|
Priarius
Priarius ( - 378) was a king of the Lentienses, a sub-tribe of the Alemanni, in the 4th century. He is mentioned by Ammianus Marcellinus. In 378, Priarius fought the Western Roman Empire at Battle of Argentovaria, near Neuf-Brisach, France, in which he was defeated and killed. References Further reading * Dieter Geuenich: ''Geschichte der Alemannen''. Kohlhammer Verlag W. Kohlhammer Verlag GmbH, or Kohlhammer Verlag, is a German publishing house headquartered in Stuttgart. History Kohlhammer Verlag was founded in Stuttgart on 30 April 1866 by . Kohlhammer had taken over the businesses of his late father-in-law ..., Stuttgart 2005, 2. revised edition., , pp. 31, 63, 162, 171 (German) * Dieter Geuenich: ''Lentienses''. In: ''Reallexikon der Germanischen Altertumskunde (RGA)''. 2. edition, volume 18, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin / New York 2001, , pp. 266–267 (German) * Moritz Schönfeld: Lentienses. In: Paulys Realencyclopädie der classischen Altertumswissenschaft (RE). Band XI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Argentovaria
The Battle of Argentovaria or Battle of Argentaria was fought in May 378 between the Western Roman Empire and the invading army of the Lentienses, a branch of the Alemanni, at Argentovaria (near Colmar, France). The Alemanni were overwhelmed by the Roman legionaries, though stood their ground bravely. Only 9,000 escaped from the field and Priarius, king of the Lentienses, was slain during the battle. The Lentienses disappear from the historical record following this defeat. Emperor Gratian, who had given the command of the army for the battle to Nannienus and Mallobaudes, gained the title of ''Alemannicus Maximus''. References * Ammianus Marcellinus Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally Anglicisation, anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Ancient history, antiquity (preceding Procopius). His w ... XV 4 and XXXI 10 378 Argentovaria Argentovaria Argentovaria Argentovari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lentienses
The Lentienses (German ''Lentienser'') were a 4th-century Germanic tribe associated with the Alemanni, in the region between the river Danube in the North, the river Iller in the East, and Lake Constance in the South, in what is now southern Germany. They were reported to be one of the most rebellious tribes at the time. There are only two mentions of the Lentienses, both by the Roman historian Ammianus Marcellinus (330–395). First, they appeared in 355 when the Roman commander Arbetio was ordered by Emperor Constantius II to fine the Lentienses for several incursions the Roman Empire. Secondly, they were mentioned when they crossed the frozen Rhine in February 378, invading the Roman Empire. They were defeated by the Roman emperor Gratianus in the Battle of Argentovaria (modern Colmar in Alsace), when their king, Priarius, died. This battle was the last campaign by any Roman Emperor behind the Limes area. It was also the last time the name Lentienses was mentioned in hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes * * * on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace, and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German language in those regions, by the eighth century named '' Alamannia''. In 496, the Alemanni were conquered by Frankish leader Clovis and incorporated into his dominions. Mentioned as still pagan allies of the Christian Franks, the Alemanni were gradually Christianized during the seventh century. The is a record of their customary law during this period. Until the eighth century, Frankish suzerainty over Alemannia was mostly nominal. After an uprising by Theudebald, Duke of Alamannia, though, Carloman executed the Alamannic nobility and installed Frankish dukes. During the later and weaker years of the Carolingian Empire, the Alemannic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally Anglicisation, anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Ancient history, antiquity (preceding Procopius). His work, known as the ''Res Gestae'', chronicled in Latin the history of Rome from the accession of the Emperor Nerva in 96 to the death of Valens at the Battle of Adrianople in 378, although only the sections covering the period 353 to 378 survive. Biography Ammianus was born in the East Mediterranean, possibly in Syria Palaestina, Syria or Phoenice (Roman province), Phoenicia, around 330. His native language is unknown but he likely knew Greek as well as Latin. The surviving books of his history cover the years 353 to 378. Ammianus served as an officer in the army of the emperors Constantius II and Julian (emperor), Julian. He served in Gaul (Julian) and in the east (twice for Constantius, once under Julian). He professes to have been "a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period from 395 to 476, where there were separate coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire in the Western and the Eastern provinces, with a distinct imperial succession in the separate courts. The terms Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire were coined in modern times to describe political entities that were ''de facto'' independent; contemporary Romans did not consider the Empire to have been split into two empires but viewed it as a single polity governed by two imperial courts as an administrative expediency. The Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476, and the Western imperial court in Ravenna was formally dissolved by Justinian in 554. The Eastern imperial court survived until 1453. Though the Empire had seen periods with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
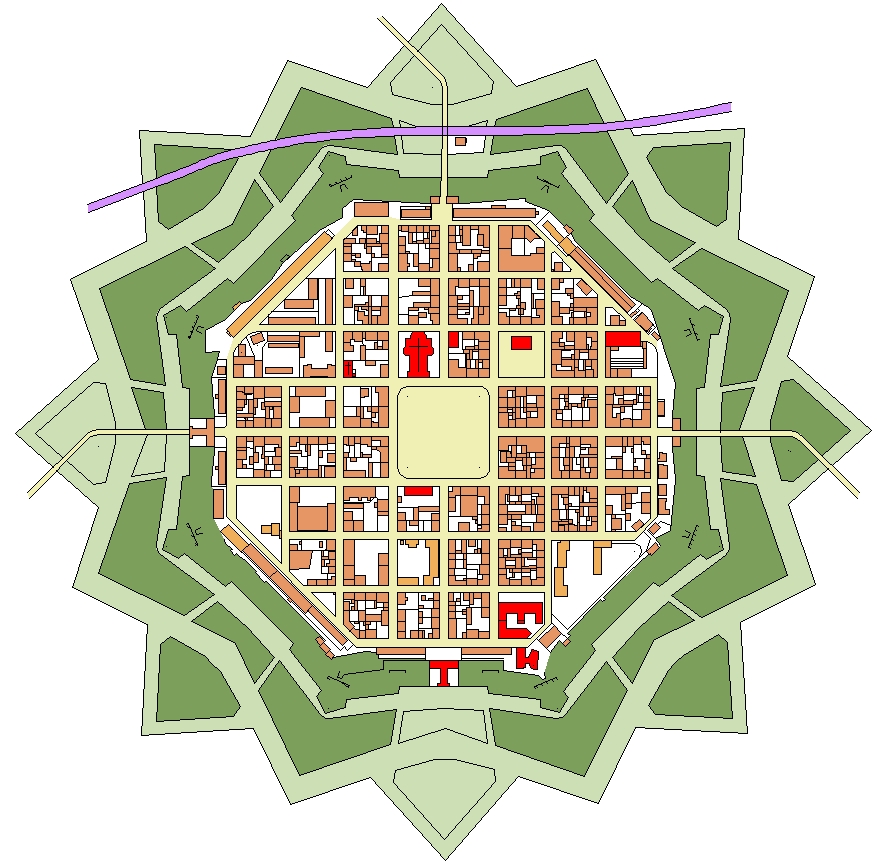
Neuf-Brisach
Neuf-Brisach ( or ; ; gsw-FR, Nei-Brisach) is a fortified town and commune of the department of Haut-Rhin in the French region of Alsace. The fortified town was intended to guard the border between France and the Holy Roman Empire and, subsequently, the German states. It was built after the Treaty of Ryswick in 1697 that resulted in France losing the town of Breisach, on the opposite bank of the Rhine. The town's name means ''New Breisach''. Today the town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of quintessential military fortifications and its testimony to the influence of Vauban on military architecture during the 17-19th centuries. History Work began on the fortified town in 1698, to plans drawn by Vauban, a military engineer at the service of Louis XIV. Vauban died in 1707 and this, his last work, was completed by Louis de Cormontaigne. The city's layout was that of an 'ideal city', as was popular at the time, with a regular square grid street pattern inside an octagonal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohlhammer Verlag
W. Kohlhammer Verlag GmbH, or Kohlhammer Verlag, is a German publishing house headquartered in Stuttgart. History Kohlhammer Verlag was founded in Stuttgart on 30 April 1866 by . Kohlhammer had taken over the businesses of his late father-in-law, a 120-year-old printer and a profitable . The printing business, operating out of the back of a commercial building at 14 Urbanstrasse, became W. Kohlhammer Verlag and was funded by proceeds from the bathhouse until it was closed in 1890. Kohlhammer purchased the ''Deutsche Feuerwehrzeitung'' in 1882 and printed that publication until 1923. In 1872 Kohlhammer started a weekly newspaper, the ''Neue Deutsche Familienblatt'' that by 1914 had a circulation of 185,000. Contemporary Employees of Kohlhammer joined those of other Stuttgart-based companies in early 2016 to petition the mayor to abate traffic congestion hindering their operations inside the city. In 2017, Kohlhammer Verlag employed about 400 people in Stuttgart, Würzburg and Aug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
378 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 378 ( CCCLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Valens and Augustus (or, less frequently, year 1131 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 378 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Spring – Emperor Valens returns to Constantinople and mobilises an army (40,000 men). He appoints Sebastianus, newly arrived from Italy, as ''magister militum'' to reorganize the Roman armies in Thrace. * February – The Lentienses (part of the Alemanni) cross the frozen Rhine and raid the countryside. They are driven back by Roman ''auxilia palatina'' (Celtae and Petulantes), who defend the western frontier. * May – Battle of Argentovaria: Emperor Gratian is forced to recall the army he has se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century Germanic People
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 ( CCCI) through 400 ( CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fell int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemannic Rulers
Alemannic (''Alamannic'') or Alamanni may refer to: * Alemannic German, a dialect family in the Upper German branch of the German languages and its speakers * Alemanni, a confederation of Suebian Germanic tribes in the Roman period * Alamanni (surname) See also *Alemannia (other) *Alemannic separatism Alemannic Separatism is a historical movement of separatism of the Alemannic-German-speaking areas of Austria, France, and Germany (viz., South Baden, Swabia (viz. most of Württemberg and Bavarian Swabia), Alsace and Vorarlberg), aiming ... * Allemand (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemannic Warriors
Alemannic (''Alamannic'') or Alamanni may refer to: * Alemannic German, a dialect family in the Upper German branch of the German languages and its speakers * Alemanni, a confederation of Suebian Germanic tribes in the Roman period * Alamanni (surname) See also *Alemannia (other) *Alemannic separatism Alemannic Separatism is a historical movement of separatism of the Alemannic-German-speaking areas of Austria, France, and Germany (viz., South Baden, Swabia (viz. most of Württemberg and Bavarian Swabia), Alsace and Vorarlberg), aiming ... * Allemand (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)