|
Plasmat Lens
The Plasmat lens is a widely used and long-established lens type invented by Paul Rudolph in 1918, especially common in large-format photography. It provides high correction of aberrations with a moderate maximum aperture (e.g. ). It is a specific instance of the Dagor type double-meniscus anastigmat. Double-meniscus anastigmats use widely separated positive and negative surfaces, generally thick meniscus lenses, to achieve a flat field. The most basic form is two sharply curved meniscus elements located symmetrically about a stop. Further refinement of the form replaces the two simple meniscus lenses with achromats for chromatic correction. The Dagor type further refines these achromats into triplets with the following design parameters: a high-index, doubly convex (DCX) lens cemented to a medium-index, doubly concave (DCV) lens cemented to a low-index meniscus lens. Up to this point, all refinements have maintained symmetry about the stop. The Plasmat further refines the Dagor f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meyer Plasmat Blue
Meyer may refer to: People *Meyer (surname), listing people so named * Meyer (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the name Companies * Meyer Burger, a Swiss mechanical engineering company * Meyer Corporation * Meyer Sound Laboratories * Meyer Turku, a Finnish shipbuilding company * Behn Meyer, a German chemical company * Fred Meyer, a American hypermarket chain and subsidiary of Kroger * Fred Meyer Jewelers Places United States * Meyer, Illinois, an unincorporated community in Adams County, Illinois * Meyer, Franklin County, Illinois, an unincorporated community in Franklin County, Illinois * Meyer, Iowa, in Mitchell County, Iowa * Myers, Montana (also spelled Meyer), an unincorporated community in Treasure County * Meyer Township, Michigan Other * Meyer House (other), multiple buildings in the U.S. * Meyer locomotive * Meyer Theatre, an historic theater in Wisconsin, U.S. * USS ''Meyer'' (DD-279), a ''Clemson''-class destroyer in the Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Lens
A camera lens (also known as photographic lens or photographic objective) is an optical lens or assembly of lenses used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image chemically or electronically. There is no major difference in principle between a lens used for a still camera, a video camera, a telescope, a microscope, or other apparatus, but the details of design and construction are different. A lens might be permanently fixed to a camera, or it might be interchangeable with lenses of different focal lengths, apertures, and other properties. While in principle a simple convex lens will suffice, in practice a compound lens made up of a number of optical lens elements is required to correct (as much as possible) the many optical aberrations that arise. Some aberrations will be present in any lens system. It is the job of the lens designer to balance these and produce a desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Rudolph (physicist)
Paul Rudolph (14 November 1858 – 8 March 1935) was a German physicist who designed the first anastigmatic lens while working for Carl Zeiss. After World War I, he joined the Hugo Meyer optical company, where he designed most of their cine lenses. Work * 1890: First anastigmat lens "protar" * 1895: Planar design * 1899: Unar design * 1902: Tessar The Tessar is a photographic lens design conceived by the German physicist Paul Rudolph in 1902 while he worked at the Zeiss optical company and patented by Zeiss in Germany; the lens type is usually known as the Zeiss Tessar. A Tessar com ... design * 1918: Plasmat design * 1922: Kino-Plasmat design * 1926: Makro-Plasmat design * 1931: Kleinbild-Plasmat design References {{DEFAULTSORT:Rudolph, Paul 1858 births 1935 deaths 19th-century German inventors 19th-century German physicists Optical physicists Optical engineers 20th-century German inventors 20th-century German physicists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Format
Large format refers to any imaging format of or larger. Large format is larger than "medium format", the or size of Hasselblad, Mamiya, Rollei, Kowa, and Pentax cameras (using 120- and 220-roll film), and much larger than the frame of 35 mm format. The main advantage of a large format, film or digital, is a higher resolution at the same pixel pitch, or the same resolution with larger pixels or grains which allows each pixel to capture more light enabling exceptional low-light capture. A 4×5 inch image (12.903 mm²) has about 15 times the area, and thus 15× the total resolution, of a 35 mm frame (864 mm²). Large format cameras were some of the earliest photographic devices, and before enlargers were common, it was normal to just make 1:1 contact prints from a 4×5, 5×7, or 8×10-inch negative. Formats The most common large format is 4×5 inches (10.2x12.7 cm), which was the size used by cameras like the Graflex Speed Graphic and Crown Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
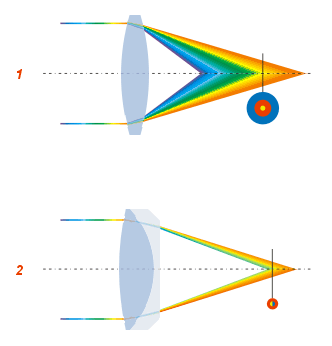
Optical Aberrations
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as lenses, that causes light to be spread out over some region of space rather than focused to a point. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred or distorted, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements. An image-forming optical system with aberration will produce an image which is not sharp. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration. Aberration can be anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. An optical system typically has many openings or structures that limit the ray bundles (ray bundles are also known as ''pencils'' of light). These structures may be the edge of a lens or mirror, or a ring or other fixture that holds an optical element in place, or may be a special element such as a diaphragm placed in the optical path to limit the light admitted by the system. In general, these structures are called stops, and the aperture stop is the stop that primarily determines the ray cone angle and brightness at the image point. In some contexts, especially in photography and astronomy, ''aperture'' refers to the diameter of the aperture stop rather than the physical stop or the opening itself. For example, in a telescope, the aperture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil plant), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
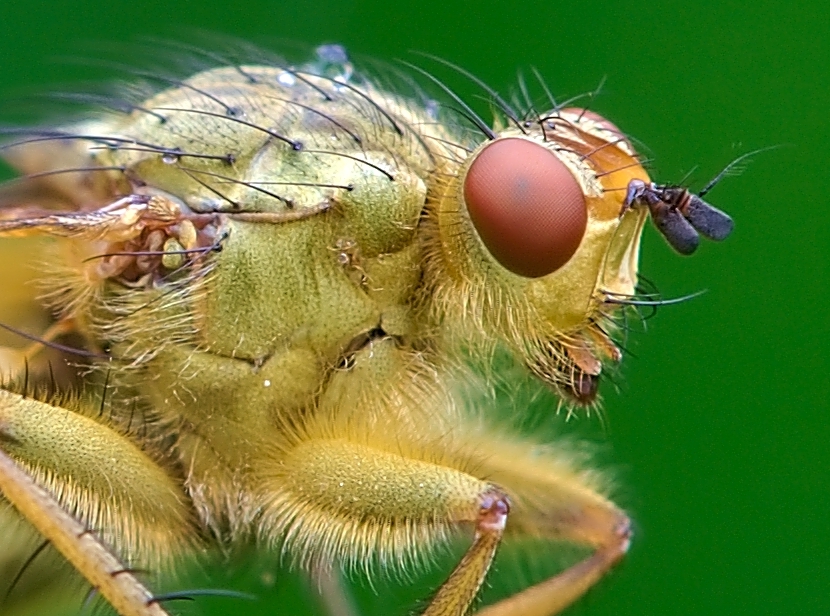
Macro Lens
Macro photography (or photomacrography or macrography, and sometimes macrophotography) is extreme close-up photography, usually of very small subjects and living organisms like insects, in which the size of the subject in the photograph is greater than life size (though ''macrophotography'' also refers to the art of making very large photographs). By the original definition, a macro photograph is one in which the size of the subject on the negative or image sensor is life size or greater. In some senses, however, it refers to a finished photograph of a subject that is greater than life size. The ratio of the subject size on the film plane (or sensor plane) to the actual subject size is known as the reproduction ratio. Likewise, a macro lens is classically a lens capable of reproduction ratios of at least 1:1, although it often refers to any lens with a large reproduction ratio, despite rarely exceeding 1:1. Apart from technical photography and film-based processes, where the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |