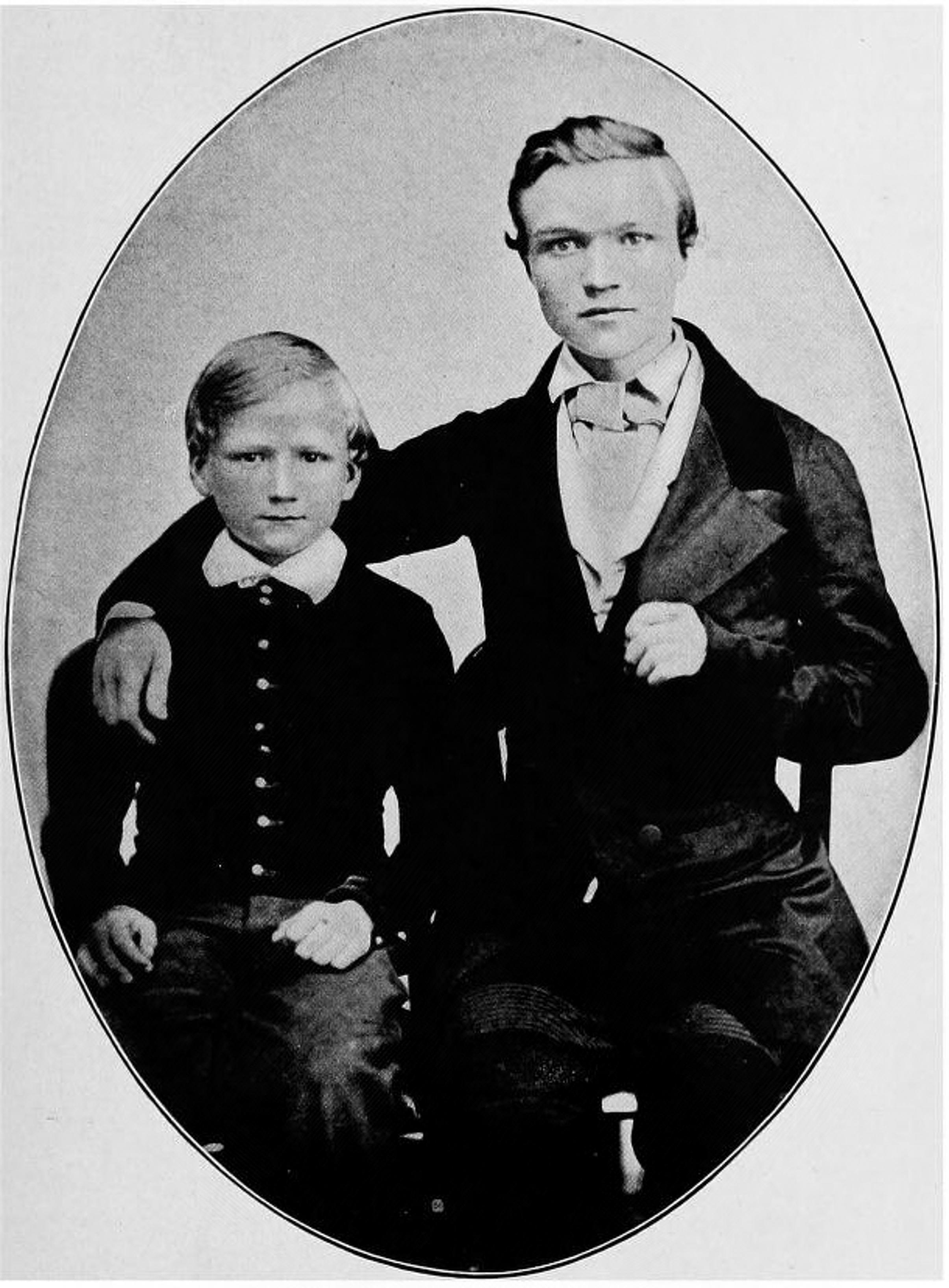
Ragnar Nurkse
Ragnar Wilhelm Nurkse (5 October 1907, Käru, Estonia – 6 May 1959, Le Mont-Pèlerin, Switzerland) was an Estonian-American economist and policy maker mainly in the fields of international finance and economic development. He is considered the pioneer of Balanced Growth Theory. Life Ragnar Nurkse was born in Käru village, in the then Governorate of Livonia of the former Russian Empire (now in Järva County, Estonia), son of an Estonian father who worked himself up from lumberjack to estate manager, and an Estonian-Swedish mother. His parents emigrated to Canada in 1928. After finishing primary school, Nurkse attended the '' Domschule zu Reval'' in Tallinn, the most prestigious, German-language secondary school in the city, from where he graduated with higher honors in 1926. He continued his education at the law and economics' departments of the University of Tartu in 1926–1928, and then in economics at the University of Edinburgh. He graduated with a first class degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Käru
Käru is a small borough () in Türi Parish, Järva County, Estonia. Before the administrative reform in 2017, Käru was the administrative centre of Käru Parish. Käru has a railway station on the Tallinn - Viljandi railway line operated by Elron (rail transit). Käru manor Käru () was established as an estate in the mid-18th century. The present building was built in 1878 and designed by Riga architect Robert Pflug. It is an eclectic building with mainly neo-Renaissance elements. It was damaged during the Revolution of 1905 and also during World War II. The manor house ensemble has several well-preserved and unusual outbuildings and annexes. Explorer Karl von Ditmar was the landowner of Käru. Economist Ragnar Nurkse Ragnar Wilhelm Nurkse (5 October 1907, Käru, Estonia – 6 May 1959, Le Mont-Pèlerin, Switzerland) was an Estonian-American economist and policy maker mainly in the fields of international finance and economic development. He is considered th ... ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ragnar Nurkse's Balanced Growth Theory
The balanced growth theory is an economic theory pioneered by the economist Ragnar Nurkse (1907–1959). The theory hypothesises that the government of any underdeveloped country needs to make large investments in a number of industries simultaneously. This will enlarge the market size, increase productivity, and provide an incentive for the private sector to invest. Nurkse was in favour of attaining balanced growth in both the industrial and agricultural sectors of the economy. He recognised that the expansion and inter-sectoral balance between agriculture and manufacturing is necessary so that each of these sectors provides a market for the products of the other and in turn, supplies the necessary raw materials for the development and growth of the other. Nurkse and Paul Rosenstein-Rodan were the pioneers of balanced growth theory and much of how it is understood today dates back to their work. Nurkse's theory discusses how the poor size of the market in underdeveloped count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bank Of Estonia
The Bank of Estonia () is the national central bank for Estonia within the Eurosystem. It was the Estonian central bank from 1919 to 2010 (albeit with a long suspension between 1940 and 1989), issuing the kroon. Name Like other central banks, the Bank of Estonia refers to itself in its native language even in English-speaking contexts. History Interwar period The bank was established on 24 February 1919 by the provisional government of Estonia following the independence of Estonia. In 1921, Eesti Pank was made the national bank and given the duty of printing the Estonian mark. The Bank of Estonia was restructured under the conditions of the stabilization loan coordinated by the Economic and Financial Organization of the League of Nations. A new version of the Statutes was approved in 1927, according to which Eesti Pank became an independent note-issuing central bank with limited functions. The main tasks of the bank remained to guarantee the value of the money throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Newspapers
A newspaper is a Periodical literature, periodical publication containing written News, information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sports, art, and science. They often include materials such as opinion columns, weather forecasts, reviews of local services, Obituary, obituaries, birth notices, crosswords, editorial cartoons, comic strips, and advice columns. Most newspapers are businesses, and they pay their expenses with a mixture of Subscription business model, subscription revenue, Newsagent's shop, newsstand sales, and advertising revenue. The journalism organizations that publish newspapers are themselves often Metonymy, metonymically called newspapers. Newspapers have traditionally been published Printing, in print (usually on cheap, low-grade paper called newsprint). However, today most newspapers are also Electronic publishing, published on webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geneva
Geneva ( , ; ) ; ; . is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland and the most populous in French-speaking Romandy. Situated in the southwest of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Canton of Geneva, Republic and Canton of Geneva, and a centre for international diplomacy. Geneva hosts the highest number of International organization, international organizations in the world, and has been referred to as the world's most compact metropolis and the "Peace Capital". Geneva is a global city, an international financial centre, and a worldwide centre for diplomacy hosting the highest number of international organizations in the world, including the headquarters of many agencies of the United Nations and the International Committee of the Red Cross, ICRC and International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, IFRC of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, Red Cross. In the aftermath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
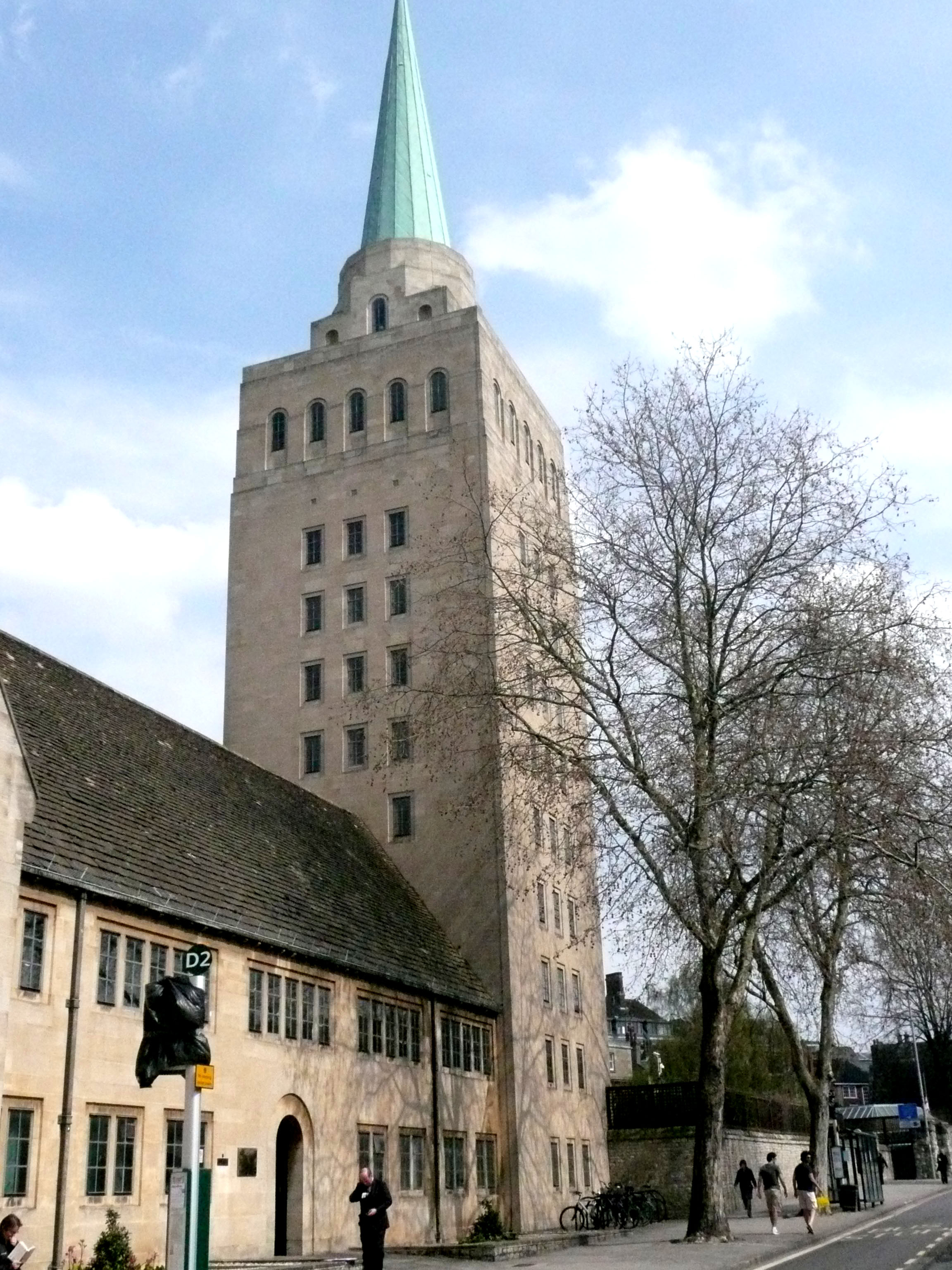
Nuffield College, Oxford
Nuffield College () is one of the Colleges of the University of Oxford, constituent colleges of the University of Oxford in England. It is a graduate college specialising in the social sciences, particularly economics, politics and sociology. Nuffield is one of Oxford's newer colleges, having been founded in 1937, as well as one of the smallest, with only around 90 students and 60 academic Oxbridge Fellow, fellows. It was also the first Oxford college to accept both men and women, having been coeducational since foundation, as well as being the first college exclusively for graduate students in either Oxford or Cambridge. As of 2021, the college had an estimated financial endowment of £282 million. Due to its small intake, it was the wealthiest educational institution per student in the world in 2013. Since 2017, Nuffield has committed to underwriting funding for all new students accepted to the college. Between 2019 and 2023, 5.1% of applicants to the college were admitted. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Princeton, New Jersey
The Municipality of Princeton is a Borough (New Jersey), borough in Mercer County, New Jersey, United States. It was established on January 1, 2013, through the consolidation of the Borough of Princeton, New Jersey, Borough of Princeton and Princeton Township, New Jersey, Princeton Township, both of which are now defunct. As of the 2020 United States census, the borough's population was 30,681, an increase of 2,109 (+7.4%) from the 2010 United States census, 2010 census combined count of 28,572. In the 2000 United States census, 2000 census, the two communities had a total population of 30,230, with 14,203 residents in the borough and 16,027 in the township. Princeton was founded before the American Revolutionary War. The borough is the home of Princeton University, one of the world's most acclaimed research universities, which bears its name and moved to the community in 1756 from the educational institution's previous location in Newark, New Jersey, Newark. Although its associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
League Of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference that ended the World War I, First World War. The main organisation ceased operations on 18 April 1946 when many of its components were relocated into the new United Nations (UN) which was created in the aftermath of the World War II, Second World War. As the template for modern global governance, the League profoundly shaped the modern world. The League's primary goals were stated in its Covenant of the League of Nations, eponymous Covenant. They included preventing wars through collective security and Arms control, disarmament and settling international disputes through negotiation and arbitration. Its other concerns included labour conditions, just treatment of native inhabitants, Human trafficking, human and Illegal drug tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Economic And Financial Organization Of The League Of Nations
The Economic and Financial Organization (EFO, ) was the largest of the technical arms of the League of Nations, and the world's first international organization dedicated to promoting economic and monetary co-operation. It took shape in the early 1920s and was in activity until the creation of the United Nations in 1945. It has been described as having had seminal influence on postwar economic institutions, notably the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Background The establishment of the EFO took place in the aftermath of unprecedented transnational cooperation initiatives among allied powers during World War I, which were also pioneering experiments in planned economy imposed by the circumstances. These included the Wheat Executive established in late 1916, and the Allied Maritime Transport Council established in late 1917. They had brought together enterprising civil servants such as Italy's Bernardo Attolico, France's Jean Monnet, and Britain's Arthur Salter, who would pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie ( , ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the History of the iron and steel industry in the United States, American steel industry in the late-19th century and became one of the List of richest Americans in history, richest Americans in history. He became a leading philanthropist in the United States, Great Britain, and the British Empire. During the last 18 years of his life, he gave away around $350 million (equivalent to $ billion in ), almost 90 percent of his fortune, to charities, foundations and universities. His 1889 article proclaiming "The Gospel of Wealth" called on the rich to use their wealth to improve society, expressed support for progressive taxation and an Inheritance tax, estate tax, and stimulated a wave of philanthropy. Carnegie was born in Dunfermline, Scotland. He immigrated to what is now Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States with his parents in 1848 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Frederick Ogilvie
Sir Frederick Wolff Ogilvie FRSE (7 February 1893 – 10 June 1949) was a British broadcasting executive and university administrator, who was Director-General of the BBC from 19 July 1938 to 26 January 1942, and was succeeded by joint Directors-General Cecil Graves and Robert Foot. He also served as Vice-Chancellor of Queen's University Belfast from 1934 to 1938. He was knighted by King George VI on 10 June 1942. Early life and education Ogilvie was born in February 1893 in Valparaíso, Chile, the youngest son of Mary Ann (née Wolff) and William Maxwell Ogilvie, an engineer from Harrow Weald in northwest London. His parents were of Scottish descent. Ogilvie was educated at Packwood Haugh School and Clifton College, before beginning studying for a Literae humaniores degree at Balliol College, Oxford in 1911. From the beginning of his undergraduate studies, he displayed an interest in economics. Having gained first class in his Honour Moderations exams, Ogilvie's studies were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tallinn Cathedral School
Tallinn Cathedral School (also Tallinn Knight and Cathedral School; , , ) is a school in Tallinn, Estonia. First written records of the school date back to 1319. In 1684, the school was destroyed in the large fire in the Toompea area. The construction of a new school building was completed seven years larter, in 1691. Since 1765, the school was managed by Estonian Knighthood. The construction of the building at Toom-Kooli Street 11 where the school located nowadays, was completed in 1845. In 1892, the school was closed due to Russification. In 1906, the school was re-opened. In 1920, Estonian Knighthood was liquidated and the school was managed by the successor organization of knighthood (). School was closed during World War II in the context of Baltic German '' Umsiedlung''. Since 1965, the school building is used by Tallinn Ballet School Tallinn Ballet School () is ballet school in Tallinn, Estonia. It is the only educational institution for professional ballet dancers in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |