|
R4600
The R4600, code-named "Orion", is a microprocessor developed by Quantum Effect Design (QED) that implemented the MIPS III instruction set architecture (ISA). As QED was a design firm that did not fabricate or sell their designs, the R4600 was first licensed to Integrated Device Technology (IDT), and later to Toshiba and then JFE Holdings, NKK. These companies fabricated the microprocessor and marketed it. The R4600 was designed as a low-end workstation or high-end embedded microprocessor. Users included Silicon Graphics, Silicon Graphics, Inc. (SGI) for their SGI Indy, Indy workstation and DeskStation Technology for their Windows NT workstations. The R4600 was instrumental in making the Indy successful by providing good integer performance at a competitive price. In embedded systems, prominent users included Cisco Systems in their network routers and Canon Inc., Canon in their printers. History IDT was the first company to fabricate and ship the R4600. IDT produced first silicon i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGI Indy
The Indy, code-named "Guinness", is a low-end multimedia workstation introduced on July 12, 1993 by Silicon Graphics Incorporated (SGI). SGI developed, manufactured, and marketed Indy as the lowest end of its product line, for computer-aided design (CAD), desktop publishing, and multimedia markets. It competed with Intel x86 computers, and with Windows and Macintosh, including using their files and running their applications via software emulation. It is the first computer to come standard with a video camera, called IndyCam. Indy was repackaged as a server model called Challenge S. Indy was discontinued on June 30, 1997, and support ended on December 31, 2011. Hardware The Indy is one of the smaller form factors of the time (41 cm × 36 cm × 8 cm). The sturdy, electric-blue colored "pizza box" chassis is comparable to a contemporary small desktop PC, and is intended to fit underneath a large CRT monitor. Designed for multimedia use, the Indy includes analog an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Effect Design
Quantum Effect Devices, Inc. (QED), was a microprocessor design company incorporated in 1991 as Quantum Effect Design. It was based in Palo Alto, California. History The three founders, Tom Riordan, Earl Killian and Ray Kunita, were senior managers at MIPS Computer Systems Inc. They left MIPS at a time when the company was having a difficult time selling entire computer systems ( MIPS Magnum) instead of concentrating on building microprocessor chips which was MIPS' original mission. Soon after, SGI purchased MIPS. IDT was a major funder and customer for the initial QED design. Business The original product plan for QED was to build a MIPS microprocessor for a laptop computer. This was during the ACE initiative from Microsoft to support multiple RISC architectures for their new Windows NT operating system. System companies like DeskStation Technology and board companies like ShaBLAMM! Computer were building products in the hope that RISC-based personal computers would become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeskStation Technology
DeskStation Technology was a manufacturer of RISC-based computer workstations intended to run Windows NT. DeskStation was based in Lenexa, Kansas. AMD Am29000-based systems DeskStation announced a range of motherboards for systems based on the AMD Am29000 processor in 1991. These ranged from the Model 162 with a 16 MHz processor achieving a claimed 9 MIPS and costing $2,495 to the Model 252 with a 25 MHz processor achieving 14 MIPS and costing $3,495. MIPS-based systems In late 1991, DeskStation announced a workstation based on the MIPS R3000A CPU, the IceStation 3000, that was to be the basis of a product compliant with the Advanced Computing Environment (ACE) specification, with this workstation already existing in prototype form and with early production models to be made available for beta-testing within a matter of weeks. However, at that time, none of the operating systems featured in the ACE specification were available: Windows NT being expected in early 1992 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIPS III
MIPS (Microprocessor without Interlocked Pipelined Stages) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures (ISA)Price, Charles (September 1995). ''MIPS IV Instruction Set'' (Revision 3.2), MIPS Technologies, Inc. developed by MIPS Computer Systems, now MIPS Technologies, based in the United States. There are multiple versions of MIPS, including MIPS I, II, III, IV, and V, as well as five releases of MIPS32/64 (for 32- and 64-bit implementations, respectively). The early MIPS architectures were 32-bit; 64-bit versions were developed later. As of April 2017, the current version of MIPS is MIPS32/64 Release 6. MIPS32/64 primarily differs from MIPS I–V by defining the privileged kernel mode System Control Coprocessor in addition to the user mode architecture. The MIPS architecture has several optional extensions: MIPS-3D, a simple set of floating-point Instruction set architecture#SIMD instruction, SIMD instructions dedicated to 3D computer gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KL Orion R4600
KL, kL, kl, or kl. may refer to: Businesses and organizations * KLM, a Dutch airline (IATA airline designator KL) * Koninklijke Landmacht, the Royal Netherlands Army * Kvenna Listin ("Women's List"), a political party in Iceland * KL FM, a Malay language radio station Places * Kaiserslautern, Germany (license plate code KL) * Kerala, India (ISO 3166-2:IN sub-code KL) * Kirkland Lake, Ontario, Canada * Kowloon, Hong Kong * Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Science, technology, and mathematics * KL engine, version of the Mazda K engine * Klepton (kl.), a type of species in zoology * Kiloliter (kL), a unit of volume * Kullback–Leibler divergence in mathematics * KL (gene), a gene which encodes the klotho enzyme in humans Other uses * Jeep Cherokee (KL) * Kalaallisut language (ISO 639 alpha-2 language code "kl") * Kl (digraph), used in the Zulu language to write /kʟ̥ʼ/ or /kxʼ/ * Konzentrationslager, or concentration camp, abbreviated KZ or KL * '' KL: A History of the Nazi Concentrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing (MP) is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. There are many variations on this basic theme, and the definition of multiprocessing can vary with context, mostly as a function of how CPUs are defined ( multiple cores on one die, multiple dies in one package, multiple packages in one system unit, etc.). A multiprocessor is a computer system having two or more processing units (multiple processors) each sharing main memory and peripherals, in order to simultaneously process programs. A 2009 textbook defined multiprocessor system similarly, but noted that the processors may share "some or all of the system’s memory and I/O facilities"; it also gave tightly coupled system as a synonymous term. At the operating system level, ''multiprocessing'' is sometimes used to refer to the executi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium
Pentium is a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel from 1993 to 2023. The Pentium (original), original Pentium was Intel's fifth generation processor, succeeding the i486; Pentium was Intel's flagship processor line for over a decade until the introduction of the Intel Core line in 2006. Pentium-branded processors released from 2009 onwards were considered entry-level products positioned above the low-end Intel Atom, Atom and Celeron series, but below the faster Core lineup and workstation/server Xeon series. The later Pentiums, which have little more than their name in common with earlier Pentiums, were based on both the architecture used in Atom and that of Core processors. In the case of Atom architectures, Pentiums were the highest performance implementations of the architecture. Pentium processors with Core architectures prior to 2017 were distinguished from the faster, higher-end i-series processors by lower clock rates and disabling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IDT R4650 Die
IDT may refer to: Technology * Information and digital technology, a digitally focused information technology landscape * Interdigital transducer, or interdigitated transducer, a sensor and transmitter for a surface acoustic wave * Interrupt descriptor table, a memory structure of x86 microprocessors * Insulation-displacement technology, or insulation-displacement termination, an electrical connector * Interactive data transformation, a form of data transformation via a visual interface intended for analysts and business users with limited technical knowledge Organisations * IDT Corporation, a long-distance telephone carrier * Integrated Device Technology, a semiconductor manufacturer * Integrated Display Technology, a Hong Kong-based producer of LCD products * Integrated DNA Technologies, a U.S. supplier of custom nucleic acids * International Display Technology, a joint-venture of IBM and the Taiwanese Chi Mei group * IDT Entertainment, film producer Other * Inherited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Signal Processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a sequence of numbers that represent Sampling (signal processing), samples of a continuous variable in a domain such as time, space, or frequency. In digital electronics, a digital signal is represented as a pulse train, which is typically generated by the switching of a transistor. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing. DSP applications include Audio signal processing, audio and speech processing, sonar, radar and other sensor array processing, spectral density estimation, statistical signal processing, digital image processing, data compression, video coding, audio coding, image compression, signal processing for telecommunications, control systems, biomedical engineering, and seismology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed-point Arithmetic
In computing, fixed-point is a method of representing fractional (non-integer) numbers by storing a fixed number of digits of their fractional part. Dollar amounts, for example, are often stored with exactly two fractional digits, representing the cents (1/100 of dollar). More generally, the term may refer to representing fractional values as integer multiples of some fixed small unit, e.g. a fractional amount of hours as an integer multiple of ten-minute intervals. Fixed-point number representation is often contrasted to the more complicated and computationally demanding floating-point representation. In the fixed-point representation, the fraction is often expressed in the same number base as the integer part, but using negative powers of the base ''b''. The most common variants are decimal (base 10) and binary (base 2). The latter is commonly known also as binary scaling. Thus, if ''n'' fraction digits are stored, the value will always be an integer multiple of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
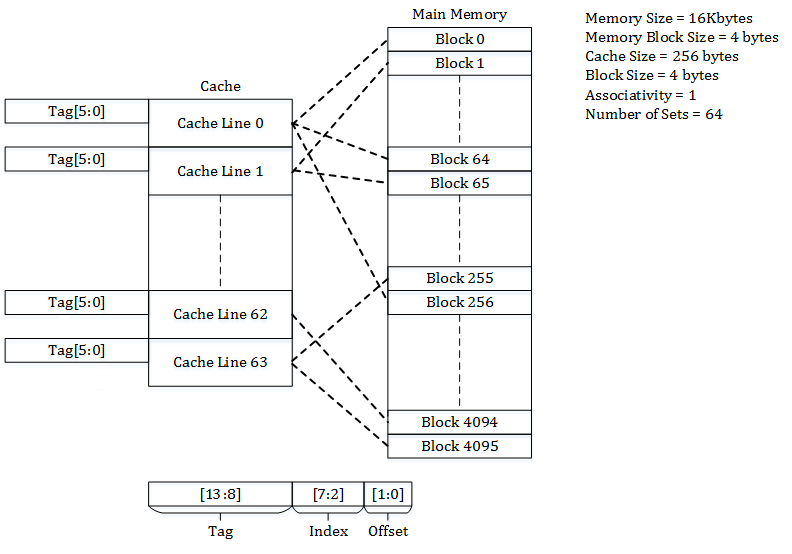
Set-associative
Cache placement policies are policies that determine where a particular memory block can be placed when it goes into a CPU cache. A block of memory cannot necessarily be placed at an arbitrary location in the cache; it may be restricted to a particular cache line or a set of cache lines by the cache's placement policy. There are three different policies available for placement of a memory block in the cache: direct-mapped, fully associative, and set-associative. Originally this space of cache organizations was described using the term "congruence mapping". Direct-mapped cache In a direct-mapped cache structure, the cache is organized into multiple sets with a single cache line per set. Based on the address of the memory block, it can only occupy a single cache line. The cache can be framed as a column matrix. To place a block in the cache * The set is determined by the index bits derived from the address of the memory block. * The memory block is placed in the set identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |