|
ROS1
Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ROS1'' gene. Function This proto-oncogene, highly expressed in a variety of tumor cell lines, belongs to the sevenless subfamily of tyrosine kinase insulin receptor genes. The protein encoded by this gene is a type I integral membrane protein with tyrosine kinase activity. The protein may function as a growth or differentiation factor receptor. Role in cancer ''ROS1'' is a receptor tyrosine kinase (encoded by the gene ''ROS1'') with structural similarity to the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) protein; it is encoded by the ''c-ros'' oncogene and was first identified in 1986. The exact role of the ''ROS1'' protein in normal development, as well as its normal physiologic ligand, have not been defined. Nonetheless, as gene rearrangement events involving ''ROS1'' have been described in lung and other cancers, and since such tumors have been found to be remarkably responsive to small mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entrectinib
Entrectinib, sold under the brand name Rozlytrek, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer and NTRK fusion-positive solid tumors. It is a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), of the tropomyosin receptor kinases (TRK) A, B and C, C-ros oncogene 1 ( ROS1) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). The most common side effects include tiredness, constipation, dysgeusia (taste disturbances), edema (swelling with fluid retention), dizziness, diarrhea, nausea (feeling sick), dysesthesia (unpleasant and abnormal feeling when touched), dyspnea (difficulty breathing), anemia (low red blood cell count), increased weight, increased blood creatinine (possible sign of kidney problems), pain, cognitive disorders (problems with ability to think, learn and remember), vomiting, cough, and fever. It was approved for medical use in the United States in August 2019, in Australia in May 2020, and in the European Union in July 2020. Medical uses In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma of the lung is the most common type of lung cancer, and like other forms of lung cancer, it is characterized by distinct cellular and molecular features. It is classified as one of several non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), to distinguish it from small cell lung cancer which has a different behavior and prognosis. Lung adenocarcinoma is further classified into several subtypes and variants. The signs and symptoms of this specific type of lung cancer are similar to other forms of lung cancer, and patients most commonly complain of persistent cough and shortness of breath. Adenocarcinoma is more common in patients with a history of cigarette smoking, and is the most common form of lung cancer in younger women and Asian populations. The pathophysiology of adenocarcinoma is complicated, but generally follows a histologic progression from cells found in healthy lungs to distinctly dysmorphic, or irregular cells. There are several distinct molecular and genetic pathwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor
Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is a rare neoplasm of the mesodermal cells that form the connective tissues which support virtually all of the organs and tissues of the body. IMT was formerly termed inflammatory pseudotumor. Currently, however, inflammatory pseudotumor designates a large and heterogeneous group of soft tissue tumors that includes inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, plasma cell granuloma, xanthomatous pseudotumor, solitary mast cell granuloma, inflammatory fibrosarcoma, pseudosarcomatous myofibroblastic proliferation, myofibroblastoma, inflammatory myofibrohistiocytic proliferation, and other tumors that develop from connective tissue cells. Inflammatory pseudotumour is a generic term applied to various neoplastic and non-neoplastic tissue lesions which share a common microscopic appearance consisting of spindle cells and a prominent presence of the white blood cells that populate chronic or, less commonly, acute inflamed tissues. Inflammatory myofibrobla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorlatinib
Lorlatinib, sold under the brand name Lorbrena in the United States, Canada, and Japan, and Lorviqua in the European Union, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. It is an orally administered inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and C-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1), two enzymes that play a role in the development of cancer. It was developed by Pfizer. The most common adverse reactions include edema, peripheral neuropathy, weight gain, cognitive effects, fatigue, dyspnea, arthralgia, diarrhea, mood effects, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and cough. Lorlatinib was approved for medical use in the United States in November 2018, and in the European Union in May 2019. Medical uses Lorlatinib is indicated for the treatment of adults with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors are anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive. Contraindications Lorlatinib must not be combined with strong inducers (i.e. activator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) also known as ALK tyrosine kinase receptor or CD246 (cluster of differentiation 246) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ALK'' gene. Identification Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) was originally discovered in 1994 in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) cells. ALCL is caused by a (2;5)(p23:q35) chromosomal translocation that generates the fusion protein NPM-ALK, in which the kinase domain of ALK is fused to the amino-terminal part of the nucleophosmin (NPM) protein. Dimerization of NPM constitutively activates the ALK kinase domain. The full-length protein ALK was identified in 1997 by two groups. The deduced amino acid sequences revealed that ALK was a novel receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), having an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. While the tyrosine kinase domain of human ALK shares a high degree of similarity with that of the insulin receptor, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crizotinib
Crizotinib, sold under the brand name Xalkori among others, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). Crizotinib inhibits the c-Met/ Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR) tyrosine kinase, which is involved in the oncogenesis of a number of other histological forms of malignant neoplasms. It also acts as an ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) and ROS1 ( c-ros oncogene 1) inhibitor. Medical uses Crizotinib is indicated for the treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or relapsed or refractory, systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) that is ALK-positive. It is also indicated for the treatment of unresectable, recurrent, or refractory inflammatory anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive myofibroblastic tumors (IMT). Mechanism of action Crizotinib has an aminopyridine structure, and functions as a protein kinase inhibitor by competitive binding within the ATP-binding pocket of target kinases. Abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or non-small-cell lung carcinoma, is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than Small-cell carcinoma#Small-cell lung cancer, small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively (Neoadjuvant therapy, neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and postoperatively (Adjuvant therapy, adjuvant chemotherapy). Types The most common types of NSCLC are squamous-cell carcinoma, large-cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma, but several other types occur less frequently. A few of the less common types are pleomorphic, carcinoid tumor, salivary gland carcinoma, and unclassified carcinoma. All types can occur in unusual histologic variants and as mixed cell-type combinations. Non-squamous-cell carci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine Kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger class of enzymes known as protein kinases which also attach phosphates to other amino acids such as serine and threonine. Phosphorylation of proteins by kinases is an important mechanism for communicating signals within a cell (signal transduction) and regulating cellular activity, such as cell division. Protein kinases can become mutated, stuck in the "on" position, and cause unregulated growth of the cell, which is a necessary step for the development of cancer. Therefore, kinase inhibitors, such as imatinib and osimertinib, are often effective cancer treatments. Most tyrosine kinases have an associated protein tyrosine phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group. Reaction Protein kinases are a group of enzymes that possess a ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
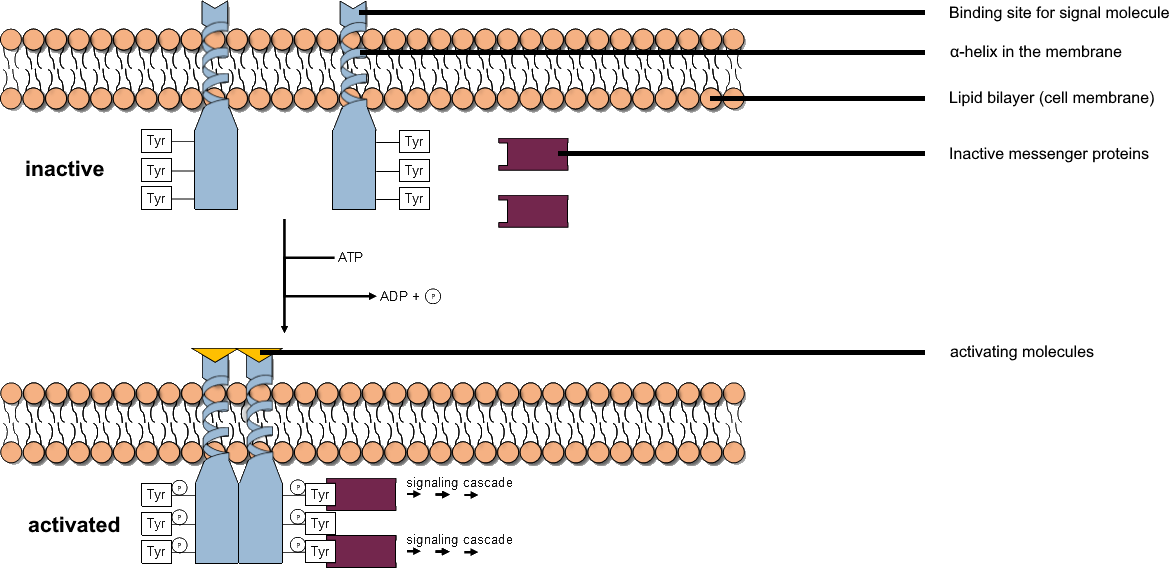
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high-affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinase proteins. Receptor tyrosine kinases have been shown not only to be key regulators of normal cellular processes but also to have a critical role in the development and progression of many types of cancer. Mutations in receptor tyrosine kinases lead to activation of a series of signalling cascades which have numerous effects on protein expression. The receptors are generally activated by dimerization and substrate presentation. Receptor tyrosine kinases are part of the larger family of protein tyrosine kinases, encompassing the receptor tyrosine kinase proteins which contain a transmembrane domain, as well as the non-receptor tyrosine kinases which do not possess transmembrane domains. History The first RTKs to be discovered were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |