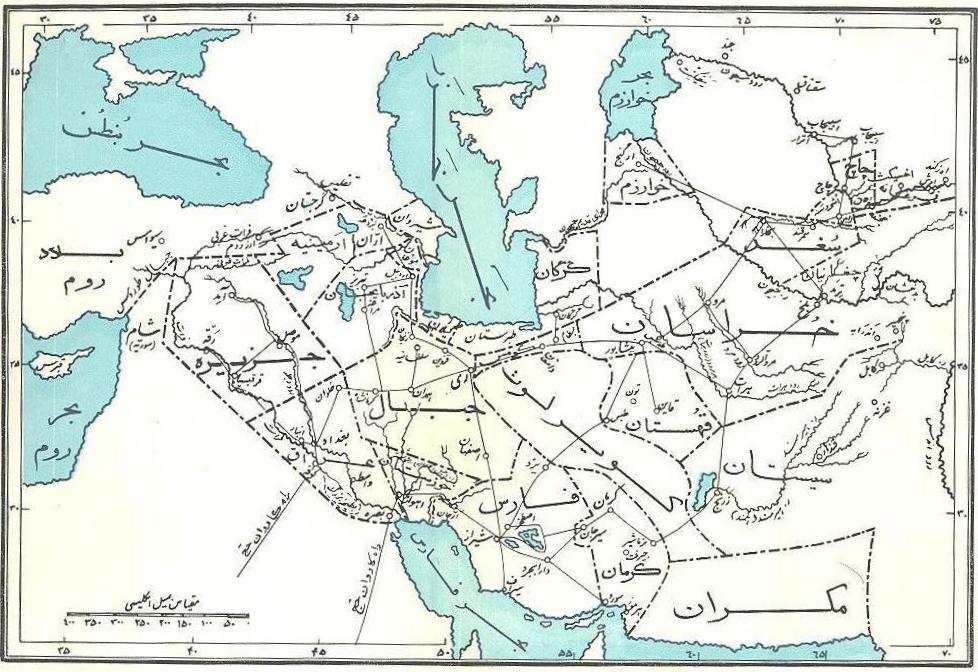
|
Quhistān
Quhistan () or Kohistan (, "mountainous land") was a region of medieval Persia, essentially the southern part of Khurasan. Its boundaries appear to have been south of Khorasan to north, Yazd to West, Sistan to South, Afghanistan to East. Quhistan was a province in old days with a rich history in Persian literature, art and science. Notable historical towns include Tun (modern-day Ferdows), Qa'in, Gunabad, Tabas, Birjand, Turshez (modern-day Kashmar), Khwaf, Taybad, and Zawah (modern-day Torbat-e Heydarieh). It is home to famous castles. Safron, berberies (Zereshk) and jujube (Annab) are among the famous agricultural products that are exclusively produced in Ghohestan. Hakim Nezari Ghohestani, Sima Bina and Professor Reza Ghohestani are among famous people who are originally from Ghohestan. Dagestan in the North Caucasus was previously and originally named ''"Quhistan"'', which has the same meaning as ''Dagestan'': ''dağ'' and ''kuh'' are the Turkic and Persian words for "mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nezari Ghohestani
Hakīm Sa'd-al-Dīn ibn Shams-al-Dīn Nizārī Bīrjandī Quhistānī (), or simply Nizari Ghohestani (died 1320 CE), was a 13th-century Nizari Ismaili author and poet, who lived in the time of the Imam Shams al-Din (Nizari) Muhammad. Nizari was born into a family of landed gentry approximately a decade after the capitulation of the Alamut state and hailed from the town of Birjand. Nizari is the only Ismaili poet of this period whose works are extant. Nizari Quhistani’s work was quoted by many later Ismaili authors, such as the Persian Khwāja Muḥammad Riḍā b. Sulṭān Ḥusayn, also known as Khayrkhvah-i Harati. Life Nizari completed his primary education in Birjand and Qa’in, and became adept in Arabic and Persian literature and philosophy. He received higher education at a college ''(madrasa)'', which he deplored as it was quite unlike the education he had received in his home town. For a time, he served as one of the only Ismaili officials at the court of Malik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Khorasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses western and northern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, the eastern halves of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, and portions of Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan. The extent of the region referred to as ''Khorasan'' varied over time. In its stricter historical sense, it comprised the present territories of Khorasan Province, northeastern Iran, parts of Afghanistan and southern parts of Central Asia, extending as far as the Amu Darya (Oxus) river. However, the name has often been used in a loose sense to include a wider region that included most of Transoxiana (encompassing Bukhara and Samarqand in present-day Uzbekistan), extended westward to the Caspian Sea, Caspian coast and to the Dasht-e Kavir southward to Sistan, and eastward to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Subdivisions Of Iran
A former is an object, such as a template, Gauge block, gauge or cutting Die (manufacturing), die, which is used to form something such as a boat's Hull (watercraft), hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the Flight control surfaces#Longitudinal_axis, longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizari Ismaili State
The Nizari state (the Alamut state) was a Nizari Isma'ili Shia state founded by Hassan-i Sabbah after he took control of the Alamut Castle in 1090 AD, which marked the beginning of an era of Ismailism known as the "Alamut period". Their people were also known as the '' Assassins'' or ''Hashashins''. The state consisted of a nexus of strongholds throughout Persia and the Levant, with their territories being surrounded by huge swathes of hostile as well as crusader territory. It was formed as a result of a religious and political movement of the minority Nizari sect supported by the anti- Seljuk population. Being heavily outnumbered, the Nizaris resisted adversaries by employing strategic, self-sufficient fortresses and the use of unconventional tactics, notably assassination of important adversaries and psychological warfare. They also had a strong sense of community as well as total obedience to their leader. Despite being occupied with survival in their hostile environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, or Ciscaucasia, is a subregion in Eastern Europe governed by Russia. It constitutes the northern part of the wider Caucasus region, which separates Europe and Asia. The North Caucasus is bordered by the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea to the west, the Caspian Sea to the east, and the Caucasus Mountains to the south. The region shares land borders with the countries of Georgia (country), Georgia and Azerbaijan in the South Caucasus. Located in the southern part of the region, Mount Elbrus is the List of European ultra-prominent peaks, tallest peak in Europe. Krasnodar is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, most populous among the urban area, urban centres in the region. The North Caucasus came under Russian control in the 19th century, following the Caucasian War between the Russian Empire and the various regional powers. The territory is the Southern Russia, southernmost portion of Russia and is divided between a number of Republics of Russia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagestan
Dagestan ( ; ; ), officially the Republic of Dagestan, is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Federal District. The republic is the southernmost tip of Russia, sharing land borders with the countries of Azerbaijan and Georgia to the south and southwest, the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia to the west and north, and with Stavropol Krai to the northwest. Makhachkala is the republic's capital and largest city; other major cities are Derbent, Kizlyar, Izberbash, Kaspiysk, and Buynaksk. Dagestan covers an area of , with a population of over 3.1 million, consisting of over 30 ethnic groups and 81 nationalities. With 14 official languages, and 12 ethnic groups each constituting more than 1% of its total population, the republic is one of Russia's most linguistically and ethnically diverse, and one of the most heteroge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Bina
Sima Bina (, ''Simā Binā'', born 4 January 1945) is an Iranian traditional musician, composer, researcher, painter and teacher, described by Radio WDR Germany as the "grand lady of Iranian folk music". Bina's performing arts career has spanned more than five decades. Bina has gathered and revived a collection of nearly forgotten Iranian folk songs and melodies. She has done extensive research on their origin, which included collecting, recording, writing and re-interpreting popular regional music. Her works cover the entire spectrum of Iranian folk music, including Mazandarani music, Kurdish music, Turkmen music, Baloch music, Lur music, Shirazi music, Bakhtiari music, and the music of North and South Khorasan. Early life and career Born in Birjand, Khorasan, in the heart of the popular tradition, she started her career on Iranian radio at the age of nine, under the guidance of her father, Ahmad Bina – a master of Iranian classical music and poet who wrote many of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torbat-e Heydarieh
Torbat-e Heydarieh () is a city in the Central District (Torbat-e Heydarieh County), Central District of Torbat-e Heydarieh County, Razavi Khorasan province, Razavi Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. The closest major city to Torbat-e Heydarieh is Mashhad, 175km away. Etymology The name ''Torbat'' in Persian means ''burial place'', thus the name of the city means ''Burial Place of Heydar'', named after Qutb ad-Dīn Haydar a Sufi mystic whose tomb lies in the heart of the city. In ancient times this city was known as Zaveh, and in the 19th century it was known as Torbat-e Ishaq Khan or Torbat-e Isa Khan after Eshaq Khan Qaraei-Torbati, Ishaq Khan Qaraei the powerful chief of the local Qarai Turks who ruled as a semi-autonomous governor of Torbat-e Heydarieh from 1775 to 1816. It derives its present name from the ''turbet'' or tomb of a holy man named Kutb ed din Haidar, the founder of the ascetic sect of dervishes known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdows
Ferdows () is a city in the Central District (Ferdows County), Central District of Ferdows County, South Khorasan province, South Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. It is about south of Mashhad and 200 km northwest of Birjand. Ferdows is on the main axis connecting Yazd, Kerman, Isfahan, Bushehr, Hormozgan province, Hormozgan and Fars province, Fars provinces to Mashhad. Ferdows city is 1293 meters above sea level. History Founded by the Medes, Ferdows is currently a city. It was a large and famous city in ancient days. There is an unproven theory that the town's name in ancient days was "Taban" (or shining; تابان in Persian language, Persian). In the Islamic era it became known as Toon or Tūn, a name retained until 1929, when it was changed to Ferdows. The first people to inhabit Ferdows were a group of Sagartians. Toon was a famous and thriving city both before and during the Islamic era. It was one of the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taybad
Taybad (, also romanized as Taīabad, Tāybād, and Tayebad), also known as Tāyebāt and Ţayyebāt, is a city in northeastern of Iran. The city is the Central District of Taybad County, Razavi Khorasan province, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Taybad is placed near the border with Afghanistan. Demographics Religion While most Iranians, and especially most Iranian Persians, are predominantly Shia, a majority of the population of Taybad are Persian Sunnis Sunni Islam is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any Succession to Muhammad, successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr .... Population At the time of the 2006 National Census, the city's population was 46,228 in 10,230 households. The 2011 census counted 52,280 people in 12,954 households. At the 2016 census, the population of the city was 56,562 people in 14,996 househo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |