|
Queqiao-1
''Queqiao'' relay satellite (), is the first of the pair of communications relay and radio astronomy satellites for the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. The China National Space Administration (CNSA) launched the Queqiao relay satellite on 20 May 2018 to a halo orbit around the Earth–Moon Lagrangian points, L2 Lagrangian point Queqiao is the first communication relay and radio astronomy satellite at this location. The name ''Queqiao'' ("Magpie Bridge") was inspired by and came from the Chinese tale ''The Cowherd and the Weaver Girl''. Design and development Queqiao was designed to function as a communication relay for the Chang'e 4 mission to the far side of the Moon, as well as a deep space radio astronomy observatory for the Chinese space program. Direct communication with Earth is impossible on the far side of the Moon, since transmissions are blocked by the Moon. Communications must go through a Communications satellite, communications relay satellite, which is placed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queqiao-2
''Queqiao-2'' relay satellite (), is the second of the communications relay and radio astronomy satellites designed to support the fourth phase the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, after Queqiao relay satellite, Queqiao-1 launched in 2018. The China National Space Administration (CNSA) launched the Queqiao-2 relay satellite on 20 March 2024 to an elliptical frozen orbit around the Moon to support communications from the far side of the Moon and the Lunar south pole. The name ''Queqiao'' (, "Magpie Bridge") was inspired by and came from the Chinese tale ''The Cowherd and the Weaver Girl''. Background and mission planning The initial phase of the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS), consisting of the Chang'e 7 and Chang'e 8 probes, was scheduled to be built in 2026 and 2028 on the southern edge of the South Pole–Aitken basin located on the far side of the Moon. While the Queqiao so far only had to connect with two probes on the far side of the Moon (Chang'e 4 lander and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queqiao Antenna
''Queqiao'' relay satellite (), is the first of the pair of communications relay and radio astronomy satellites for the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. The China National Space Administration (CNSA) launched the Queqiao relay satellite on 20 May 2018 to a halo orbit around the Earth–Moon L2 Lagrangian point Queqiao is the first communication relay and radio astronomy satellite at this location. The name ''Queqiao'' ("Magpie Bridge") was inspired by and came from the Chinese tale ''The Cowherd and the Weaver Girl''. Design and development Queqiao was designed to function as a communication relay for the Chang'e 4 mission to the far side of the Moon, as well as a deep space radio astronomy observatory for the Chinese space program. Direct communication with Earth is impossible on the far side of the Moon, since transmissions are blocked by the Moon. Communications must go through a communications relay satellite, which is placed at a location that has a clear view of both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 5-T1
Chang'e 5-T1 () was an experimental robotic spacecraft that was launched to the Moon on 23 October 2014, by the China National Space Administration (CNSA) to conduct atmospheric re-entry tests on the capsule design planned to be used in the Chang'e 5 mission. As part of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, Chang'e 5, launched in 2020, was a Moon sample return mission. Like its predecessors, the spacecraft is named after the Chinese Moon goddess Chang'e. The craft consisted of a return vehicle capsule and a service module orbiter. The return capsule of Chang'e 5-T1, named ''Xiaofei'' (), meaning "little flyer" in Chinese, landed in Siziwang Banner, Inner Mongolia, on 31 October 2014, 22:42 UTC. The CE-5-T1 Service Module entered lunar orbit on 13 January 2015. Its initial orbit was 200 x 5,300 km with a period of 8 hours. Characteristics It consisted of a DFH-3A " Chang'e 2 type" spacecraft with a mass of approximately 2,215 kg (including 1,065 kg of fuel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 4
Chang'e 4 (; ) is a robotic spacecraft mission in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program of the CNSA. It made a soft landing on the far side of the Moon, the first spacecraft to do so, on 3 January 2019. A communication relay satellite, , was first launched to a halo orbit near the Earth–Moon L2 point in May 2018. The robotic lander and '' Yutu-2'' () rover were launched on 7 December 2018 and entered lunar orbit on 12 December 2018, before landing on the Moon's far side. On 15 January it was announced that seeds had sprouted in the lunar lander's biological experiment, the first plants to sprout on the Moon. The mission is the follow-up to Chang'e 3, the first Chinese landing on the Moon. The spacecraft was originally built as a backup for Chang'e 3 and became available after Chang'e 3 landed successfully in 2013. The configuration of Chang'e 4 was adjusted to meet new scientific and performance objectives. Like its predecessors, the mission is named after Chang'e, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e 2
Chang'e 2 (; ) is a Chinese uncrewed lunar probe that was launched on 1 October 2010. It was a follow-up to the Chang'e 1 lunar probe, which was launched in 2007. Chang'e 2 was part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, and conducted research from a 100-km-high lunar orbit in preparation for the December 2013 soft landing by the Chang'e 3 lander and rover. Chang'e 2 was similar in design to Chang'e 1, although it featured some technical improvements, including a more advanced onboard camera. Like its predecessor, the probe was named after Chang'e, an ancient Chinese moon goddess. After completing its primary objective, the probe left lunar orbit for the Earth–Sun Lagrangian point, to test the Chinese tracking and control network, making the China National Space Administration the third space agency after NASA and ESA to have visited this point. It entered orbit around L2 on 25 August 2011, and began transmitting data from its new position in Septem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert W
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Band
The X band is the designation for a band of frequencies in the microwave radio region of the electromagnetic spectrum. In some cases, such as in communication engineering, the frequency range of the X band is set at approximately 7.0–11.2 GHz. In radar engineering, the frequency range is specified by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as 8.0–12.0 GHz. The X band is used for radar, satellite communication, and wireless computer networks. Radar X band is used in radar applications, including continuous-wave, pulsed, single- polarization, dual-polarization, synthetic aperture radar, and phased arrays. X-band radar frequency sub-bands are used in civil, military, and government institutions for weather monitoring, air traffic control, maritime vessel traffic control, defense tracking, and vehicle speed detection for law enforcement. X band is often used in modern radars. The shorter wavelengths of the X band provide higher-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Planetary Society
The Planetary Society is an American internationally-active non-governmental nonprofit organization. It is involved in research, public outreach, and political space advocacy for engineering projects related to astronomy, planetary science, and space exploration. It was founded in 1980 by Carl Sagan, Bruce Murray, and Louis Friedman, and has about 60,000 members from more than 100 countries around the world. The Society is dedicated to the exploration of the Solar System, the search for near-Earth objects, and the search for extraterrestrial life. The society's mission is stated as: "Empowering the world’s citizens to advance space science and exploration." The Planetary Society is a strong advocate for space funding and missions of exploration within NASA. They lobby Congress and engage their membership in the United States to write and call their representatives in support of NASA funding. In addition to public outreach, The Planetary Society has sponsored solar sai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
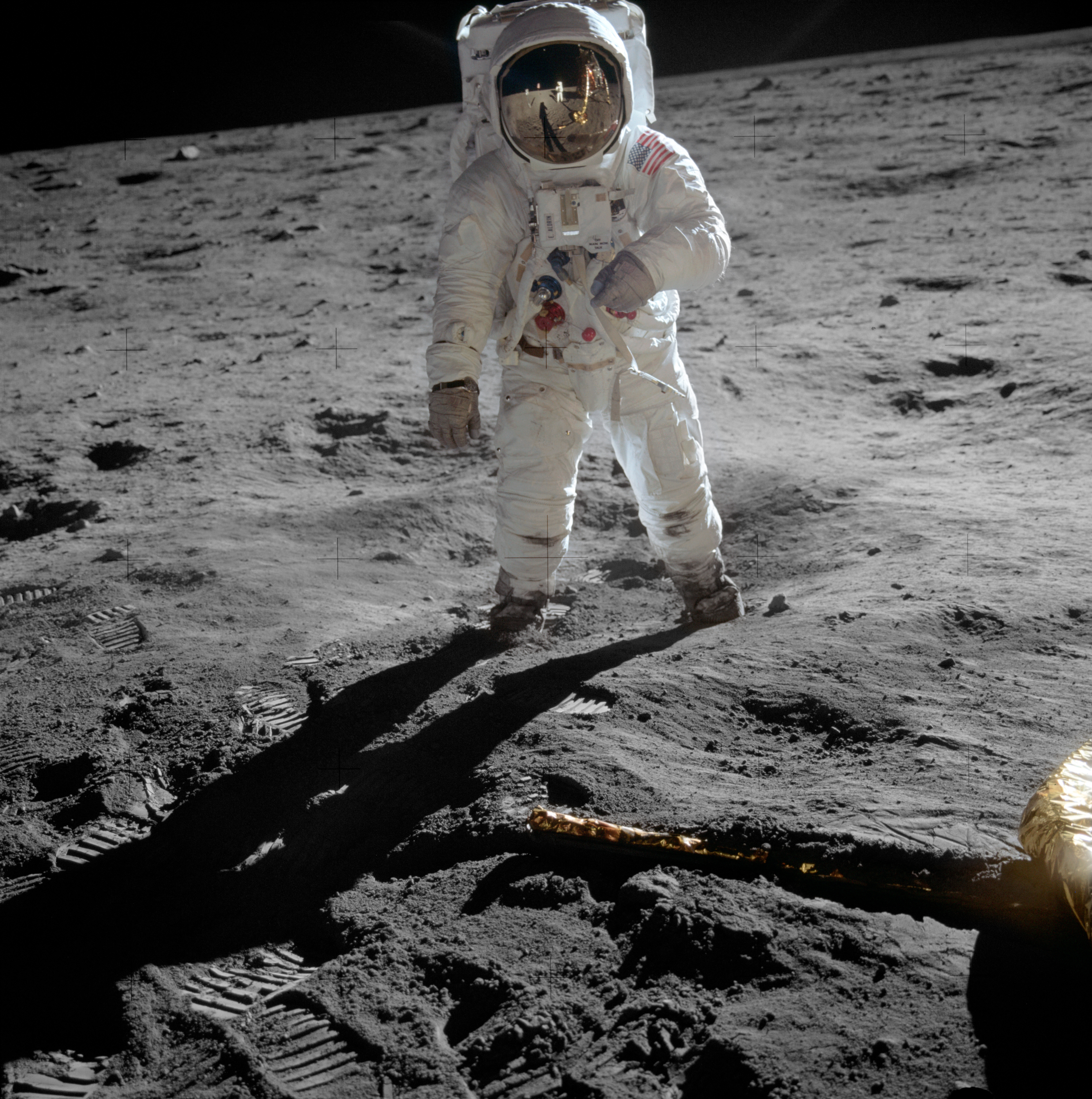
Apollo Program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in space. It was conceived in 1960 as a three-person spacecraft during President Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower, Dwight D. Eisenhower's administration. Apollo was later dedicated to President John F. Kennedy's national goal for the 1960s of "landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth" in an address to United States Congress, Congress on May 25, 1961. It was the third American human spaceflight program to fly, preceded by Project Gemini conceived in 1961 to extend spaceflight capability in support of Apollo. Kennedy's goal was accomplished on the Apollo 11 mission when astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin landed their Apollo Lunar Module (LM) on July 20, 1969, and walked on the lunar surface, while Michael Collins ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Space Exploration
Deep-space exploration is the branch of astronomy, astronautics, and space technology that is involved with exploring the distant regions of outer space. However, little consensus has been reached on the meaning of "distant" regions. In some contexts, it is used to refer to interstellar space. The International Telecommunication Union defines ''deep space'' to start at a distance of (about 0.01 AU) from Earth's surface. NASA's Deep Space Network has variously used criteria of from Earth. Physical exploration of space is conducted both by human spaceflights (deep-space astronautics) and by robotic spacecraft. At present the farthest space probe humankind has constructed and launched from Earth is ''Voyager 1'', which was announced on December 5, 2011, to have reached the outer edge of the Solar System, and entered interstellar space on August 25, 2012. Deep space exploration further than this vessel's capacity is not yet possible due to limitations in the propulsion tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Station-keeping
In astrodynamics, orbital station-keeping is keeping a spacecraft at a fixed distance from another spacecraft or celestial body. It requires a series of orbital maneuvers made with thruster burns to keep the active craft in the same orbit as its target. For many low Earth orbit satellites, the effects of non-Keplerian forces, i.e. the deviations of the gravitational force of the Earth from that of a homogeneous sphere, gravitational forces from Sun/Moon, solar radiation pressure and air drag, must be counteracted. For spacecraft in a halo orbit around a Lagrange point, station-keeping is even more fundamental, as such an orbit is unstable; without an active control with thruster burns, the smallest deviation in position or velocity would result in the spacecraft leaving orbit completely. Perturbations The deviation of Earth's gravity field from that of a homogeneous sphere and gravitational forces from the Sun and Moon will in general perturb the orbital plane. For a Sun-syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |