|
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. The reverse process, deplasmolysis or cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a lower external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell. Through observation of plasmolysis and deplasmolysis, it is possible to determine the tonicity of the cell's environment as well as the rate solute molecules cross the cellular membrane. Etymology The term plasmolysis is derived from the Latin word ‘plasma’ meaning ‘matrix’ and the Greek word ‘lysis’, meaning ‘loosening’. Turgidity A plant cell in hypotonic solution will absorb water by endosmosis, so that the increased volume of water in the cell will increase pressure, making the protoplasm push against the cell wall, a condition known as turgor. Turgor makes plant cells push against each other in the same way and is the main line method of support in non-woody plant tissue. Plant cell walls resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmolysed Plant Cell
Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. The reverse process, deplasmolysis or cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a lower external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell. Through observation of plasmolysis and deplasmolysis, it is possible to determine the tonicity of the cell's environment as well as the rate solute molecules cross the cellular membrane. Etymology The term plasmolysis is derived from the Latin word ‘plasma’ meaning ‘matrix’ and the Greek word ‘lysis’, meaning ‘loosening’. Turgidity A plant cell in hypotonic solution will absorb water by endosmosis, so that the increased volume of water in the cell will increase pressure, making the protoplasm push against the cell wall, a condition known as turgor. Turgor makes plant cells push against each other in the same way and is the main line method of support in non-woody plant tissue. Plant cell walls resist fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytorrhysis
Cytorrhysis is the permanent and irreparable damage to the cell wall after the complete collapse of a plant cell due to the loss of internal positive pressure (hydraulic turgor pressure). Positive pressure within a plant cell is required to maintain the upright structure of the cell wall. Desiccation (relative water content of less than or equal to 10%) resulting in cellular collapse occurs when the ability of the plant cell to regulate turgor pressure is compromised by environmental stress. Water continues to diffuse out of the cell after the point of zero turgor pressure, where internal cellular pressure is equal to the external atmospheric pressure, has been reached, generating negative pressure within the cell. That negative pressure pulls the center of the cell inward until the cell wall can no longer withstand the strain. The inward pressure causes the majority of the collapse to occur in the central region of the cell, pushing the organelles within the remaining cytoplasm agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turgor Pressure On Plant Cells Diagram
Turgor pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall. It is also called ''hydrostatic pressure'', and is defined as the pressure in a fluid measured at a certain point within itself when at equilibrium. Generally, turgor pressure is caused by the osmotic flow of water and occurs in plants, fungi, and bacteria. The phenomenon is also observed in protists that have cell walls. This system is not seen in animal cells, as the absence of a cell wall would cause the cell to lyse when under too much pressure. The pressure exerted by the osmotic flow of water is called turgidity. It is caused by the osmotic flow of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from a volume with a low solute concentration to one with a higher solute concentration is called osmotic flow. In plants, this entails the water moving from the low concentration solute outside the cell into the cell's vacuole. Mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turgor
Turgor pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall. It is also called ''hydrostatic pressure'', and is defined as the pressure in a fluid measured at a certain point within itself when at equilibrium. Generally, turgor pressure is caused by the osmotic flow of water and occurs in plants, fungi, and bacteria. The phenomenon is also observed in protists that have cell walls. This system is not seen in animal cells, as the absence of a cell wall would cause the cell to lyse when under too much pressure. The pressure exerted by the osmotic flow of water is called turgidity. It is caused by the osmotic flow of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from a volume with a low solute concentration to one with a higher solute concentration is called osmotic flow. In plants, this entails the water moving from the low concentration solute outside the cell into the cell's vacuole. Mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytolysis
Cytolysis, or osmotic lysis, occurs when a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to diffuse into the cell. Water can enter the cell by diffusion through the cell membrane or through selective membrane channels called aquaporins, which greatly facilitate the flow of water. It occurs in a hypotonic environment, where water moves into the cell by osmosis and causes its volume to increase to the point where the volume exceeds the membrane's capacity and the cell bursts. The presence of a cell wall prevents the membrane from bursting, so cytolysis only occurs in animal and protozoa cells which do not have cell walls. The reverse process is plasmolysis. In bacteria Osmotic lysis would be expected to occur when bacterial cells are treated with a hypotonic solution with added lysozyme, which destroys the bacteria's cell walls. Prevention Different cells and organisms have adapted different ways of preventing cytolysis from occurring. For example, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onion Epidermal Cell
The epidermal cells of onions provide a protective layer against viruses and fungi that may harm the sensitive tissues. Because of their simple structure and transparency they are often used to introduce students to plant anatomy or to demonstrate plasmolysis. The clear epidermal cells exist in a single layer and do not contain chloroplasts, because the onion fruiting body (bulb) is used for storing energy, not photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in .... Each plant cell has a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and a large vacuole. The nucleus is present at the periphery of the cytoplasm. The vacuole is prominent and present at the center of the cell, surrounded by cytoplasm. Firm, small onions are best for microscopy. Remove the epidermal layers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
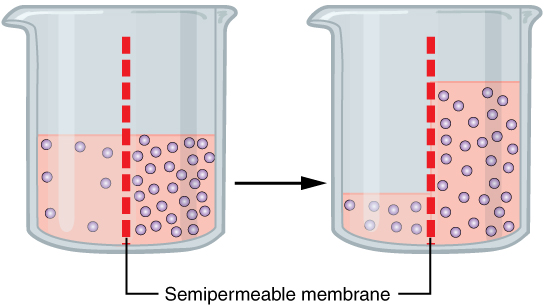
Osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to be applied so that there is no net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exosmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to be applied so that there is no net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semipermeab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endosmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to be applied so that there is no net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semipermeab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crenation
Crenation (from modern Latin ''crenatus'' meaning "scalloped or notched", from popular Latin ''crena'' meaning "notch") in botany and zoology, describes an object's shape, especially a leaf or shell, as being round-toothed or having a scalloped edge. The descriptor can apply to objects of different types, including cells, where one mechanism of crenation is the contraction of a cell after exposure to a hypertonic solution, due to the loss of water through osmosis. In a hypertonic environment, the cell has a lower concentration of solutes than the surrounding extracellular fluid, and water diffuses out of the cell by osmosis, causing the cytoplasm to decrease in volume. As a result, the cell shrinks and the cell membrane develops abnormal notchings. Pickling cucumbers and salt-curing of meat are two practical applications of crenation. Plasmolysis is the term which describes plant cells when the cytoplasm shrinks from the cell wall in a hypertonic environment. In plasmolysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotonic
In chemical biology, tonicity is a measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient; the water potential of two solutions separated by a partially-permeable cell membrane. Tonicity depends on the relative concentration of selective membrane-impermeable solutes across a cell membrane which determine the direction and extent of osmotic flux. It is commonly used when describing the swelling-versus-shrinking response of cells immersed in an external solution. Unlike osmotic pressure, tonicity is influenced only by solutes that cannot cross the membrane, as only these exert an effective osmotic pressure. Solutes able to freely cross the membrane do not affect tonicity because they will always equilibrate with equal concentrations on both sides of the membrane without net solvent movement. It is also a factor affecting imbibition. There are three classifications of tonicity that one solution can have relative to another: ''hypertonic'', ''hypotonic'', and ''isotonic''.A hypotonic so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
