|
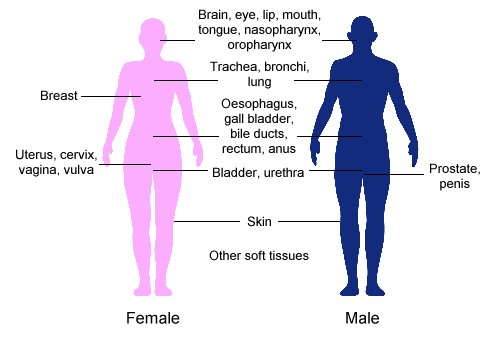
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle accelerator. Radiation therapy may be cure, curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body, and have not metastasis, spread to other parts. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the canc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs and the rectum, while the pelvic flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging. Measurement and recording techniques that are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others, represent other technologies that produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph versus time or maps that contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular Schwannoma
A vestibular schwannoma (VS), also called acoustic neuroma, is a benign tumor that develops on the vestibulocochlear nerve that passes from the inner ear to the brain. The tumor originates when Schwann cells that form the insulating myelin sheath on the nerve malfunction. Normally, Schwann cells function beneficially to protect the nerves which transmit balance and sound information to the brain. However, sometimes a mutation in the tumor suppressor gene, NF2, located on chromosome 22, results in abnormal production of the cell protein named ''Merlin'', and Schwann cells multiply to form a tumor. The tumor originates mostly on the vestibular division of the nerve rather than the cochlear division, but hearing as well as balance will be affected as the tumor enlarges. The great majority of these VSs (95%) are unilateral, in one ear only. They are called "sporadic" (i.e., by-chance, non-hereditary). Although non-cancerous, they can do harm or even become life-threatening if they gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN or TGN), also called Fothergill disease, tic douloureux, trifacial neuralgia, is a chronic pain, long-term pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, the nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. It is a form of neuropathic pain. There are two main types: typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia. The typical form results in episodes of severe, sudden, shock-like pain in one side of the face that lasts for seconds to a few minutes. Groups of these episodes can occur over a few hours. The atypical form results in a constant burning pain that is less severe. Episodes may be triggered by any touch to the face. Both forms may occur in the same person. Pain from the disease has been linked to mental health issues, especially depression (mood), depression. The exact cause is unknown, but believed to involve loss of the myelin of the trigeminal nerve. This might occur due to Nerve compression syndrome, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Source
A radioactive source is a known quantity of a radionuclide which emits ionizing radiation, typically one or more of the radiation types gamma rays, alpha particles, beta particles, and neutron radiation. Sources can be used for irradiation, where the radiation performs a significant ionising function on a target material, or as a radiation metrology source, which is used for the calibration of radiometric process and radiation protection instrumentation. They are also used for industrial process measurements, such as thickness gauging in the paper and steel industries. Sources can be sealed in a container (highly penetrating radiation) or deposited on a surface (weakly penetrating radiation), or they can be in a fluid. As an irradiation source they are used in medicine for radiation therapy and in industry for such as industrial radiography, food irradiation, sterilization (microbiology), sterilization, vermin disinfestation, and Cross-linked polyethylene, irradiation crosslinki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy is a form of radiation therapy where a sealed radiation, radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment. The word "brachytherapy" comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek word , meaning "short-distance" or "short". Brachytherapy is commonly used as an effective treatment for cervical cancer, cervical, Prostate cancer, prostate, Breast cancer, breast, Esophageal cancer, esophageal and skin cancer and can also be used to treat tumours in many other body sites. Treatment results have demonstrated that the cancer-cure rates of brachytherapy are either comparable to surgery and external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) or are improved when used in combination with these techniques. Brachytherapy can be used alone or in combination with other therapies such as surgery, EBRT and chemotherapy. Brachytherapy contrasts with unsealed source radiotherapy, in which a therapeutic radionuclide (radioisotope) is injected into the body to chemically localize to the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Marrow Transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce additional normal blood cells. HSCT may be autologous (the patient's own stem cells are used), syngeneic (stem cells from an identical twin), or allogeneic (stem cells from a donor). It is most often performed for patients with certain cancers of the blood or bone marrow, such as multiple myeloma, leukemia, some types of lymphoma and immune deficiencies. In these cases, the recipient's immune system is usually suppressed with radiation or chemotherapy before the transplantation. Infection and graft-versus-host disease are major complications of allogeneic HSCT. HSCT remains a dangerous procedure with many possible complications; it is reserved for patients with life-threatening diseases. As survival following the procedure has increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Body Irradiation
Total body irradiation (TBI) is a form of radiotherapy used primarily as part of the preparative regimen for haematopoietic stem cell (or bone marrow) transplantation. As the name implies, TBI involves irradiation of the entire body, though in modern practice the lungs are often partially shielded to lower the risk of radiation-induced lung injury. Total body irradiation in the setting of bone marrow transplantation serves to destroy or suppress the recipient's immune system, preventing immunologic rejection of transplanted donor bone marrow or blood stem cells. Additionally, high doses of total body irradiation can eradicate residual cancer cells in the transplant recipient, increasing the likelihood that the transplant will be successful. Dosage Doses of total body irradiation used in bone marrow transplantation typically range from 10 to >12 Gy. For reference, an unfractionated (i.e. single exposure) dose of 4.5 Gy is fatal in 50% of exposed individuals without ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoadjuvant Therapy
Neoadjuvant therapy is the administration of therapeutic agents before a main treatment. One example is neoadjuvant hormone therapy prior to radical radiotherapy for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Neoadjuvant therapy aims to reduce the size or extent of the cancer before using radical treatment intervention, thus both making procedures easier and more likely to succeed and reducing the consequences of a more extensive treatment technique, which would be required if the tumor were not reduced in size or extent. Another related concept is that neoadjuvant therapy acts on micrometastatic disease. The downstaging is then a surrogate marker of efficacy on undetected dissemination, resulting in improved longtime survival compared to the surgery-alone strategy. This systemic therapy (chemotherapy, immunotherapy or hormone therapy) or radiation therapy is commonly used in cancers that are locally advanced, and clinicians plan an operation at a later stage, such as pancreatic cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy or biological therapy is the treatment of disease by activating or suppressing the immune system. Immunotherapies designed to elicit or amplify an immune response are classified as ''activation immunotherapies,'' while immunotherapies that reduce or suppress are classified as '' suppression immunotherapies''. Immunotherapy is under preliminary research for its potential to treat various forms of cancer. Cell-based immunotherapies are effective for some cancers. Immune effector cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes work together to defend the body against cancer by targeting abnormal antigens expressed on the surface of tumor cells. Vaccine-induced immunity to COVID-19 relies mostly on an immunomodulatory T-cell response. Therapies such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), interferons, imiquimod and cellular membrane fractions from bacteria are licensed for medical use. Others in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormonal Therapy (oncology)
Hormonal therapy in oncology is hormone therapy for cancer and is one of the major modalities of oncology, medical oncology (pharmacotherapy for cancer), others being chemotherapy, cytotoxic chemotherapy and targeted therapy (biotherapeutics). It involves the manipulation of the endocrine system through exogenous or external administration of specific hormones, particularly steroid hormones, or drugs which inhibit the production or activity of such hormones (hormone antagonists). Because steroid hormones are powerful drivers of gene expression in certain cancer cell (biology), cells, changing the levels or activity of certain hormones can cause certain cancers to cease growing, or even undergo cell death. Surgical removal of endocrine organs, such as orchiectomy and oophorectomy can also be employed as a form of hormonal therapy. Hormonal therapy is used for several types of cancers derived from hormonally responsive tissue (biology), tissues, including the breast cancer, breast, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |