|
Quintus Caecilius Bassus
Quintus Caecilius Bassus () was a Roman equestrian who fought during Caesar's civil war under Pompey before the Battle of Pharsalus. After the battle, he commandeered two mutinous legions in Syria and defended against a Caesarian siege at Apamea. There, he negotiated with Deiotarus, the king of Galatia, and the Parthians. After Caesar's death, both his men and those of his besiegers defected to Gaius Cassius Longinus; Bassus was then dismissed unharmed. He then disappears from history, possibly dying during the Battle of Philippi. His opposition to Caesar in late 45 BC, after the defeat of Gnaeus Pompey at the Battle of Munda, marked him as one of the last open combatants of the civil war. See also * Caesar's Civil War Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected ret ... Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Equites
The (; , though sometimes referred to as " knights" in English) constituted the second of the property/social-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian order was known as an (). Description During the Roman Kingdom and the first century of the Roman Republic, legionary cavalry was recruited exclusively from the ranks of the patricians, who were expected to provide six (hundreds) of cavalry (300 horses for each consular legion). Around 400BC, 12 more of cavalry were established and these included non-patricians (plebeians). Around 300 BC the Samnite Wars obliged Rome to double the normal annual military levy from two to four legions, doubling the cavalry levy from 600 to 1,200 horses. Legionary cavalry started to recruit wealthier citizens from outside the 18 . These new recruits came from the first class of commoners in the Centuriate Assembly organisation, and were not granted the same privileges. By the time of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caesar's Civil War
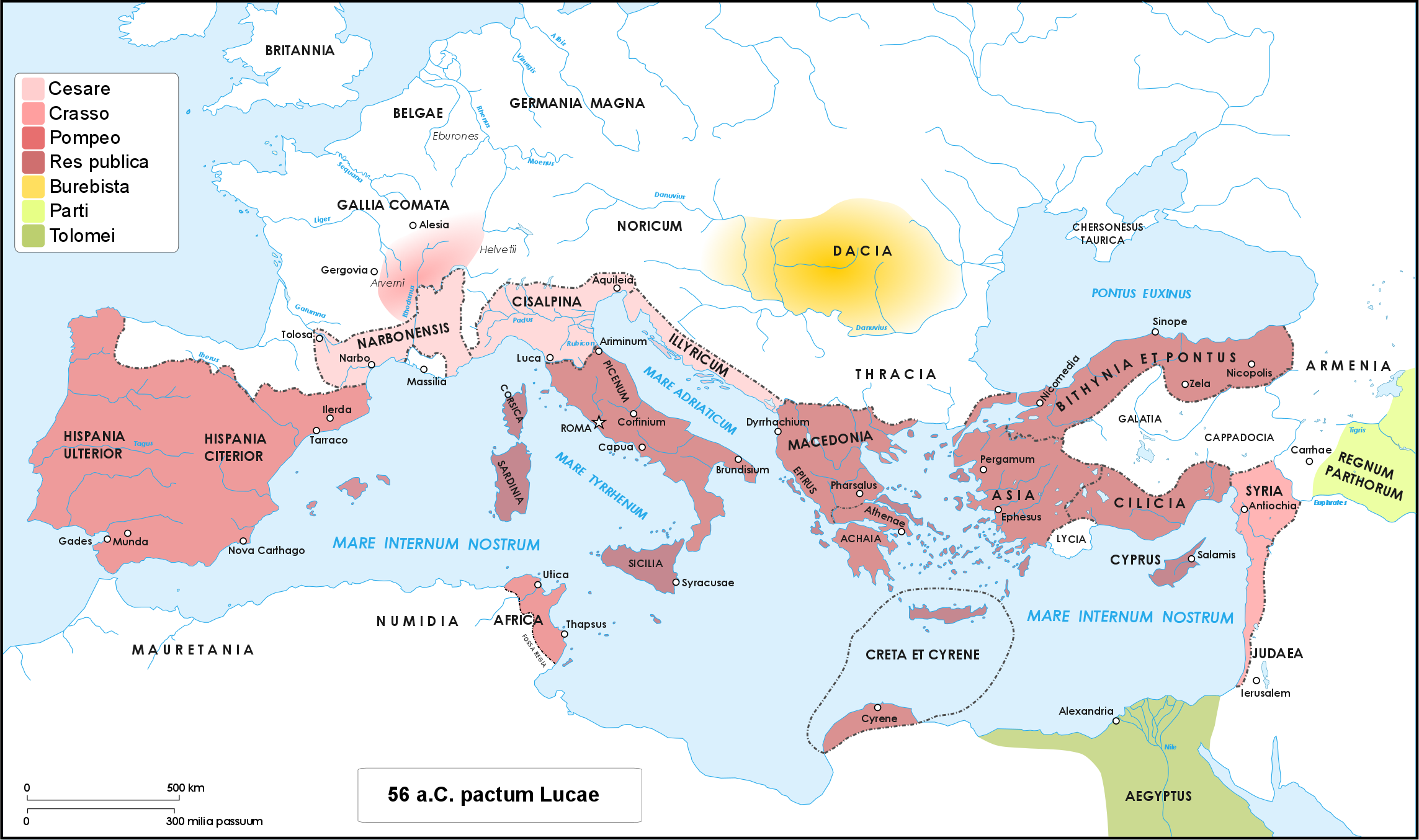
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected return to Rome on the expiration of his Lex Vatinia, governorship in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Before the war, Caesar had led an Gallic Wars, invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 50 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down, led to the outbreak of civil war. Pompey and his allies induced the Roman Senate, Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies in the opening days of 49 BC. Caesar refused and instead Crossing the Rubicon, marched on Rome. The war was fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece in the Roman era, Greece, Ptolemaic Egypt, Egypt, Africa (Roman province), Africa, and Hispania. The decisive events occurred in Greece in 48 BC: Pompey defeated Caesar at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. As a young man, he was a partisan and protégé of the dictator Sulla, after whose death he achieved much military and political success himself. He was an ally and a rival of Julius Caesar, and died in civil war with him. A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving Sulla as a commander in the civil war of 83–81 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first consulship without following the traditional '' cursus honorum'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as consul on three occasions (70, 55, 52 BC). He celebrated three triumphs, served as a commander in the Sertorian War, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
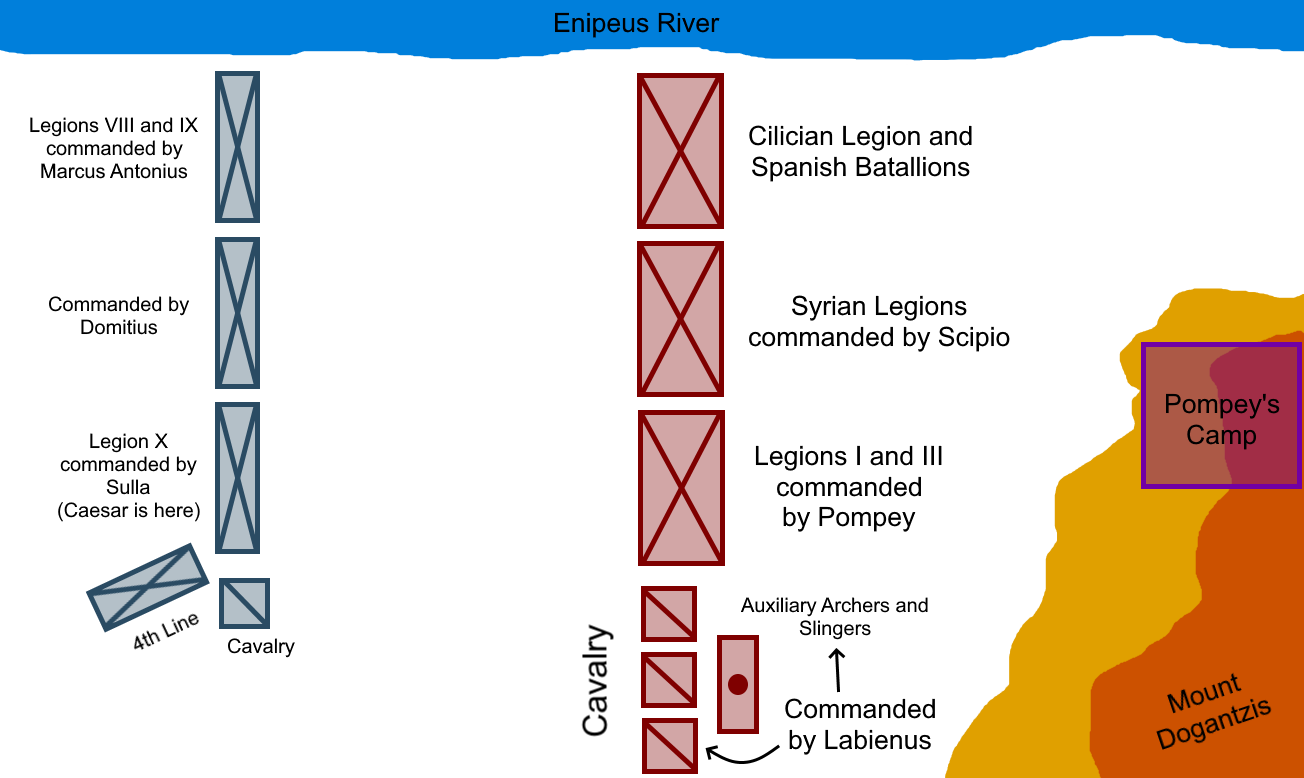
Battle Of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in Central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey. Pompey had the backing of a majority of Roman senators and his army significantly outnumbered the veteran Caesarian legions. Pressured by his officers, Pompey reluctantly engaged in battle and suffered an overwhelming defeat, ultimately fleeing the camp and his men, disguised as an ordinary citizen. Eventually making his way to Egypt, he was assassinated upon his arrival at the order of Ptolemy XIII. Prelude Following the start of the Civil War, Caesar had captured Rome, forced Pompey and his allies to withdraw from Italy, and defeated Pompey's legates in Spain. In the campaign season for 48 BC, Caesar crossed the Adriatic and advanced on Dyrrachium. There, he besieged it, but was defeated. Caesar then withdrew east into Thess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Syria (Roman Province)
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great, who had become the protector of the Hellenistic kingdom of Syria. Following the partition of the Herodian Kingdom of Judea into a tetrarchy in 4 BC, it was gradually absorbed into Roman provinces, with Roman Syria annexing Iturea and Trachonitis. By the late 2nd century AD, the province was divided into Coele Syria and Syria Phoenice. Provincia Syria Syria was annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC, when Pompey the Great had the Seleucid king Antiochus XIII Asiaticus executed and deposed his successor Philip II Philoromaeus. Pompey appointed Marcus Aemilius Scaurus to the post of governor of Syria. Following the fall of the Roman Republic and its transformation into the Roman Empire, Syria became a Roman imperial province, governed by a Legate. During the early empire, the Roman army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Apamea, Syria
Apamea (, ''Apameia''; ), on the right bank of the Orontes river, Orontes River, was an ancient Greek and Roman city. It was the capital of Apamene under the Macedonians, became the capital and Metropolitan Archbishopric of late Roman province Roman Syria, Syria Secunda, again in the crusader period. Amongst the impressive ancient remains, the site includes the Great Colonnade at Apamea, Great Colonnade which ran for nearly making it among the longest in the Roman Empire, Roman world and the Roman Theatre at Apamea, Roman Theatre, one of the largest surviving theatres of the Roman Empire with an estimated seating capacity in excess of 20,000. The site lies on the edge of the modern town of Qalaat al-Madiq, about to the northwest of Hama, Syria, overlooking the Ghab valley. History Hellenistic era After the conquest of the region by Alexander the Great and the subsequent wars between his generals, and according to the new interpretation of a new historical and iconograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Deiotarus
Deiotarus of Galatia (in Galatian and Greek Deiotaros, surnamed Philoromaios ("Friend of the Romans"); 42 BC, 41 BC or 40 BC) was a Chief Tetrarch of the Tolistobogii in western Galatia, Asia Minor, and a King of Galatia ("Gallo-Graecia"). He was considered one of the most adept of Celtic kings, ruling the three tribes of Celtic Galatia from his fortress in Blucium. The name Deiotarus is generally translated as Galatian Celtic "Divine-bull" (*''deiuo-tauros''; cf. Old Irish ''dia'', Welsh ''duw'', Old Welsh ''duiu'', "God" and Old Irish ''tarb'', Welsh ''tarw'' "bull", with Western Celtic metathesis of the cluster ''-uro''- to ''-ruo-''). Biography Deiotarus was a faithful ally of the Romans and became involved in the struggles between the Roman generals that led to the fall of the Republic from 44 BC. He changed sides and supported the triumvirs, keeping his kingdom until his death. He is first heard of at the beginning of the Third Mithridatic War, when he drove the troop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Galatia
Galatia (; , ''Galatía'') was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here and became a small transient foreign tribe in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of the East. Geography Galatia was bounded to the north by Bithynia and Paphlagonia, to the east by Pontus and Cappadocia, to the south by Cilicia and Lycaonia, and to the west by Phrygia. Its capital was Ancyra (i.e. Ankara, today the capital of modern Turkey). Celtic Galatia The terms "Galatians" came to be used by the Greeks for the three Celtic peoples of Anatolia: the Tectosages, the Trocmii, and the Tolistobogii. By the 1st century BC, the Celts had become so Hellenized that some Greek writers called them ''Hellenogalatai'' (Ἑλληνογαλάται). The Romans cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquering the region of Parthia in Iran's northeast, then a satrapy (province) under Andragoras, who was rebelling against the Seleucid Empire. Mithridates I ( BC) greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce. The Parthians largely adopted the art, architecture, religious beliefs, and regalia of their culturally heterogeneous empire, which encompassed Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Assassination Of Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar, the Roman dictator, was assassinated on the Ides of March (15 March) 44 BC by a group of senators during a Roman Senate, Senate session at the Curia of Pompey, located within the Theatre of Pompey in Ancient Rome, Rome. The conspirators, numbering between 60 and 70 individuals and led by Marcus Junius Brutus, Gaius Cassius Longinus, and Decimus Junius Brutus Albinus, stabbed Caesar approximately 23 times. They justified the act as a preemptive defense of the Roman Republic, asserting that Caesar's accumulation of lifelong political authority—including his perpetual dictatorship and other honors—threatened republican traditions. The assassination failed to achieve its immediate objective of restoring the Republic's institutions. Instead, it precipitated Caesar's posthumous Roman imperial cult, deification, triggered the Liberators' civil war (43–42 BC) between his supporters and the conspirators, and contributed to the collapse of the Republic. These ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gaius Cassius Longinus
Gaius Cassius Longinus (; – 3 October 42 BC) was a Roman senator and general best known as a leading instigator of the plot to assassinate Julius Caesar on 15 March 44 BC. He was the brother-in-law of Brutus, another leader of the conspiracy. He commanded troops with Brutus during the Battle of Philippi against the combined forces of Mark Antony and Octavian, Caesar's former supporters, and committed suicide after being defeated by Mark Antony. Cassius was elected as tribune of the plebs in 49 BC. He opposed Caesar, and eventually he commanded a fleet against him during Caesar's Civil War: after Caesar defeated Pompey in the Battle of Pharsalus, Caesar overtook Cassius and forced him to surrender. After Caesar's death, Cassius fled to the east to Syria, where he amassed an army of twelve legions. He was supported and made governor by the Senate. Later he and Brutus marched west against the allies of the Second Triumvirate. He followed the teachings of the philosopher Ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |