|
R0 Space
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a T1 space is a topological space in which, for every pair of distinct points, each has a neighborhood not containing the other point. An R0 space is one in which this holds for every pair of topologically distinguishable points. The properties T1 and R0 are examples of separation axioms. Definitions Let ''X'' be a topological space and let ''x'' and ''y'' be points in ''X''. We say that ''x'' and ''y'' are if each lies in a neighbourhood that does not contain the other point. * ''X'' is called a T1 space if any two distinct points in ''X'' are separated. * ''X'' is called an R0 space if any two topologically distinguishable points in ''X'' are separated. A T1 space is also called an accessible space or a space with Fréchet topology and an R0 space is also called a symmetric space. (The term also has an entirely different meaning in functional analysis. For this reason, the term ''T1 space'' is preferred. There is also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology
Topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a Mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformations, such as Stretch factor, stretching, Torsion (mechanics), twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a Set (mathematics), set endowed with a structure, called a ''Topology (structure), topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of List of continuity-related mathematical topics, continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of topological spaces, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and Homotopy, homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofinite
In mathematics, a cofinite subset of a set X is a subset A whose complement in X is a finite set. In other words, A contains all but finitely many elements of X. If the complement is not finite, but is countable, then one says the set is cocountable. These arise naturally when generalizing structures on finite sets to infinite sets, particularly on infinite products, as in the product topology or direct sum. This use of the prefix "" to describe a property possessed by a set's mplement is consistent with its use in other terms such as " meagre set". Boolean algebras The set of all subsets of X that are either finite or cofinite forms a Boolean algebra, which means that it is closed under the operations of union, intersection, and complementation. This Boolean algebra is the on X. In the other direction, a Boolean algebra A has a unique non-principal ultrafilter (that is, a maximal filter not generated by a single element of the algebra) if and only if there exists an inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Set
In geometry, topology, and related branches of mathematics, a closed set is a Set (mathematics), set whose complement (set theory), complement is an open set. In a topological space, a closed set can be defined as a set which contains all its limit points. In a complete metric space, a closed set is a set which is Closure (mathematics), closed under the limit of a sequence, limit operation. This should not be confused with closed manifold. Sets that are both open and closed and are called clopen sets. Definition Given a topological space (X, \tau), the following statements are equivalent: # a set A \subseteq X is in X. # A^c = X \setminus A is an open subset of (X, \tau); that is, A^ \in \tau. # A is equal to its Closure (topology), closure in X. # A contains all of its limit points. # A contains all of its Boundary (topology), boundary points. An alternative characterization (mathematics), characterization of closed sets is available via sequences and Net (mathematics), net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Set
In mathematics, an open set is a generalization of an Interval (mathematics)#Definitions_and_terminology, open interval in the real line. In a metric space (a Set (mathematics), set with a metric (mathematics), distance defined between every two points), an open set is a set that, with every point in it, contains all points of the metric space that are sufficiently near to (that is, all points whose distance to is less than some value depending on ). More generally, an open set is a member of a given Set (mathematics), collection of Subset, subsets of a given set, a collection that has the property of containing every union (set theory), union of its members, every finite intersection (set theory), intersection of its members, the empty set, and the whole set itself. A set in which such a collection is given is called a topological space, and the collection is called a topology (structure), topology. These conditions are very loose, and allow enormous flexibility in the choice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition (set Theory)
In mathematics, a partition of a set is a grouping of its elements into non-empty subsets, in such a way that every element is included in exactly one subset. Every equivalence relation on a set defines a partition of this set, and every partition defines an equivalence relation. A set equipped with an equivalence relation or a partition is sometimes called a setoid, typically in type theory and proof theory. Definition and notation A partition of a set ''X'' is a set of non-empty subsets of ''X'' such that every element ''x'' in ''X'' is in exactly one of these subsets (i.e., the subsets are nonempty mutually disjoint sets). Equivalently, a family of sets ''P'' is a partition of ''X'' if and only if all of the following conditions hold: *The family ''P'' does not contain the empty set (that is \emptyset \notin P). *The union of the sets in ''P'' is equal to ''X'' (that is \textstyle\bigcup_ A = X). The sets in ''P'' are said to exhaust or cover ''X''. See also collecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalence Relation
In mathematics, an equivalence relation is a binary relation that is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive. The equipollence relation between line segments in geometry is a common example of an equivalence relation. A simpler example is equality. Any number a is equal to itself (reflexive). If a = b, then b = a (symmetric). If a = b and b = c, then a = c (transitive). Each equivalence relation provides a partition of the underlying set into disjoint equivalence classes. Two elements of the given set are equivalent to each other if and only if they belong to the same equivalence class. Notation Various notations are used in the literature to denote that two elements a and b of a set are equivalent with respect to an equivalence relation R; the most common are "a \sim b" and "", which are used when R is implicit, and variations of "a \sim_R b", "", or "" to specify R explicitly. Non-equivalence may be written "" or "a \not\equiv b". Definitions A binary relation \,\si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetric Relation
A symmetric relation is a type of binary relation. Formally, a binary relation ''R'' over a set ''X'' is symmetric if: : \forall a, b \in X(a R b \Leftrightarrow b R a) , where the notation ''aRb'' means that . An example is the relation "is equal to", because if is true then is also true. If ''R''T represents the converse of ''R'', then ''R'' is symmetric if and only if . Symmetry, along with reflexivity and transitivity, are the three defining properties of an equivalence relation. Examples In mathematics * "is equal to" ( equality) (whereas "is less than" is not symmetric) * "is comparable to", for elements of a partially ordered set * "... and ... are odd": :::::: Outside mathematics * "is married to" (in most legal systems) * "is a fully biological sibling of" * "is a homophone of" * "is a co-worker of" * "is a teammate of" Relationship to asymmetric and antisymmetric relations By definition, a nonempty relation cannot be both symmetric and asymmetric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specialization Preorder
In the branch of mathematics known as topology, the specialization (or canonical) preorder is a natural preorder on the set of the points of a topological space. For most spaces that are considered in practice, namely for all those that satisfy the T0 separation axiom, this preorder is even a partial order (called the specialization order). On the other hand, for T1 spaces the order becomes trivial and is of little interest. The specialization order is often considered in applications in computer science, where T0 spaces occur in denotational semantics. The specialization order is also important for identifying suitable topologies on partially ordered sets, as is done in order theory. Definition and motivation Consider any topological space ''X''. The specialization preorder ≤ on ''X'' relates two points of ''X'' when one lies in the closure of the other. However, various authors disagree on which 'direction' the order should go. What is agreed is that if :''x'' is contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closure (topology)
In topology, the closure of a subset of points in a topological space consists of all points in together with all limit points of . The closure of may equivalently be defined as the union of and its boundary, and also as the intersection of all closed sets containing . Intuitively, the closure can be thought of as all the points that are either in or "very near" . A point which is in the closure of is a point of closure of . The notion of closure is in many ways dual to the notion of interior. Definitions Point of closure For S as a subset of a Euclidean space, x is a point of closure of S if every open ball centered at x contains a point of S (this point can be x itself). This definition generalizes to any subset S of a metric space X. Fully expressed, for X as a metric space with metric d, x is a point of closure of S if for every r > 0 there exists some s \in S such that the distance d(x, s) < r ( is allowed). Another way to expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
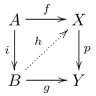
Lifting Property
In mathematics, in particular in category theory, the lifting property is a property of a pair of morphisms in a category. It is used in homotopy theory within algebraic topology to define properties of morphisms starting from an explicitly given class of morphisms. It appears in a prominent way in the theory of model categories, an axiomatic framework for homotopy theory introduced by Daniel Quillen. It is also used in the definition of a factorization system, and of a weak factorization system, notions related to but less restrictive than the notion of a model category. Several elementary notions may also be expressed using the lifting property starting from a list of (counter)examples. Formal definition A morphism i in a category has the ''left lifting property'' with respect to a morphism p, and p also has the ''right lifting property'' with respect to i, sometimes denoted i\perp p or i\downarrow p, iff the following implication holds for each morphism f and g in the cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierpiński Space
In mathematics, the Sierpiński space is a finite topological space with two points, only one of which is closed. It is the smallest example of a topological space which is neither trivial nor discrete. It is named after Wacław Sierpiński. The Sierpiński space has important relations to the theory of computation and semantics, because it is the classifying space for open sets in the Scott topology. Definition and fundamental properties Explicitly, the Sierpiński space is a topological space ''S'' whose underlying point set is \ and whose open sets are \. The closed sets are \. So the singleton set \ is closed and the set \ is open (\varnothing = \ is the empty set). The closure operator on ''S'' is determined by \overline = \, \qquad \overline = \. A finite topological space is also uniquely determined by its specialization preorder. For the Sierpiński space this preorder is actually a partial order and given by 0 \leq 0, \qquad 0 \leq 1, \qquad 1 \leq 1. Topol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neighbourhood (topology)
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a neighbourhood (or neighborhood) is one of the basic concepts in a topological space. It is closely related to the concepts of open set and interior. Intuitively speaking, a neighbourhood of a point is a set of points containing that point where one can move some amount in any direction away from that point without leaving the set. Definitions Neighbourhood of a point If X is a topological space and p is a point in X, then a neighbourhood of p is a subset V of X that includes an open set U containing p, p \in U \subseteq V \subseteq X. This is equivalent to the point p \in X belonging to the topological interior of V in X. The neighbourhood V need not be an open subset of X. When V is open (resp. closed, compact, etc.) in X, it is called an (resp. closed neighbourhood, compact neighbourhood, etc.). Some authors require neighbourhoods to be open, so it is important to note their conventions. A set that is a neighbourhood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |