|
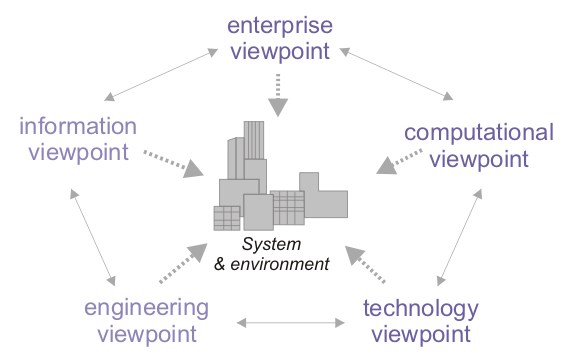
RM-ODP Viewpoints
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems. RM-ODP, also named ''ITU-T Rec. X.901-X.904'' and ''ISO/IEC 10746'', is a joint effort by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T). Overview The RM-ODP is a reference model based on precise concepts derived from current distributed processing developments and, as far as possible, on the use of formal description techniques for specification of the architecture. Many RM-ODP concepts, possibly under different names, have been around for a long time and have been rigorously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Hayek
Friedrich August von Hayek (8 May 1899 – 23 March 1992) was an Austrian-born British academic and philosopher. He is known for his contributions to political economy, political philosophy and intellectual history. Hayek shared the 1974 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with Gunnar Myrdal for work on money and economic fluctuations, and the interdependence of economic, social and institutional phenomena. His account of how prices communicate information is widely regarded as an important contribution to economics that led to him receiving the prize. He was a major contributor to the Austrian school of economics. During his teenage years, Hayek fought in World War I. He later said this experience, coupled with his desire to help avoid the mistakes that led to the war, drew him into economics. He earned doctoral degrees in law in 1921 and political studies in 1923 from the University of Vienna. He subsequently lived and worked in Austria, Great Britain, the United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zachman Framework
The Zachman Framework is a structured tool used in enterprise architecture to organize and understand complex business systems. It acts as an Ontology (information science), ontology, providing a clear and formal way to describe an enterprise through a two-dimensional grid. This grid combines two key perspectives: the basic questions of Five Ws, What, How, When, Who, Where, and Why, and the process of turning abstract ideas into concrete realities, known as Reification (fallacy), reification. These reification stages include identification, definition, representation, specification, configuration, and instantiation. While influential in shaping enterprise architecture, the framework is often considered theoretical, with limited direct adoption in fast-paced industries like technology, where agile methods are preferred. Unlike a methodology, the Zachman Framework does not prescribe specific steps or processes for gathering or using information. Instead, it serves as a Conceptual m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE 1471
IEEE 1471 is a superseded IEEE standard for describing the architecture of a "software-intensive system", also known as software architecture. In 2011 it was superseded by ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010, ''Systems and software engineering — Architecture description''. Overview IEEE 1471 is the short name for a standard formally known as ANSI/IEEE 1471-2000, ''Recommended Practice for Architecture Description of Software-Intensive Systems.'' Within Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) parlance, this is a "recommended practice", the least normative of its standards. In 2007 this standard was adopted by ISO/IEC JTC1/SC7 as ISO/IEC 42010:2007, ''Systems and Software Engineering -- Recommended practice for architectural description of software-intensive systems''. It has long been recognized that "architecture" has a strong influence over the life cycle of a system. However, until relatively recently, hardware issues have tended to dominate architectural thinking, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viewpoint Modeling
Viewpoint may refer to: * Scenic viewpoint, a high place where people can gather to view scenery In computing * Viewpoint model, a computer science technique for making complex systems more comprehensible to human engineers * Viewpoint Corporation, a digital media company known for its subsidiary Fotomat ** Viewpoint Media Player, a software product made by Viewpoint Corporation, and the associated file format * ViewPoint, the operating system of the Xerox Daybreak computer In arts and entertainment * Viewpoints, an acting technique based on improvisation * Camera angle, in photography, filmmaking, and other visual arts Games * ''Viewpoint'' (video game), shooter video game * Viewpoint (card game), dedicated deck card game Television * ''Viewpoint'' (Australian TV program), a 2012–2017 Australian current affairs television program broadcast on Sky News Australia * ''Viewpoint'' (British TV series), a 2021 British drama television series * ''Viewpoint'' (Canadian TV progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of ISO Standards
This is a list of publishedThis list generally excludes draft versions. standardization, standards and other deliverables of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).ISO deliverables include "specifications" (ISO/PAS, ISO/TS), "reports" (ISO/TR), etc, which are not referred to by ISO as "standards". For a complete and up-to-date list of all the ISO standards, see the ISO catalogue. The standards are protected by copyright and most of them must be purchased. However, about 300 of the standards produced by ISO and International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC's Joint Technical Committee 1 (ISO/IEC JTC 1, JTC 1) have been made freely and publicly available. ISO 1 – ISO 19999 * List of ISO standards 1–1999, ISO 1 – ISO 1999 * List of ISO standards 2000–2999, ISO 2000 – ISO 2999 * Li ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO Standard
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Article 3 of the ISO Statutes. ISO was founded on 23 February 1947, and () it has published over 25,000 international standards covering almost all aspects of technology and manufacturing. It has over 800 technical committees (TCs) and subcommittees (SCs) to take care of standards development. The organization develops and publishes international standards in technical and nontechnical fields, including everything from manufactured products and technology to food safety, transport, IT, agriculture, and healthcare. More specialized topics like electrical and electronic engineering are instead handled by the International Electrotechnical Commission.Editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. 3 June 2021.Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Herbert
Andrew James Herbert, OBE, FREng (born 1954) is a British computer scientist, formerly Chairman of Microsoft Research, for the Europe, Middle East and Africa region. Biography Herbert received a bachelor's of science degree in computational science from the Leeds University in 1975, and a PhD degree in computer science from Cambridge University in 1978 for his work on "A Microprogrammed Operating System Kernel". In 1978 he started working at the University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory as assistant lecturer under Maurice Wilkes and Roger Needham in the Computer Laboratory, and worked with others on the "Cambridge Model Distributed System". In 1985 he left Cambridge to found his own contract research company (Architecture Projects Ltd – APM Ltd), which led projects to develop ANSA, the Advanced Network Systems Architecture. In 1996 he had founded another sister company called Digitivity to develop a product to enable the secure deployment of Java clients for business-to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformance Testing
Conformance testing and also known as compliance testing or type testing, is testing or other activities that determine whether a process, product, or service complies with the requirements of a specification, technical standard, contract, or regulation. It is an element of the more general conformity assessment. Testing is often either logical testing or physical testing. The test procedures may involve other criteria from mathematical testing or chemical testing. Beyond simple conformance, other requirements for efficiency, interoperability, or compliance may apply. Conformance testing may be undertaken by the producer of the product or service being assessed, by a user, or by an accredited independent organization, which can sometimes be the author of the standard being used. When testing is accompanied by certification, the products or services may then be advertised as being certified in compliance with the referred technical standard. Manufacturers and suppliers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transparency (human–computer Interaction)
Any change in a computing system, such as a new feature or new component, is transparent if the system after change adheres to previous external interface as much as possible while changing its internal behaviour. The purpose is to shield from change all systems (or human users) on the other end of the interface. Confusingly, the term refers to overall ''invisibility'' of the component, it does not refer to ''visibility of component's internals'' (as in white box or open system). The term ''transparent'' is widely used in computing marketing in substitution of the term ''invisible'', since the term ''invisible'' has a bad connotation (usually seen as something that the user can't see, and has no control over) while the term ''transparent'' has a good connotation (usually associated with not hiding anything). The vast majority of the times, the term ''transparent'' is used in a misleading way to refer to the actual invisibility of a computing process, which is also described by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object-oriented Analysis And Design
Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a technical approach for analyzing and designing an application, system, or business by applying object-oriented programming, as well as using visual modeling throughout the software development process to guide stakeholder communication and product quality. OOAD in modern software engineering is typically conducted in an iterative and incremental way. The outputs of OOAD activities are analysis models (for OOA) and design models (for OOD) respectively. The intention is for these to be continuously refined and evolved, driven by key factors like risks and business value. History In the early days of object-oriented technology before the mid-1990s, there were many different competing methodologies for software development and object-oriented modeling, often tied to specific Computer Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tool vendors. No standard notations, consistent terms and process guides were the major concerns at the time, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |