|
RGB LED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LED Operation
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that Light#Light sources, emits light when Electric current, current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in Remote control, remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small Incandescent light bulb, incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LED Symbol
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV), an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types
Type may refer to: Science and technology Computing * Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc. * Data type, collection of values used for computations. * File type * TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file. * Type (Unix), a command in POSIX shells that gives information about commands. * Type safety, the extent to which a programming language discourages or prevents type errors. * Type system, defines a programming language's response to data types. Mathematics * Type (model theory) * Type theory, basis for the study of type systems * Arity or type, the number of operands a function takes * Type, any proposition or set in the intuitionistic type theory * Type, of an entire function#Order and type, entire function ** Exponential type Biology * Type (biology), which fixes a scientific name to a taxon * Dog type, categorization by use or function of domestic dogs Lettering * Type is a design concept for lettering used in typography which helped b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Gap
In solid-state physics and solid-state chemistry, a band gap, also called a bandgap or energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap refers to the energy difference (often expressed in electronvolts) between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors. It is the energy required to promote an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. The resulting conduction-band electron (and the electron hole in the valence band) are free to move within the crystal lattice and serve as charge carriers to conduct electric current. It is closely related to the HOMO/LUMO gap in chemistry. If the valence band is completely full and the conduction band is completely empty, then electrons cannot move within the solid because there are no available states. If the electrons are not free to move within the crystal lattice, then there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigation Light
A navigation light, also known as a running or position light, is a source of illumination on a watercraft, aircraft or spacecraft, meant to give information on the craft's position, heading, or status. Some navigation lights are colour-coded red and green to aid traffic control by identifying the craft's orientation. Their placement is mandated by international conventions or civil authorities such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO). A common misconception is that marine or aircraft navigation lights indicate which of two approaching vessels has the "right of way" as in ground traffic; this is never true. However, the red and green colours are chosen to indicate which vessel has the duty to "give way" or "stand on" (obligation to hold course and speed). Consistent with the ground traffic convention, the rightmost of the two vehicles is usually given stand-on status and the leftmost must give way. Therefore a red light is used on the ( left (port)) side to indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the spectral band, band of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visual perception, visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' (or simply light). The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well, known collectively as ''optical radiation''. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 Terahertz (unit), terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions, these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm (near infrared). The spectrum does not contain all the colors that the human visual system can distinguish. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
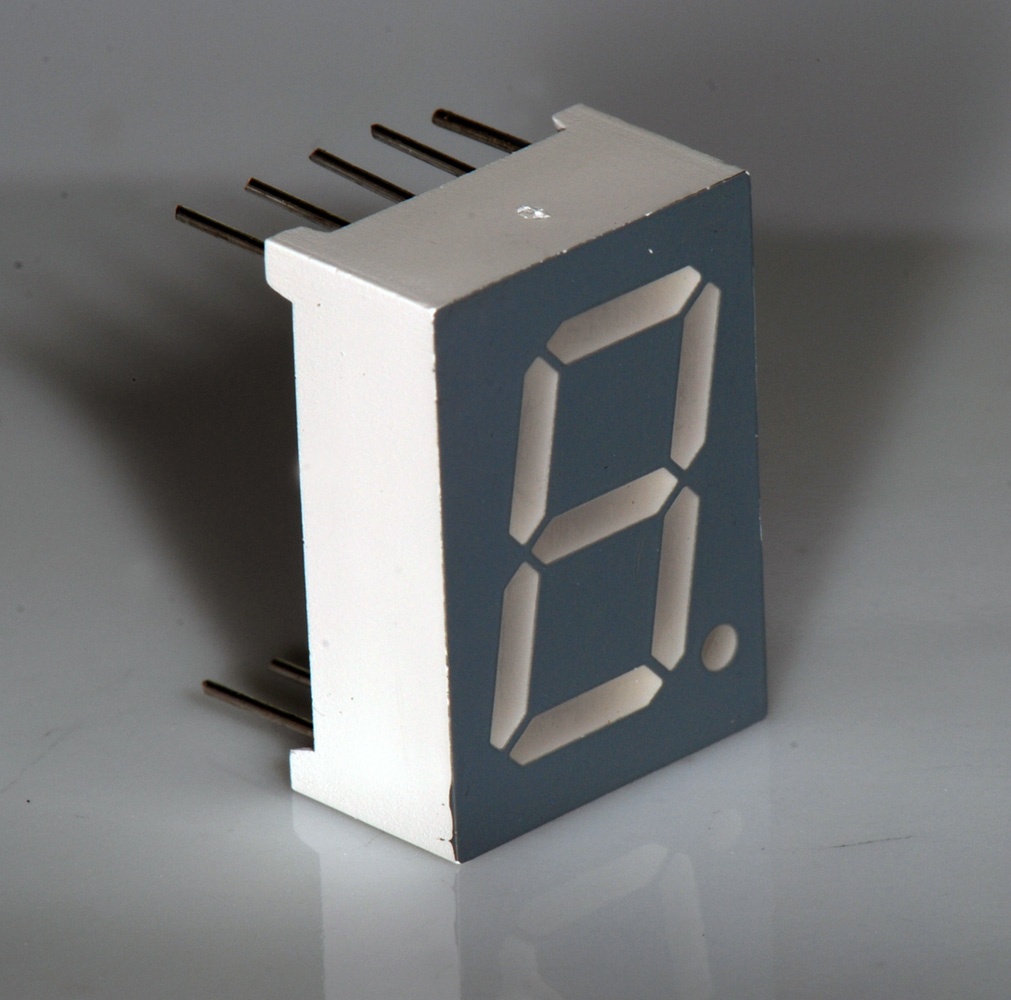
Seven-segment Display
A seven-segment display is a display device for Arabic numerals, less complex than a device that can show more characters such as dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, and other electronic devices that display numerical information. History Seven-segment representation of figures can be found in patents as early as 1903 (in ), when Carl Kinsley invented a method of telegraphically transmitting letters and numbers and having them printed on tape in a segmented format. In 1908, F. W. Wood invented an 8-segment display, which displayed the number 4 using a diagonal bar (). In 1910, a seven-segment display illuminated by incandescent bulbs was used on a power-plant boiler room signal panel. They were also used to show the dialed telephone number to operators during the transition from manual to automatic telephone dialing. They did not achieve widespread use until the advent of light-emitting diode, LEDs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incandescent Light Bulb
An incandescent light bulb, also known as an incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe, is an electric light that produces illumination by Joule heating a #Filament, filament until it incandescence, glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb that is either vacuum, evacuated or filled with inert gas to protect the filament from oxidation. Electric current is supplied to the filament by terminals or wires embedded in the glass. A bulb socket provides mechanical support and electrical connections. Incandescent bulbs are manufactured in a wide range of sizes, light output, and voltage ratings, from 1.5 volts to about 300 volts. They require no external Regulator (automatic control), regulating equipment, have low manufacturing costs, and work equally well on either alternating current or direct current. As a result, the incandescent bulb became widely used in household and commercial lighting, for portable lighting such as table lamps, car headlamps, and flashlights, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Control
A remote control, also known colloquially as a remote or clicker, is an consumer electronics, electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operate devices such as a television set, DVD player or other digital home media appliance. A remote control can allow operation of devices that are out of convenient reach for direct operation of controls. They function best when used from a short distance. This is primarily a convenience feature for the user. In some cases, remote controls allow a person to operate a device that they otherwise would not be able to reach, as when a garage door opener is triggered from outside. Early television remote controls (1956–1977) used ultrasonics, ultrasonic tones. Present-day remote controls are commonly consumer IR, consumer infrared devices which send digitally-coded pulses of infrared radiation. They control functions such as power, volume, chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edison Tech Center
The Edison Tech Center is an interactive learning center with a central emphasis on electricity and engineering. The organization was founded in 2001 under the name Edison Exploratorium, and changed to Edison Steinmetz Center and finally the Edison Tech Center in 2009. It is located at 136 Broadway, Schenectady, New York. The Center was created to have a focus on engineering education while keeping the connection to the historical and human story behind the field. Electrical Engineer and founder John D. Harnden Jr. saw a need to keep the focus on engineering after witnessing many museums diffusing their limited resources on science, entertainment, art and other wide subjects. Founding The Edison Tech Center was founded by John D. Harnden Jr. of the General Electric Research Laboratory and General Engineering Laboratory. Harnden established himself as an electrical engineer in the beginning of the solid-state age. Through the 1950s and 60s he worked on LCDs, piezoelectric devices, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |