|
Proconsul Nyanzae
''Ekembo nyanzae'', originally classed as a species of ''Proconsul'', is a species of fossil primate first discovered by Louis Leakey on Rusinga Island in 1942, which he published in ''Nature'' in 1943. It is also known by the name ''Dryopithecus africanus''. A joint publication of Wilfrid Le Gros Clark and Louis Leakey in 1951, "The Miocene Hominoidea of East Africa", first defines ''Proconsul nyanzae''. In 1965 Simons and Pilbeam replaced ''Proconsul'' with ''Dryopithecus'', using the same species names. In 1967, Louis defined '' Kenyapithecus africanus'' on seven fossils from Rusinga Island. He saw it as an ancestor of ''wickeri'' and also of man, with a date of 20 mya in the middle Miocene. Another fossil found by the VanCouverings on Rusinga in 1967 seemed to confirm ''africanus''. In 1969 Simons and Pilbeam moved ''Kenyapithecus africanus'' into ''Dryopithecus nyanzae''. By 1978 the genus had recovered from the Dryopithecine event and was back to ''Proconsul''. In that y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have '' heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as '' diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed ''polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are set in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Apes
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samburupithecus
''Samburupithecus'' is an extinct primate that lived in Kenya during the middle to late Miocene. The one species in this genus, ''Samburupithecus kiptalami'', is known only from a maxilla fragment dated to discovered in 1982 and formally described by . The type specimen KNM-SH 8531 was discovered by the Joint Japan-Kenya Expedition at the SH22 fossil site in the Samburu District, a locality where several other researchers found no ape fossils. ''Samburupithecus'' lived during the so-called "African ape gap" , a period from which very few hominoid fossils have been found in Africa until relatively recently. This apparent gap, however, is now populated by a diversity of apes such as ''Nakalipithecus'', '' Chororapithecus abyssinicus'', '' Otavipithecus'', and '' Nacholapithecus''. Characteristics ''Samburupithecus'' was approximately and was most likely a frugivorous terrestrial quadruped. Paleoenvironmental reconstructions indicate that ''Samburupithecus'' most likely li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierolapithecus
''Pierolapithecus catalaunicus'' is an extinct species of primate which lived about 13 million years ago during the Miocene in what is now Hostalets de Pierola, Catalonia, Spain, giving it its scientific name. It is believed by some to be a common ancestor of both modern humans and the other great apes, or at least a species that is closer to a common ancestor than any previous fossil discovery. The species was described by a team of Spanish paleoanthropologists led by Salvador Moyà-Solà on the basis of a fossil specimen discovered in December 2002. The finding was first reported in the journal Science on November 19, 2004. As do humans and other great apes, ''Pierolapithecus'' had specialized adaptations for tree climbing: a wide, flat ribcage, a stiff lower spine, flexible wrists, and shoulder blades that lay along its back. It also has plesiomorphic monkey-like features such as a sloped face and short fingers and toes. (gibbons and Old World monkeys show more generali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakalipithecus
''Nakalipithecus nakayamai'' is an extinct species of great ape from Nakali, Kenya, from about 9.9–9.8 million years ago during the Late Miocene. It is known from a right jawbone with 3 molars and from 11 isolated teeth, and the specimen is presumed female as the teeth are similar in size to those of female gorillas and orangutans. Compared to other great apes, the canines are short, the enamel is thin, and the molars are flatter. ''Nakalipithecus'' seems to have inhabited a sclerophyllous woodland environment. Taxonomy ''Nakalipithecus'' was first described from a right jawbone, the holotype KNM-NA46400, and eleven isolated teeth excavated in 2005 by a team of Japanese and Kenyan researchers in mud flow deposits in the Nakali area of northern Kenya's former Rift Valley Province, hence the genus name ''Nakalipithecus'' ("Nakali ape"). The species name is in honour of the late Japanese geologist Katsuhiro Nakayama who worked on the expedition. The specimen dates to about 9.9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryopithecus
''Dryopithecus'' is a genus of extinct great apes from the middle– late Miocene boundary of Europe 12.5 to 11.1 million years ago (mya). Since its discovery in 1856, the genus has been subject to taxonomic turmoil, with numerous new species being described from single remains based on minute differences amongst each other, and the fragmentary nature of the holotype specimen makes differentiating remains difficult. There is currently only one uncontested species, the type species ''D. fontani'', though there may be more. The genus is placed into the tribe Dryopithecini, which is either an offshoot of orangutans, African apes, or is its own separate branch. A male specimen was estimated to have weighed in life. ''Dryopithecus'' likely predominantly ate ripe fruit from trees, suggesting a degree of suspensory behaviour to reach them, though the anatomy of a humerus and femur suggest a greater reliance on walking on all fours (quadrupedalism). The face was similar to gorilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chororapithecus
''Chororapithecus'' is an extinct great ape from the Afar region of Ethiopia roughly 8 million years ago during the Late Miocene, comprising one species, ''C. abyssinicus''. It is known from 9 isolated teeth discovered in a 2005–2007 survey of the Chorora Formation. The teeth are indistinguishable from those of gorillas in terms of absolute size and relative proportions, and it has been proposed to be an early member of Gorillini. However, this is controversial given the paucity of remains, and notable anatomical differences between ''Chororapithecus'' and gorilla teeth. The Kenyan ape ''Nakalipithecus'' has been proposed to be an ancestor of ''Chororapithecus'' or at least closely related. If correct, they would be the only identified fossil members of any modern non-human great ape lineage, and would push the gorilla–human last common ancestor from 8 million years ago (identified by molecular analysis) to 10 million years ago. The teeth are adapted for processing tough plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and microbes. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal Environmental factor, factors. External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem but are not themselves influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see differences between British, American, and Australian English explained below). Woodlands may support an understory of shrubs and herbaceous plants including grasses. Woodland may form a transition to shrubland under drier conditions or during early stages of primary or secondary succession. Higher-density areas of trees with a largely closed canopy that provides extensive and nearly continuous shade are often referred to as forests. Extensive efforts by conservationist groups have been made to preserve woodlands from urbanization and agriculture. For example, the woodlands of Northwest Indiana have been preserved as part of the Indiana Dunes. Definitions United Kingdom ''Woodland'' is used in British woodland management to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Afric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
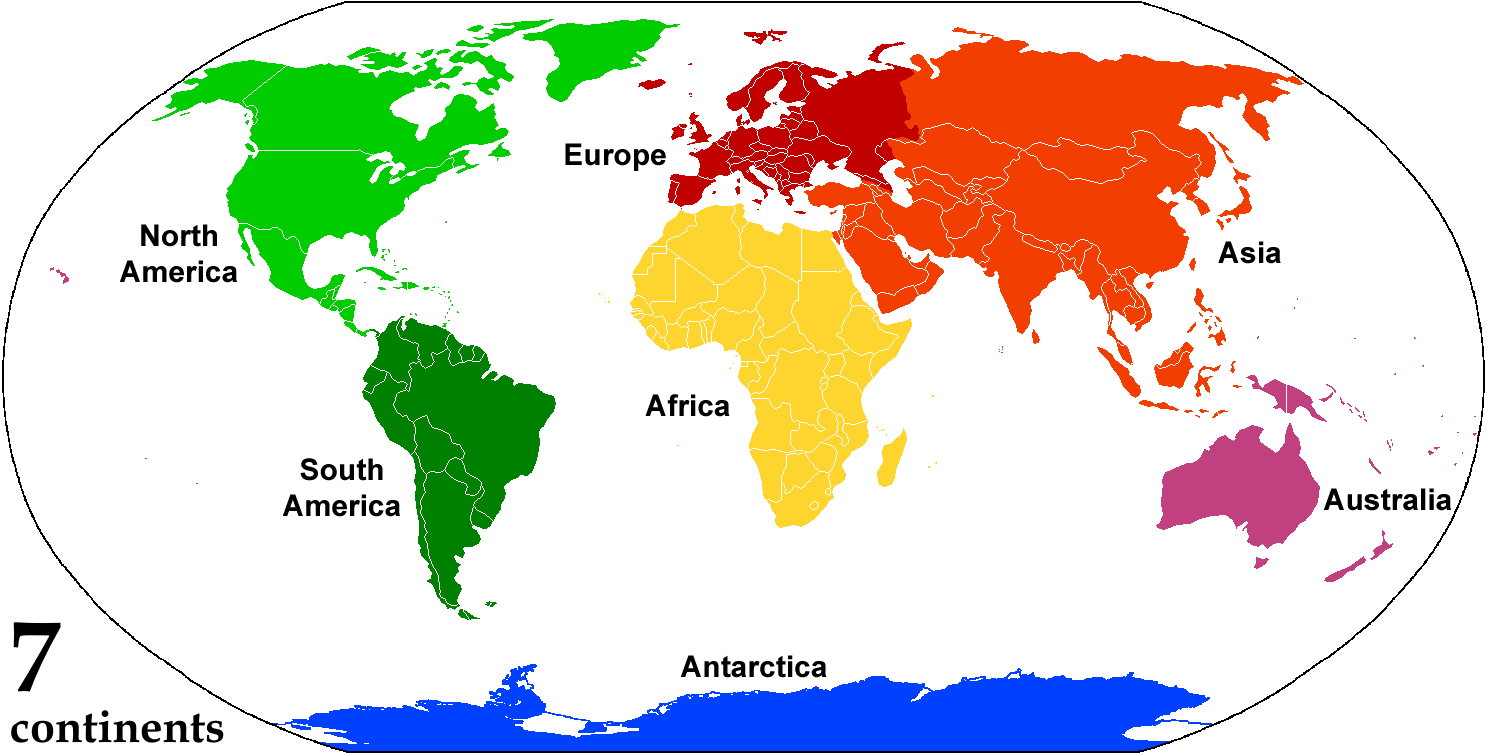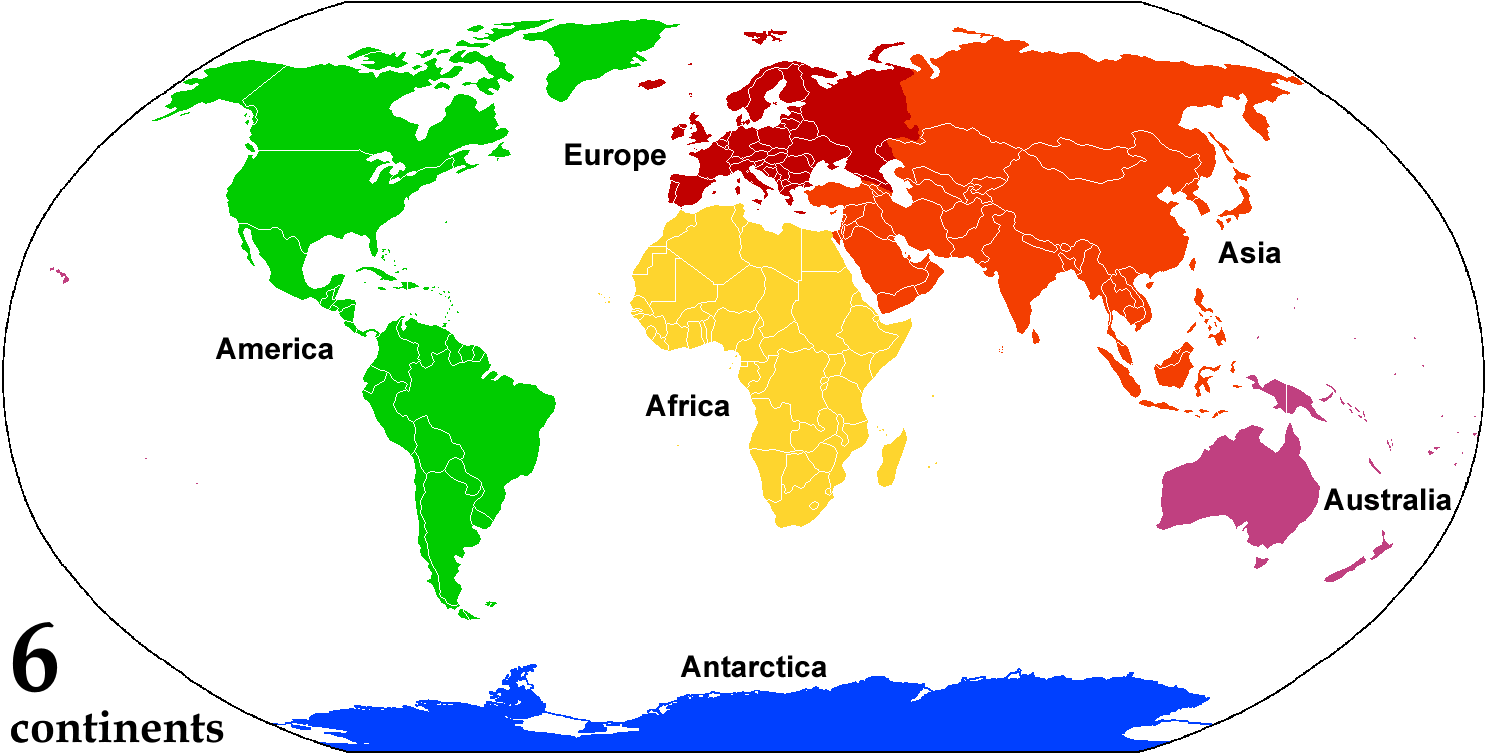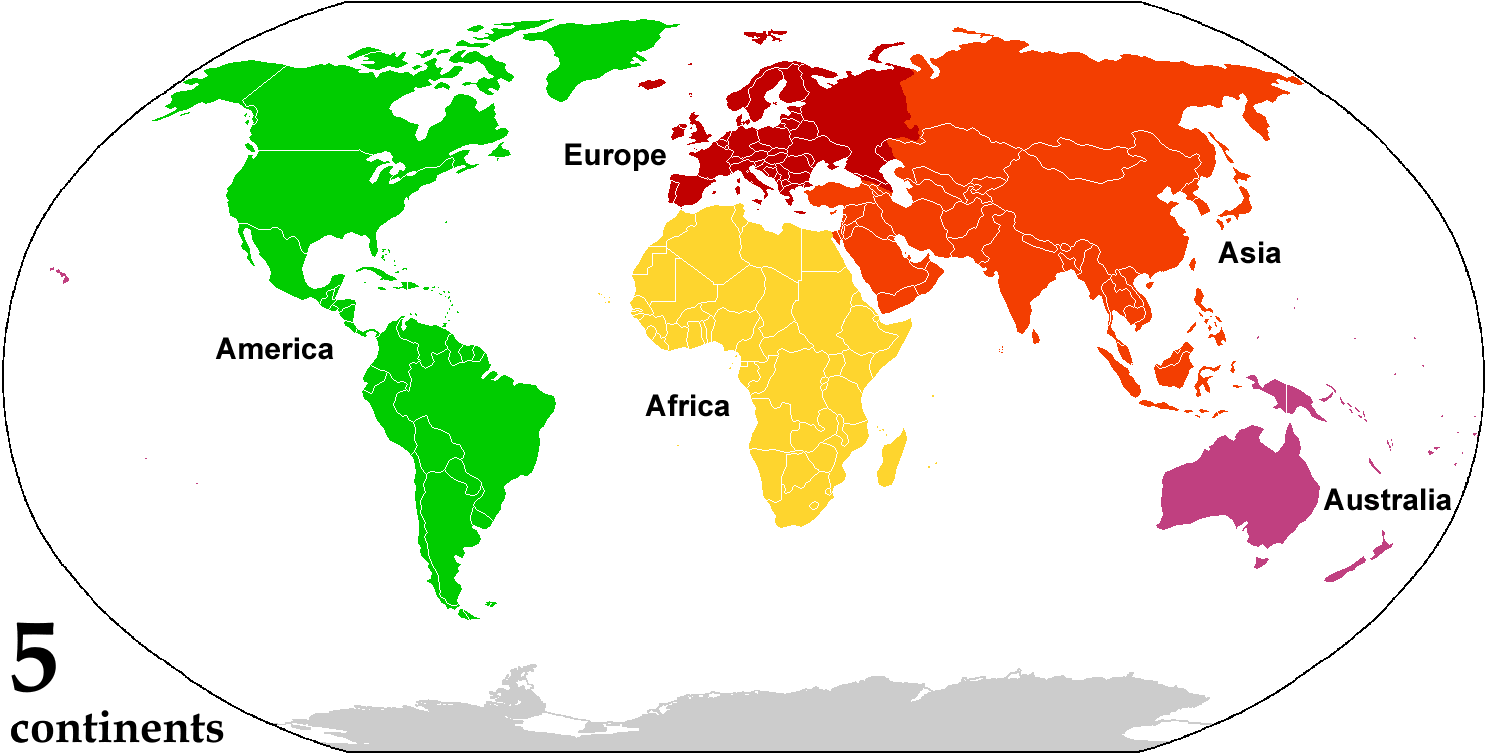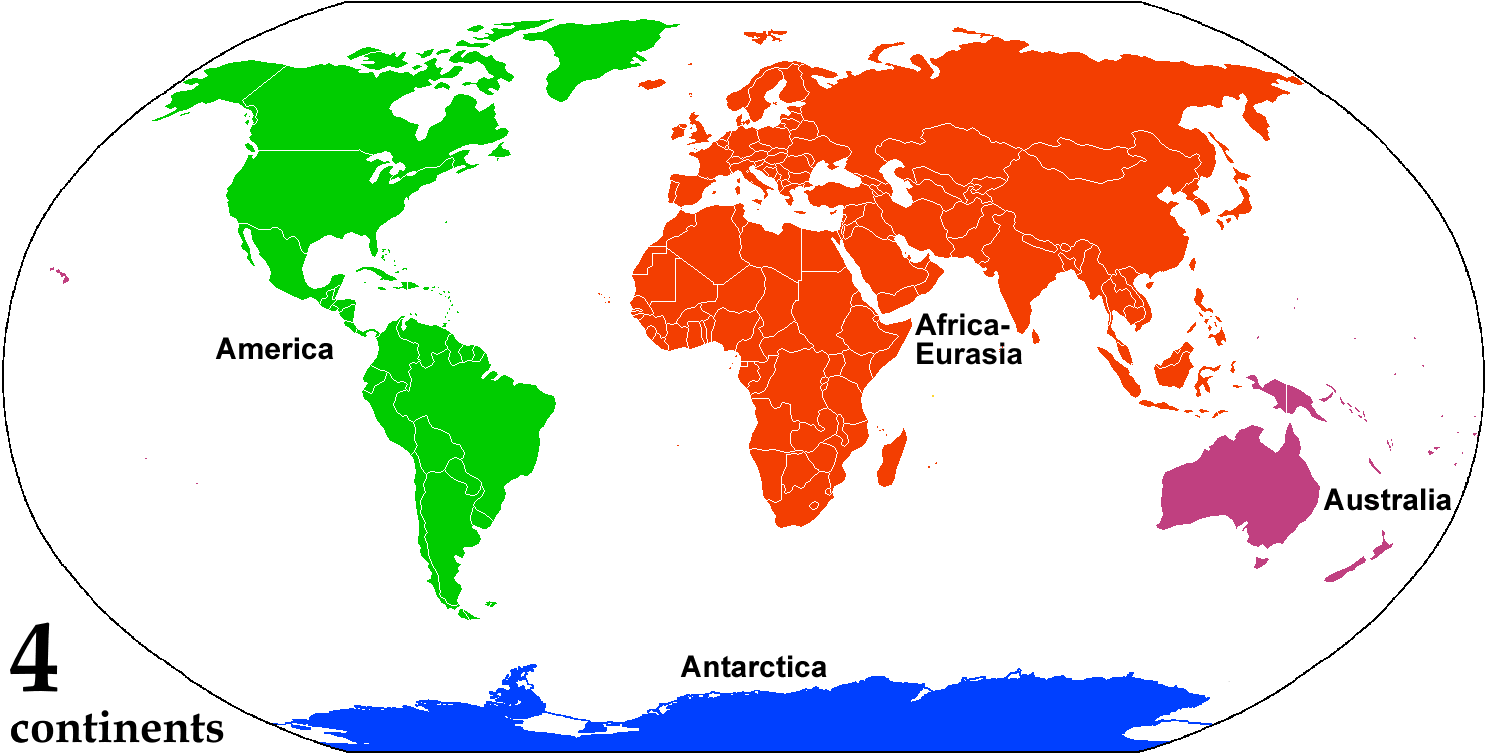
Continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ... are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven regions are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia (continent), Australia. "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia, from largest to smallest—although sometimes Asia and Europe are considered a single continent, Eurasia." Variations with fewer continents may merge some of these, for example Americas, America, Eurasia, or Afro-Eurasia are sometimes treated as single contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |