|
Prophase
Prophase () is the first stage of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis. Beginning after interphase, DNA has already been replicated when the cell enters prophase. The main occurrences in prophase are the condensation of the chromatin reticulum and the disappearance of the nucleolus. Staining and microscopy Microscopy can be used to visualize condensed chromosomes as they move through meiosis and mitosis. Various DNA stains are used to treat cells such that condensing chromosomes can be visualized as the move through prophase. The giemsa G-banding technique is commonly used to identify mammalian chromosomes, but utilizing the technology on plant cells was originally difficult due to the high degree of chromosome compaction in plant cells. G-banding was fully realized for plant chromosomes in 1990. During both meiotic and mitotic prophase, giemsa staining can be applied to cells to elicit G-banding in chromosomes. Silver staining, a more modern technology, in conjunction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prophase Eukaryotic Mitosis
Prophase () is the first stage of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis. Beginning after interphase, DNA has already been replicated when the cell enters prophase. The main occurrences in prophase are the condensation of the chromatin reticulum and the disappearance of the nucleolus. Staining and microscopy Microscopy can be used to visualize condensed chromosomes as they move through meiosis and mitosis. Various DNA stains are used to treat cells such that condensing chromosomes can be visualized as the move through prophase. The giemsa G-banding technique is commonly used to identify mammalian chromosomes, but utilizing the technology on plant cells was originally difficult due to the high degree of chromosome compaction in plant cells. G-banding was fully realized for plant chromosomes in 1990. During both meiotic and mitotic prophase, giemsa staining can be applied to cells to elicit G-banding in chromosomes. Silver staining, a more modern technology, in conjun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome ( haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and female will fuse to create a cell with two copies of each chromosome again, the zygote. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome ( haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and female will fuse to create a cell with two copies of each chromosome again, the zygote. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), prophase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), prophase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interphase
Interphase is the portion of the cell cycle that is not accompanied by visible changes under the microscope, and includes the G1, S and G2 phases. During interphase, the cell grows (G1), replicates its DNA (S) and prepares for mitosis (G2). A cell in interphase is not simply quiescent. The term quiescent (i.e. dormant) would be misleading since a cell in interphase is very busy synthesizing proteins, copying DNA into RNA, engulfing extracellular material, processing signals, to name just a few activities. The cell is quiescent only in the sense of cell division (i.e. the cell is out of the cell cycle, G0). Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which a typical cell spends most of its life. Interphase is the 'daily living' or metabolic phase of the cell, in which the cell obtains nutrients and metabolizes them, grows, replicates its DNA in preparation for mitosis, and conducts other "normal" cell functions. Interphase was formerly called the resting phase. However, interp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. The centrosome provides structure for the cell. The centrosome is thought to have evolved only in the metazoan lineage of eukaryotic cells. Fungi and plants lack centrosomes and therefore use other structures to organize their microtubules. Although the centrosome has a key role in efficient mitosis in animal cells, it is not essential in certain fly and flatworm species. Centrosomes are composed of two centrioles arranged at right angles to each other, and surrounded by a dense, highly structured mass of protein termed the pericentriolar material (PCM). The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring — including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. In general, each centriole of the centrosome is based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to the centromere via the kinetochore. The physical role of the centromere is to act as the site of assembly of the kinetochores – a highly complex multiprotein structure that is responsible for the actual events of chromosome segregation – i.e. binding microtubules and signaling to the cell cycle machinery when all chromosomes have adopted correct attachments to the spindle, so that it is safe for cell division to proceed to completion and for cells to enter anaphase. There are, broadly speaking, two types of centromeres. "Point centromeres" bind to specific proteins that recognize particular DNA sequences with high efficiency. Any piece of DNA with the point centromere DNA sequence on it will typically form a centromere if pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
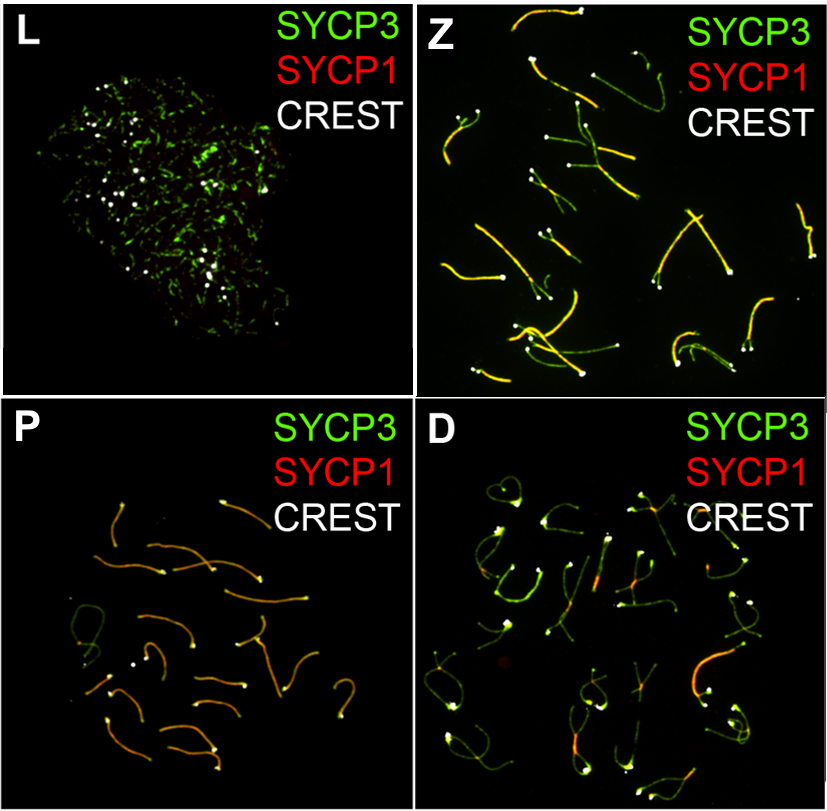
Synaptonemal Complex
The synaptonemal complex (SC) is a protein structure that forms between homologous chromosomes (two pairs of sister chromatids) during meiosis and is thought to mediate synapsis and recombination during meiosis I in eukaryotes. It is currently thought that the SC functions primarily as a scaffold to allow interacting chromatids to complete their crossover activities. Composition The synaptonemal complex is a tripartite structure consisting of two parallel lateral regions and a central element. This "tripartite structure" is seen during the pachytene stage of the first meiotic prophase, both in males and in females during gametogenesis. Previous to the pachytene stage, during leptonema, the lateral elements begin to form and they initiate and complete their pairing during the zygotene stage. After pachynema ends, the SC usually becomes disassembled and can no longer be identified. In humans, three specific components of the synaptonemal complex have been characterized: SC pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Banding
G-banding, G banding or Giemsa banding is a technique used in cytogenetics to produce a visible karyotype by staining condensed chromosomes. It is the most common chromosome banding method. It is useful for identifying genetic diseases through the photographic representation of the entire chromosome complement.Speicher, Michael R. and Nigel P. Carter. "The New Cytogenetics: Blurring the Boundaries with Molecular Biology." ''Nature'' Reviews Genetics, Vol 6. Oct 2005. The metaphase chromosomes are treated with trypsin (to partially digest the chromosome) and stained with Giemsa stain. Heterochromatic regions, which tend to be rich with adenine and thymine (AT-rich) DNA and relatively gene-poor, stain more darkly in G-banding. In contrast, less condensed chromatin (Euchromatin)—which tends to be rich with guanine and cytosine ( GC-rich) and more transcriptionally active—incorporates less Giemsa stain, and these regions appear as light bands in G-banding. The pattern of bands are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spindle Apparatus
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus refers to the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis, a process that produces genetically identical daughter cells, or the meiotic spindle during meiosis, a process that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Besides chromosomes, the spindle apparatus is composed of hundreds of proteins. Microtubules comprise the most abundant components of the machinery. Spindle structure Attachment of microtubules to chromosomes is mediated by kinetochores, which actively monitor spindle formation and prevent premature anaphase onset. Microtubule polymerization and depolymerization dynamic drive chromosome congression. Depolymerization of microtubules generates tension at kinetochores; bipolar attachment of sister kinetochores to microtubules emanating from opposite cell pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |