|
Polycotylus
''Polycotylus'' is a genus of plesiosaur within the family Polycotylidae. The type species is ''P. latippinis'' and was named by American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope in 1869. Eleven other species have been identified. The name means 'much-cupped vertebrae', referring to the shape of the vertebrae. It lived in the Western Interior Seaway of North America toward the end of the Cretaceous. One fossil preserves an adult with a single large fetus inside of it, indicating that ''Polycotylus'' gave live birth, an unusual adaptation among reptiles. History Edward Drinker Cope named ''Polycotylus'' from the Niobrara Formation in Kansas in 1869. The holotype bones from which he based his description were fragmentary, representing only a small portion of the skeleton. A more complete skeleton was later found in Kansas and was described in 1906. A nearly complete skeleton was found in 1949 from the Mooreville Chalk Formation in Alabama, but was not described until 2002. A new species, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycotylus Latipinnis Paddle Williston
''Polycotylus'' is a genus of plesiosaur within the family (biology), family Polycotylidae. The type species is ''P. latippinis'' and was named by American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope in 1869. Eleven other species have been identified. The name means 'much-cupped vertebrae', referring to the shape of the vertebrae. It lived in the Western Interior Seaway of North America toward the end of the Late Cretaceous, Cretaceous. One fossil preserves an adult with a single large fetus inside of it, indicating that ''Polycotylus'' gave live birth, an unusual adaptation among reptiles. History Edward Drinker Cope named ''Polycotylus'' from the Niobrara Formation in Kansas in 1869. The holotype bones from which he based his description were fragmentary, representing only a small portion of the skeleton. A more complete skeleton was later found in Kansas and was described in 1906. A nearly complete skeleton was found in 1949 from the Mooreville Chalk Formation in Alabama, but was not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
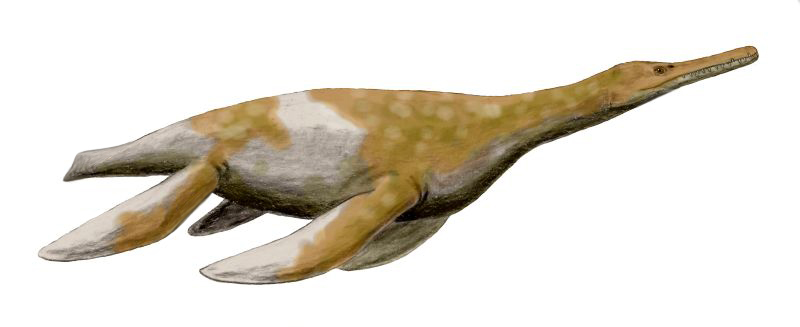
Polycotylus NT
''Polycotylus'' is a genus of plesiosaur within the family Polycotylidae. The type species is ''P. latippinis'' and was named by American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope in 1869. Eleven other species have been identified. The name means 'much-cupped vertebrae', referring to the shape of the vertebrae. It lived in the Western Interior Seaway of North America toward the end of the Cretaceous. One fossil preserves an adult with a single large fetus inside of it, indicating that ''Polycotylus'' gave live birth, an unusual adaptation among reptiles. History Edward Drinker Cope named ''Polycotylus'' from the Niobrara Formation in Kansas in 1869. The holotype bones from which he based his description were fragmentary, representing only a small portion of the skeleton. A more complete skeleton was later found in Kansas and was described in 1906. A nearly complete skeleton was found in 1949 from the Mooreville Chalk Formation in Alabama, but was not described until 2002. A new species, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasmosaurus
''Elasmosaurus'' (;) is a genus of plesiosaur that lived in North America during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, about 80.5million years ago. The first specimen was discovered in 1867 near Fort Wallace, Kansas, US, and was sent to the American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope, who named it ''E.platyurus'' in 1868. The generic name means "thin-plate reptile", and the specific name means "flat-tailed". Cope originally reconstructed the skeleton of ''Elasmosaurus'' with the skull at the end of the tail, an error which was made light of by the paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh, and became part of their "Bone Wars" rivalry. Only one incomplete ''Elasmosaurus'' skeleton is definitely known, consisting of a fragmentary skull, the spine, and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, and a single species is recognized today; other species are now considered invalid or have been moved to other genera. Measuring in length and in body mass, ''Elasmosaurus'' would have ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosaur
The Plesiosauria (; Greek: πλησίος, ''plesios'', meaning "near to" and ''sauros'', meaning "lizard") or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous ''Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred valid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1869 In Paleontology
Arthropods Insects Dinosaurs Plesiosaurs New taxa Pterosaurs New taxa Paleontologists * Death of German Paleontologist Christian Hermann Erich von Meyer.{{cite book, last = Farlow, first = James O., author2= M. K. Brett-Surmann, title = The Complete Dinosaur, publisher = Indiana University Press, year = 1999, location = Bloomington, Indiana, pages = 11, isbn = 0-253-21313-4 References 1860s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... Paleontology 9 Paleontology, 1869 In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycotylidae
Polycotylidae is a family of plesiosaurs from the Cretaceous, a sister group to Leptocleididae. Polycotylids first appeared during the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous, before becoming abundant and widespread during the early Late Cretaceous. Several species survived into the final stage of the Cretaceous, the Maastrichtian. With their short necks and large elongated heads, they resemble the pliosaurs, but closer phylogenetic studies indicate that they share many common features with the Leptocleididae and Elasmosauridae. They have been found worldwide, with specimens reported from New Zealand, Australia, Japan, Morocco, the US, Canada, Eastern Europe, and South America. Phylogeny Cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... after Albright, Gillette and Tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliosaur
Pliosauroidea is an extinct clade of plesiosaurs, known from the earliest Jurassic to early Late Cretaceous. They are best known for the subclade Thalassophonea, which contained crocodile-like short-necked forms with large heads and massive toothed jaws, commonly known as pliosaurs. More primitive non-thalassophonean pliosauroids resembled pleisiosaurs in possessing relatively long necks and smaller heads. They originally included only members of the family Pliosauridae, of the order Plesiosauria, but several other genera and families are now also included, the number and details of which vary according to the classification used. The distinguishing characteristics are a short neck and an elongated head, with larger hind flippers compared to the fore flippers, the opposite of the plesiosaurs. They were carnivorous and their long and powerful jaws carried many sharp, conical teeth. Pliosaurs range from 4 to 15 metres and more in length. Their prey may have included fish, sharks, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosauroidea
Plesiosauroidea (; Greek: 'near, close to' and 'lizard') is an extinct clade of carnivorous marine reptiles. They have the snake-like longest neck to body ratio of any reptile. Plesiosauroids are known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. After their discovery, some plesiosauroids were said to have resembled "a snake threaded through the shell of a turtle", although they had no shell. Plesiosauroidea appeared at the Early Jurassic Period (late Sinemurian stage) and thrived until the K-Pg extinction, at the end of the Cretaceous Period. The oldest confirmed plesiosauroid is ''Plesiosaurus'' itself, as all younger taxa were recently found to be pliosauroids. While they were Mesozoic diapsid reptiles that lived at the same time as dinosaurs, they did not belong to the latter. Gastroliths are frequently found associated with plesiosaurs. History of discovery The first complete plesiosauroid skeletons were found in England by Mary Anning, in the early 19th century, and wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptocleidoidea
Cryptoclidia is a clade of plesiosaurs. Cryptoclidia was named and defined as a node clade in 2010 by Hilary Ketchum and Roger Benson: the group consisting of the last common ancestor of ''Cryptoclidus eurymerus'' and ''Polycotylus latipinnis''; and all its descendants. The following cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... follows an analysis by Benson & Druckenmiller (2014). References Plesiosaurs {{plesiosaur-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittal Crest
A sagittal crest is a ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline of the top of the skull (at the sagittal suture) of many mammalian and reptilian skulls, among others. The presence of this ridge of bone indicates that there are exceptionally strong jaw muscles. The sagittal crest serves primarily for attachment of the temporalis muscle, which is one of the main chewing muscles. Development of the sagittal crest is thought to be connected to the development of this muscle. A sagittal crest usually develops during the juvenile stage of an animal in conjunction with the growth of the temporalis muscle, as a result of convergence and gradual heightening of the temporal lines. Function A sagittal crest tends to be present on the skulls of adult animals that rely on powerful biting and clenching of their teeth, usually as a part of their hunting strategy. Skulls of some dinosaur species, including tyrannosaurs, possessed well developed sagittal crests. Among mammals, dogs, cats, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloneustes
''Peloneustes'' (meaning "mud swimmer") is a genus of pliosaurid plesiosaur from the Middle Jurassic of England. Its remains are known from the Peterborough Member of the Oxford Clay Formation, which is Callovian in age. It was originally described as a species of ''Plesiosaurus'' by palaeontologist Harry Govier Seeley in 1896, before being given its own genus by naturalist Richard Lydekker in 1889. While many species have been assigned to ''Peloneustes'', ''P. philarchus'' is currently the only one still considered valid, with the others moved to different genera, considered '' nomina dubia'', or synonymised with ''P. philarchus''. Some of the material formerly assigned to ''P. evansi'' have since been reassigned to ''"Pliosaurus" andrewsi''. ''Peloneustes'' is known from many specimens, including some very complete material. With a total length of , ''Peloneustes'' is not a large pliosaurid. It had a large, triangular skull, which occupied about a fifth of its body length. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |