|
Qingming Festival
The Qingming Festival or Ching Ming Festival, also known as Tomb-Sweeping Day in English (sometimes also called Chinese Memorial Day, Ancestors' Day, the Clear Brightness Festival, or the Pure Brightness Festival), is a traditional Chinese festival observed by ethnic Chinese in mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Malaysia, Singapore, Cambodia, Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam. A celebration of spring, it falls on the first day of the fifth solar term (also called Qingming) of the traditional Chinese lunisolar calendar. This makes it the 15th day after the Spring Equinox, either 4, 5 or 6 April in a given year. During Qingming, Chinese families visit the tombs of their ancestors to clean the gravesites and make ritual offerings to their ancestors. Offerings would typically include traditional food dishes and the burning of joss sticks and joss paper. The holiday recognizes the traditional reverence of one's ancestors in Chinese culture. The origins o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese People
The Chinese people, or simply Chinese, are people or ethnic groups identified with Greater China, China, usually through ethnicity, nationality, citizenship, or other affiliation. Chinese people are known as Zhongguoren () or as Huaren () by speakers of standard Chinese, including those living in Greater China as well as overseas Chinese. Although both terms both refer to Chinese people, their usage depends on the person and context. The former term is commonly (but not exclusively) used to refer to the citizens of the People's Republic of China—especially mainland China. The term Huaren is used to refer to ethnic Chinese, and is more often used for those who reside overseas or are non-citizens of China. The Han Chinese are the largest ethnic group in China, comprising approximately 92% of its Mainland China, Mainland population. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
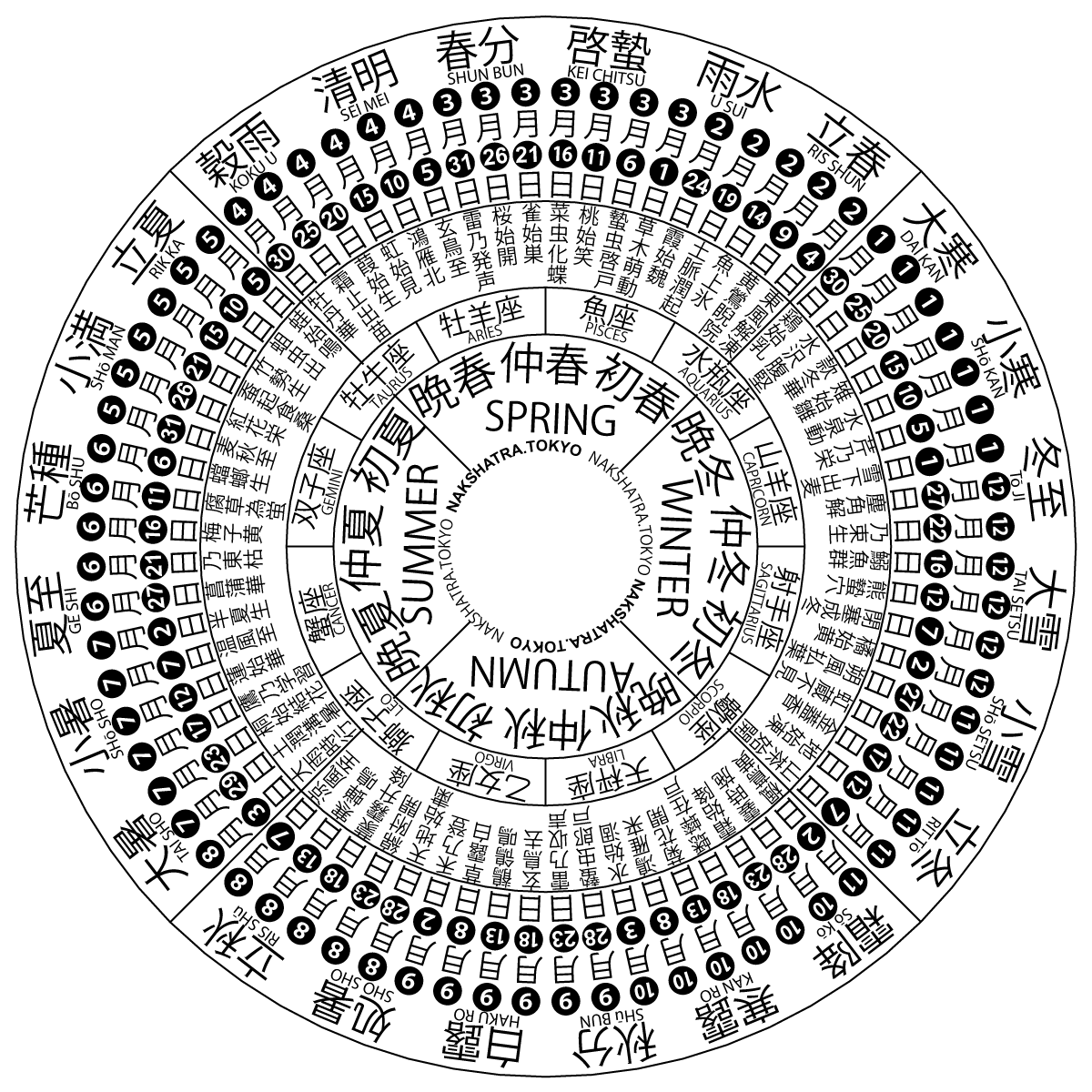
Solar Term
A solar term (or ''jiéqì'', zh, t=節氣, s=节气) is any of twenty-four periods in traditional Chinese lunisolar calendars that matches a particular astronomical event or signifies some natural phenomenon. The points are spaced 15° apart along the ecliptic and are used by lunisolar calendars to stay synchronized with the seasons, which is crucial for agrarian societies. The solar terms are also used to calculate intercalary months; which month is repeated depends on the position of the sun at the time. According to the '' Book of Documents'', the first determined term was Dongzhi (Winter Solstice) by Dan, the Duke of Zhou, while he was trying to locate the geological center of the Western Zhou dynasty, by measuring the length of the sun's shadow on an ancient type of sundial called (). Then four terms of seasons were set, which were soon evolved as eight terms; not until the Taichu Calendar of 104 BC were all twenty-four solar terms officially included in the Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Holidays In Taiwan
The following are considered holidays in Taiwan. Some are official holidays, and some are not. History In 2016, the Tsai Ing-wen government removed seven public holidays. The holidays were removed due to a political compromise arising from a campaign promise Tsai made while running for president that committed her government to providing two days off per week for all workers. When implementing the change, the government faced opposition from various interests including businesses, and a compromise was reached to provide two days off per week and remove seven paid public holidays. The removed public holidays were: * January 2, the day after New Year's Day * March 29, Youth Day (commemorating the Huanghuagang Uprising) * September 28, Confucius' Birthday * October 25, Retrocession Day (commemorating the end of Taiwan under Japanese rule, Japanese rule of Taiwan and Penghu and the return of Taiwan to the Taiwan, Republic of China) * October 31, Chiang Kai-shek, Chiang Kai-she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikelets and making it much easier to harvest. Its use then spread throughout Eurasia by 2000 BC. Barley prefers relatively low temperatures and well-drained soil to grow. It is relatively tolerant of drought and soil salinity, but is less winter-hardy than wheat or rye. In 2023, barley was fourth among grains in quantity produced, 146 million tonnes, behind maize, rice, and wheat. Globally, 70% of barley production is used as animal feed, while 30% is used as a source of fermentable material for beer, or further distilled into whisky, and as a component of various foods. It is used in soups and stews and in barley bread of various cultures. Barley grains are commonly made into malt using a traditional and ancient method of preparatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Mugwort
Chinese mugwort is a common name for several plants and may refer to: *'' Artemisia argyi'' *'' Artemisia verlotiorum'' {{Plant common name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutinous Rice
Domestication syndrome refers to two sets of phenotypic traits that are common to either domesticated plants or domesticated animals. Domesticated animals tend to be smaller and less aggressive than their wild counterparts; they may also have floppy ears, variations to coat color, a smaller brain, and a shorter muzzle. Other traits may include changes in the endocrine system and an extended breeding cycle. These animal traits have been claimed to emerge across the different species in response to selection for tameness, which was purportedly demonstrated in a famous Russian fox breeding experiment, though this claim has been disputed. Other research suggested that pleiotropic change in neural crest cell regulating genes was the common cause of shared traits seen in many domesticated animal species. However, several recent publications have either questioned this neural crest cell explanation or cast doubt on the existence of domestication syndrome itself. One recent publica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qingtuan
''Qīngtuán'' (), also written as ''Tsingtuan'', is a green-colored dumpling originating from Jiangnan and common throughout China. It is made of glutinous rice mixed with Chinese mugwort or barley grass. It is usually filled with sweet red or black bean paste. The exact technique for making ''qingtuan'' is quite complicated and the grass involved is only edible in the early spring, so it is typically only available around the time of the Qingming Festival , with which the rice cake has become associated. Nowadays, ''qingtuan'' sold in most convenience stores in China are made of glutinous rice mixed with matcha. Modern versions use a wider variety of fillings, such as rousong or salted egg yolk. Much of the ''qingtuan'' consumed in China is prepared and consumed as street food from local vendors. Origin The tradition of eating ''qingtuan'' at Qingming Festival evolved from the ancient Chinese Cold Food Day (one or two days before Qingming Festival). As the name suggest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Holidays In China
There are currently seven official public holidays in China. Each year's holidays are announced about one month before the start of the year by the General Office of the State Council. A notable feature of mainland Chinese holidays is that weekends are usually swapped with the weekdays next to the actual holiday to create a longer holiday period. History Festivals in China have been around since the Qin dynasty around 221–206 BC. During the more prosperous Tang dynasty from AD 618–907, festivals involved less sacrifice and mystery to more entertainment. Culminating to the modern era Between the 1920s until around the 1970s, the Chinese began observing two sets of holidays, which were the traditional and what became "official", celebrating the accomplishments of the communist regime. There was then a major reform in 2008, abolishing the Labour Day Golden Week and adding three traditional Chinese holidays (Qingming Festival, Duanwu Festival, and Mid-Autumn Festival). From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filial Piety
Filial piety is the virtue of exhibiting love and respect for one's parents, elders, and ancestors, particularly within the context of Confucian ethics, Confucian, Chinese Buddhism, Chinese Buddhist ethics, Buddhist, and Daoism, Daoist ethics. The Confucian ''Classic of Filial Piety'', thought to be written around the late Warring States-Qin dynasty, Qin-Han dynasty, Han period, has historically been the authoritative source on the Confucian tenet of filial piety. The book—a purported dialogue between Confucius and his student Zengzi—is about how to set up a good society using the principle of filial piety. Filial piety is central to Confucian role ethics. In more general terms, filial piety means to be good to one's parents; to take care of one's parents; to engage in good conduct, not just towards parents but also outside the home so as to bring a good name to one's parents and ancestors; to show love, respect, and support; to display courtesy; to ensure male heirs; to uph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Beijinger
''The Beijinger'' (, stylized as "the Beijinger" or "thebeijinger") is a free monthly English language listings and entertainment website and magazine produced by True Run Media in Beijing, China. It was founded in October 2001, as ''that's Beijing''. In June 2008, True Run Media was required to rename ''that's Beijing'' to ''The Beijinger'' because of trademark issues. A newly created and unrelated '' that's Beijing'' magazine was launched under the ownership of China Electric Media, and China International Press. The magazine has a weekly newsletter discussing the city's events and lists places' addresses in both Chinese characters and pinyin. It has classified advertising and personal advertisement sections that allow users to find housing, employment, and relationships as well as buy and sell goods. History ''The Beijinger'' is a free listings and lifestyle magazine published at the beginning of each month by expatriates and available in numerous restaurants bars, hotels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
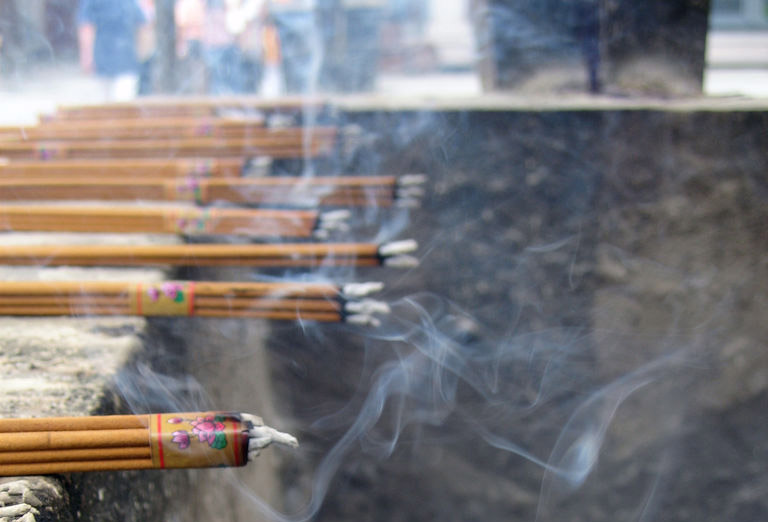
Incense
Incense is an aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremonial reasons. It may also be used as a simple deodorant or insect repellent. Incense is composed of aromatic plant materials, often combined with essential oils. The forms taken by incense differ with the underlying culture, and have changed with advances in technology and increasing number of uses. Incense can generally be separated into two main types: "indirect-burning" and "direct-burning." Indirect-burning incense (or "non-combustible incense") is not capable of burning on its own, and requires a separate heat source. Direct-burning incense (or "combustible incense") is lit directly by a flame and then fanned or blown out, leaving a glowing ember that smoulders and releases a smoky fragrance. Direct-burning incense is either a paste formed around a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |