|
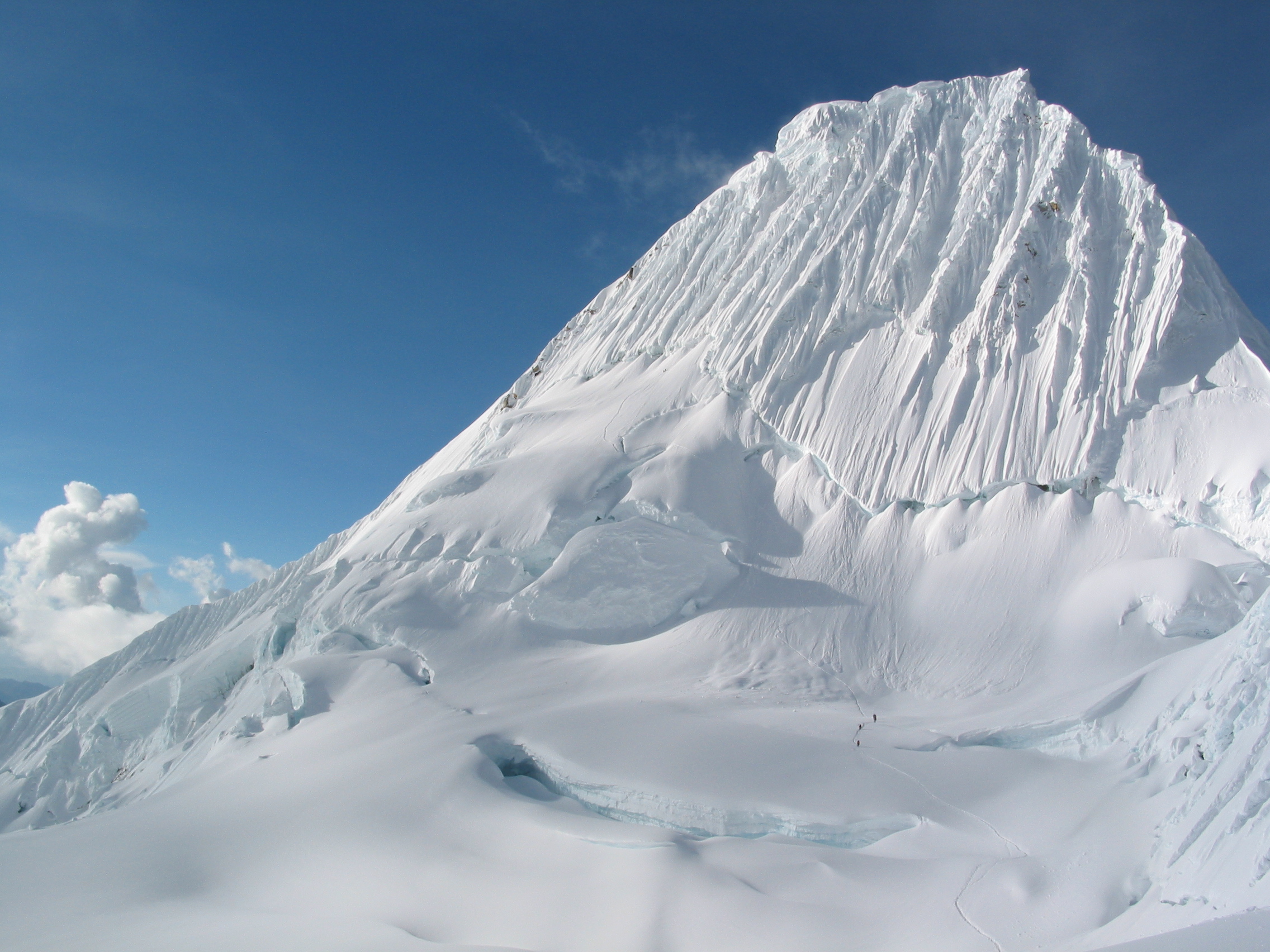
Quitaraju
Quitaraju or Kitaraju (possibly from Ancash Quechua ''kita'' dam, Quechua language, Quechua ''rahu'' snow, ice) is a mountain in the Cordillera Blanca in the Andes of Peru, about high. It is situated in the Ancash Region, Huaylas Province, Santa Cruz District, Ancash, Santa Cruz District. Quitaraju lies north of the Santa Cruz Creek and the lakes named Ichikqucha, Ichiccocha, Hatunqucha (Qaras), Jatuncocha and Quitacocha, between Santa Cruz (mountain), Santa Cruz in the west and Alpamayo in the northeast. Its slopes are within the Huascarán National Park. Elevation Other data from available digital elevation models: SRTM 6010 metres, ASTER filled 6010 metres and TanDEM-X 5961 metres. The height of the nearest key col is 3253 meters, leading to a topographic prominence of 2783 meters. Quitaraju is considered a Mountain Sub-System according to the ''Dominance System'' and its dominance is 46.11%. Its parent peak is Santa Cruz (mountain), Nevado Santa Cruz and the Topographic is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Cruz Creek
Santa Cruz, (called Yuraqmayu or Yuracma near its end) is a creek in Peru located in Santa Cruz District, Ancash, Santa Cruz District, Huaylas Province, Ancash Region, Ancash. It is a right tributary of the Santa River, Santa River. It originates in the Cordillera Blanca southwest of Taulliraju, near a lake named Tawlliqucha (Ancash), Tawlliqucha. It flows from northeast to southwest through lakes Jatuncocha (Caraz), Jatuncocha and Ichiccocha and passing by the village of Llamacorral, flanked by the mountains Pucajirca, Quitaraju and Santa Cruz (mountain), Santa Cruz in the north and by Sintiru, Artesonraju and Caraz (mountain), Caraz in the south. Southwest of Santa Cruz, near the village of Cashapampa, it turns to the northwest and then joins the Santa River near the villages of Colcas and Pacamayo, 140 km before the Santa River reaches the Pacific Ocean. The toponymy Yuraqmayu is of Quechua language, Quechua origin, possibly meaning: ''yuraq'' white, ''mayu'' river,Teofil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpamayo
Alpamayo (possibly from Quechua ''allpa'' earth, ''mayu'' river, "earth river") or Shuyturaju (possibly from Ancash Quechua ''huytu, shuytu'' oblong, slim and long, Quechua ''rahu'' snow, ice, mountain covered in snow) is one of the most conspicuous peaks in the Cordillera Blanca of the Peruvian Andes. Alpamayo Creek originates northwest of it. The Alpamayo lies next to the slightly higher Quitaraju. In July 1966, the German magazine ''"Alpinismus"'', published a photo of Alpamayo taken by American photographer Leigh Ortenburger accompanied by an article on a survey among mountaineering experts, who chose Alpamayo as "The Most Beautiful Mountain in the World". Climbing history and routes Most popular routes start from the village of Caraz, on the north of the Cordillera Blanca. A French-Belgian expedition including George and Claude Kogan claimed to have made the first ascent in 1951. After studying the photos in George Kogan's book ''The Ascent of Alpamayo'', the German te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordillera Blanca
The Cordillera Blanca (Spanish for "white range") is a mountain range in Peru that is part of the larger Andes range and extends for between 8°08' and 9°58'S and 77°00' and 77°52'W, in a northwesterly direction. It includes several peaks over high and 722 individual glaciers. The highest mountain in Peru, Huascarán, at high, is located there. The Cordillera Blanca lies in the Ancash Region, Ancash region and runs parallel to the Santa River valley (also called Callejón de Huaylas in its upper and midsections) on the west. Huascarán National Park, established in 1975, encompasses almost the entire range of the Cordillera Blanca. Snowmelt from the Cordillera Blanca provides part of northern Peru with its year-round water supply, while 5% of Peru's power comes from a Hydroelectricity, hydro-electrical plant located in the Santa River valley. The area of permanent ice cover shrank by about a third between the 1970s and 2006. Geography The Cordillera Blanca is the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatunqucha (Qaras)
Jatuncocha (possibly from Quechua ''hatun'' (in Bolivia always ''jatun'') big, large ''qucha'' lake, "big lake") is a lake in the Cordillera Blanca in the Andes of Peru located in the Ancash Region, Huaylas Province, Santa Cruz District. It is situated at a height of comprising an area of . Jatunccocha lies in the Santa Cruz gorge between the peaks of Quitaraju in the north and Caraz in the south, northeast of a smaller lake named Ichiccocha (Quechua for "little lake"). The Santa Cruz Creek flows through the lake. It is a right tributary of the Santa River The Santa River () is a river in the South American Andes mountain range in the Ancash Region of northwest central Peru. River course Lake Conococha, at an altitude of 4,050 m above sea level and at , is considered the headwaters of the Santa R .... References Lakes of Peru Lakes of the Department of Ancash {{Ancash-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilometers
The kilometre ( SI symbol: km; or ), spelt kilometer in American and Philippine English, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one thousand metres (kilo- being the SI prefix for ). It is the preferred measurement unit to express distances between geographical places on land in most of the world; notable exceptions are the United States and the United Kingdom where the statute mile is used. Pronunciation There are two common pronunciations for the word. # # The first pronunciation follows a pattern in English whereby SI units are pronounced with the stress on the first syllable (as in kilogram, kilojoule and kilohertz) and the pronunciation of the actual base unit does not change irrespective of the prefix (as in centimetre, millimetre, nanometre and so on). It is generally preferred by the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC), the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC), and the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC). Many othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographic Isolation
The topographic isolation of a summit is the minimum geographical distance, horizontal distance to a point of equal elevation, representing a radius of dominance in which the peak is the highest point. It can be calculated for small hills and islands as well as for major summit (topography), mountain peaks and can even be calculated for submarine summits. Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth, has an undefined isolation, since there are no higher points to reference. Because topographic isolation can be difficult to determine, a common approximation is the distance to a peak called the nearest higher neighbour (NHN). Isolation table The following sortable table lists Earth's 40 most topographically isolated summits. Examples *The nearest peak to Germany's highest mountain, the high Zugspitze, that has a contour is the Zwölferkogel (Stubai Alps), Zwölferkogel in Austria's Stubai Alps. The distance between the Zugspitze and this contour is ; the Zugspitze is thus the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parent Peak
In topography, prominence or relative height (also referred to as autonomous height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. The key col ("saddle") around the peak is a unique point on this contour line and the ''parent peak'' (if any) is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria. Definitions The prominence of a peak is the least drop in height necessary in order to get from the summit to any higher terrain. This can be calculated for a given peak in the following manner: for every path connecting the peak to higher terrain, find the lowest point on the path; the ''key col'' (or ''highest saddle'', or ''linking col'', or ''link'') is defined as the highest of these points, along all connecting paths; the prominence is the difference between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meters
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of a second, where the second is defined by a hyperfine transition frequency of caesium. The metre was originally defined in 1791 by the French National Assembly as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's polar circumference is approximately . In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar. The bar used was changed in 1889, and in 1960 the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the path trave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Col
In topography, prominence or relative height (also referred to as autonomous height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. The key col ("saddle") around the peak is a unique point on this contour line and the ''parent peak'' (if any) is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria. Definitions The prominence of a peak is the least drop in height necessary in order to get from the summit to any higher terrain. This can be calculated for a given peak in the following manner: for every path connecting the peak to higher terrain, find the lowest point on the path; the ''key col'' (or ''highest saddle (landform), saddle'', or ''linking col'', or ''link'') is defined as the highest of these points, along all connecting paths; the prominence is the differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TanDEM-X
TanDEM-X (TerraSAR-X add-on for Digital Elevation Measurement) is a German twin satellite mission using interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR). It is developed in a public-private partnership between the German Aerospace centre (DLR Institute for Planetary Research, DLR) and EADS Astrium (now Airbus Defence and Space). It consists of the original TerraSAR-X satellite (TSX) and an identical spacecraft (TDX) in formation flying, with typical distances between 250 and 500 m.German Aerospace CenterTanDEM-X - A New High Resolution Interferometric SAR MissionVerified 2010-10-16. The two satellite constellation allowed the generation of the WorldDEM global digital elevation models starting in 2014. WorldDEM The primary mission objective is the generation of WorldDEM, a consistent global Digital Elevation Model (DEM) with an unprecedented accuracy according to better than DTED Level 2 specifications. WorldDEM resolution will correspond to DTED Level 3 (post spacing of better t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Elevation Models
A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refers to a discrete global grid. DEMs are used often in geographic information systems (GIS), and are the most common basis for digitally produced relief maps. A digital terrain model (DTM) represents specifically the ground surface while DEM and DSM may represent tree top canopy or building roofs. While a DSM may be useful for landscape modeling, city modeling and visualization applications, a DTM is often required for flood or drainage modeling, land-use studies, geological applications, and other applications, and in planetary science. Terminology There is no universal usage of the terms ''digital elevation model'' (DEM), ''digital terrain model'' (DTM) and ''digital surface model'' (DSM) in scientific literature. In most cases the term ''digital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |