|
Prepositions
Prepositions and postpositions, together called adpositions (or broadly, in traditional grammar, simply prepositions), are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in'', ''under'', ''towards'', ''before'') or mark various semantic roles (''of'', ''for''). A preposition or postposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement, or sometimes object. A preposition comes before its complement; a postposition comes after its complement. English generally has prepositions rather than postpositions – words such as ''in'', ''under'' and ''of'' precede their objects, such as ''in England'', ''under the table'', ''of Jane'' – although there are a few exceptions including "ago" and "notwithstanding", as in "three days ago" and "financial limitations notwithstanding". Some languages that use a different word order have postpositions instead, or have both types. The phrase formed by a preposition or postposition together with its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Grammar
English grammar is the set of structural rules of the English language. This includes the structure of words, phrases, clauses, Sentence (linguistics), sentences, and whole texts. This article describes a generalized, present-day Standard English – a form of speech and writing used in public discourse, including broadcasting, education, entertainment, government, and news, over a range of Register (sociolinguistics), registers, from formal to informal. Divergences from the grammar described here occur in some historical, social, cultural, and regional List of dialects of the English language, varieties of English, although these are more minor than differences in English phonology, pronunciation and lexicon, vocabulary. Modern English has largely abandoned the inflectional grammatical case, case system of Indo-European in favor of analytic language, analytic constructions. The personal pronouns retain morphological case more strongly than any other word class (a remnant of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Grammar
Ancient Greek grammar is morphologically complex and preserves several features of Proto-Indo-European morphology. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, articles, numerals and especially verbs are all highly inflected. A complication of Greek grammar is that different Greek authors wrote in different dialects, all of which have slightly different grammatical forms (see Ancient Greek dialects). For example, the history of Herodotus and medical works of Hippocrates are written in Ionic, the poems of Sappho in Aeolic, and the odes of Pindar in Doric; the poems of Homer are written in a mixed dialect, mostly Ionic, with many archaic and poetic forms. The grammar of Koine Greek (the Greek lingua franca spoken in the Hellenistic and later periods) also differs slightly from classical Greek. This article primarily discusses the morphology and syntax of Attic Greek, that is the Greek spoken at Athens in the century from 430 BC to 330 BC, as exemplified in the historical works of Thucydides and Xeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object (grammar)
In linguistics, an object is any of several types of arguments. In subject-prominent, nominative-accusative languages such as English, a transitive verb typically distinguishes between its subject and any of its objects, which can include but are not limited to direct objects, indirect objects, and arguments of adpositions ( prepositions or postpositions); the latter are more accurately termed ''oblique arguments'', thus including other arguments not covered by core grammatical roles, such as those governed by case morphology (as in languages such as Latin) or relational nouns (as is typical for members of the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area). In ergative-absolutive languages, for example most Australian Aboriginal languages, the term "subject" is ambiguous, and thus the term "agent" is often used instead to contrast with "object", such that basic word order is often spoken of in terms such as Agent-Object-Verb (AOV) instead of Subject-Object-Verb (SOV). Topic-prominent lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
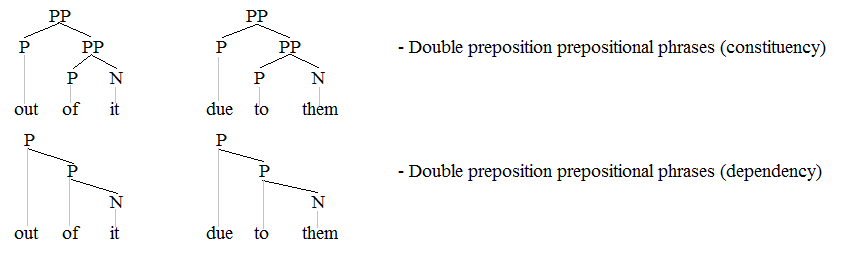
Adpositional Phrase
An adpositional phrase, in linguistics, is a syntactic category that includes ''prepositional phrases'', ''postpositional phrases'', and ''circumpositional phrases''. Adpositional phrases contain an adposition (preposition, postposition, or circumposition) as head and usually a complement such as a noun phrase. Language syntax treats adpositional phrases as units that act as arguments or adjuncts. Prepositional and postpositional phrases differ by the order of the words used. Languages that are primarily head-initial such as English predominantly use prepositional phrases whereas head-final languages predominantly employ postpositional phrases. Many languages have both types, as well as circumpositional phrases. Types There are three types of adpositional phrases: prepositional phrases, postpositional phrases, and circumpositional phrases. Prepositional phrases The underlined phrases in the following sentences are examples of prepositional phrases in English. The preposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prepositional Phrase
An adpositional phrase, in linguistics, is a syntactic category that includes ''prepositional phrases'', ''postpositional phrases'', and ''circumpositional phrases''. Adpositional phrases contain an adposition (preposition, postposition, or circumposition) as head and usually a complement such as a noun phrase. Language syntax treats adpositional phrases as units that act as arguments or adjuncts. Prepositional and postpositional phrases differ by the order of the words used. Languages that are primarily head-initial such as English predominantly use prepositional phrases whereas head-final languages predominantly employ postpositional phrases. Many languages have both types, as well as circumpositional phrases. Types There are three types of adpositional phrases: prepositional phrases, postpositional phrases, and circumpositional phrases. Prepositional phrases The underlined phrases in the following sentences are examples of prepositional phrases in English. The prepos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerund
In linguistics, a gerund ( abbreviated ) is any of various nonfinite verb forms in various languages; most often, but not exclusively, one that functions as a noun. In English, it has the properties of both verb and noun, such as being modifiable by an adverb and being able to take a direct object. The term "''-ing'' form" is often used in English to refer to the gerund specifically. Traditional grammar makes a distinction within ''-ing'' forms between present participles and gerunds, a distinction that is not observed in such modern grammars as ''A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language'' and '' The Cambridge Grammar of the English Language''. Traditional use The Latin gerund, in a restricted set of syntactic contexts, denotes the sense of the verb in isolation after certain prepositions, and in certain uses of the genitive, dative, and ablative cases. It is very rarely combined with dependent sentence elements such as object. To express such concepts, the constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
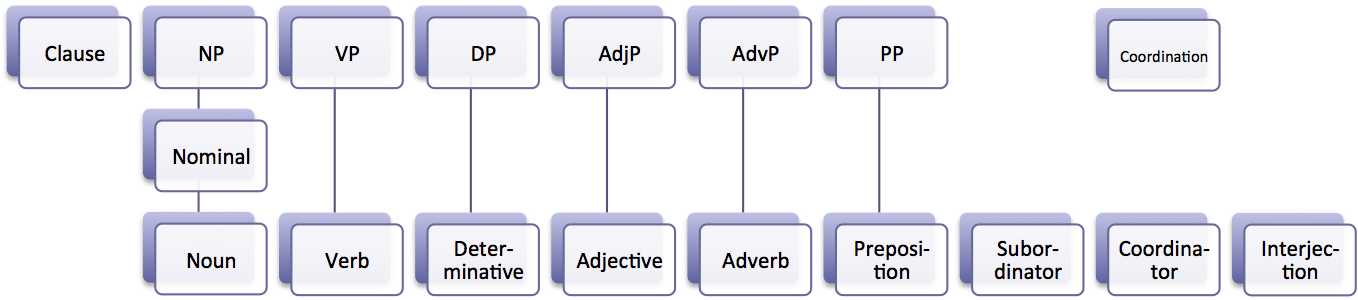
Part Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine ( Subcarpathia), central and western Romania ( Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Prekmurje), and eastern Austria. It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the United States and Canada) and Israel. With 17 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's largest member by number of speakers. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family itself (then called Finno-Ugric) was established in 1717. Hungarian has traditionally been assigned to the Ugric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes domains such as phonology, morphology, and syntax, often complemented by phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are currently two different approaches to the study of grammar: traditional grammar and theoretical grammar. Fluent speakers of a language variety or ''lect'' have effectively internalized these constraints, the vast majority of which – at least in the case of one's native language(s) – are acquired not by conscious study or instruction but by hearing other speakers. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later in life usually involves more explicit instruction. In this view, grammar is understood as the cognitive information underlying a specific instance of language productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Article (grammar)
An article is any member of a class of dedicated words that are used with noun phrases to mark the identifiability of the referents of the noun phrases. The category of articles constitutes a part of speech. In English, both "the" and "a(n)" are articles, which combine with nouns to form noun phrases. Articles typically specify the grammatical definiteness of the noun phrase, but in many languages, they carry additional grammatical information such as gender, number, and case. Articles are part of a broader category called determiners, which also include demonstratives, possessive determiners, and quantifiers. In linguistic interlinear glossing, articles are abbreviated as . Types Definite article A definite article is an article that marks a definite noun phrase. Definite articles such as English ''the'' are used to refer to a particular member of a group. It may be something that the speaker has already mentioned or it may be otherwise something uniquely speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Language
Finnish ( endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedish). In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent. Finnish is typologically agglutinative and uses almost exclusively suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numerals and verbs are inflected depending on their role in the sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, although the extensive use of inflection allows them to be ordered differently. Word order variations are often reserved for differences in information structure. Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thematic Relations
In certain theories of linguistics, thematic relations, also known as semantic roles, are the various roles that a noun phrase may play with respect to the action or state described by a governing verb, commonly the sentence's main verb. For example, in the sentence "Susan ate an apple", ''Susan'' is the doer of the eating, so she is an agent; ''an apple'' is the item that is eaten, so it is a patient. Since their introduction in the mid 1960s by Jeffrey Gruber and Charles Fillmore, semantic roles have been a core linguistic concept and ground of debate between linguist approaches, because of their potential in explaining the relationship between syntax and semantics (also known as the syntax-semantics interface), that is how meaning affects the surface syntactic codification of language. The notion of semantic roles play a central role especially in functionalist and language-comparative ( typological) theories of language and grammar. While most modern linguistic theories m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |