|
Phosphorescence
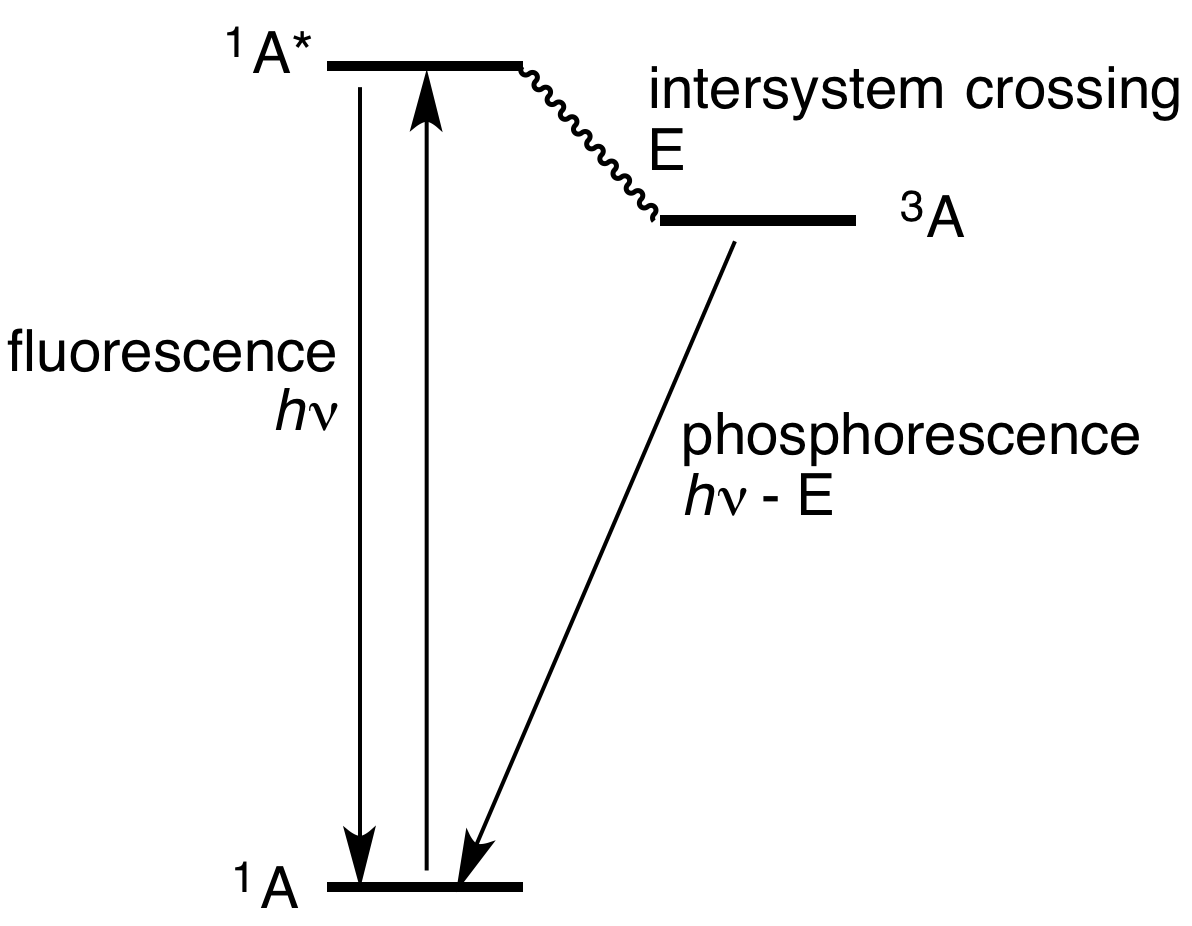
Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluorescence, a phosphorescent material does not immediately reemit the radiation it absorbs. Instead, a phosphorescent material absorbs some of the radiation energy and reemits it for a much longer time after the radiation source is removed. In a general sense, there is no distinct boundary between the emission times of fluorescence and phosphorescence (i.e.: if a substance glows under a black light it is generally considered fluorescent, and if it glows in the dark it is often simply called phosphorescent). In a modern, scientific sense, the phenomena can usually be classified by the three different mechanisms that produce the light, and the typical timescales during which those mechanisms emit light. Whereas fluorescent materials stop emit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorescence
Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluorescence, a phosphorescent material does not immediately reemit the radiation it absorbs. Instead, a phosphorescent material absorbs some of the radiation energy and reemits it for a much longer time after the radiation source is removed. In a general sense, there is no distinct boundary between the emission times of fluorescence and phosphorescence (i.e.: if a substance glows under a black light it is generally considered fluorescent, and if it glows in the dark it is often simply called phosphorescent). In a modern, scientific sense, the phenomena can usually be classified by the three different mechanisms that produce the light, and the typical timescales during which those mechanisms emit light. Whereas fluorescent materials stop emit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorescent
Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluorescence, a phosphorescent material does not immediately reemit the radiation it absorbs. Instead, a phosphorescent material absorbs some of the radiation energy and reemits it for a much longer time after the radiation source is removed. In a general sense, there is no distinct boundary between the emission times of fluorescence and phosphorescence (i.e.: if a substance glows under a black light it is generally considered fluorescent, and if it glows in the dark it is often simply called phosphorescent). In a modern, scientific sense, the phenomena can usually be classified by the three different mechanisms that produce the light, and the typical timescales during which those mechanisms emit light. Whereas fluorescent materials stop emitti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible spectrum, visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to blacklight, UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescence, phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors (fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoluminescence
Photoluminescence (abbreviated as PL) is light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons (electromagnetic radiation). It is one of many forms of luminescence (light emission) and is initiated by photoexcitation (i.e. photons that excite electrons to a higher energy level in an atom), hence the prefix ''photo-''. Following excitation, various relaxation processes typically occur in which other photons are re-radiated. Time periods between absorption and emission may vary: ranging from short femtosecond-regime for emission involving free-carrier plasma in inorganic semiconductorsHayes, G.R.; Deveaud, B. (2002). "Is Luminescence from Quantum Wells Due to Excitons?". ''Physica Status Solidi A'' 190 (3): 637–640doi:10.1002/1521-396X(200204)190:33.0.CO;2-7/ref> up to milliseconds for phosphoresence processes in molecular systems; and under special circumstances delay of emission may even span to minutes or hours. Observation of photoluminescence at a certain e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
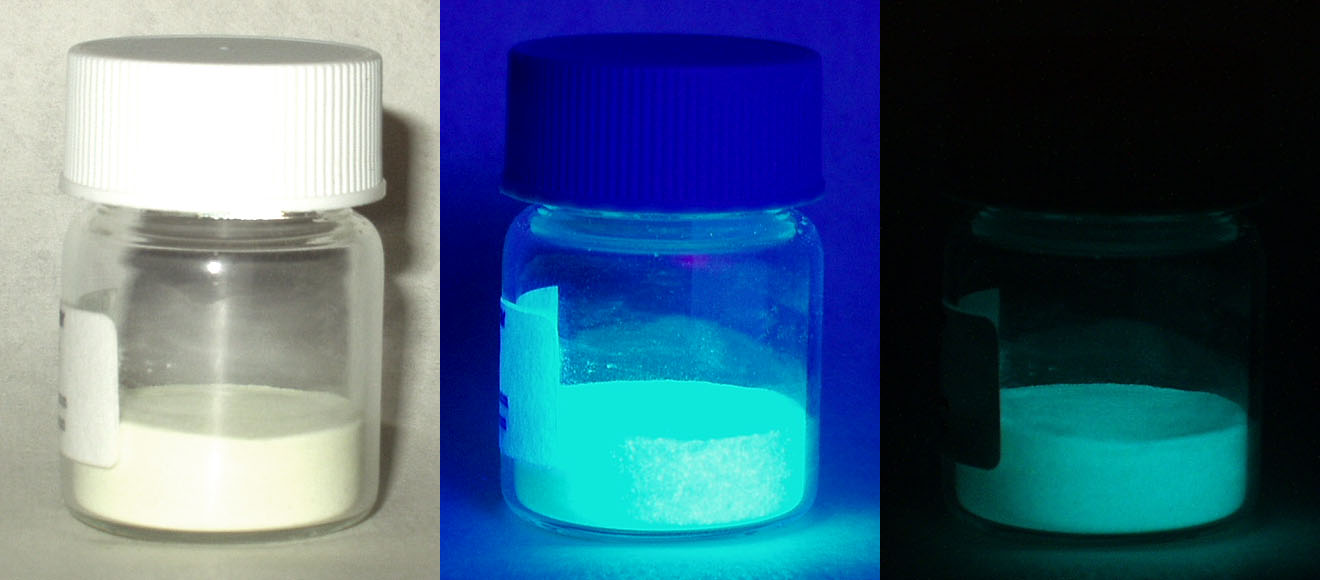
Persistent Luminescence
Commonly referred as phosphorescence, persistent luminescence is the emission of light by a phosphorescent material after an excitation by ultraviolet or visible light. Such materials would "glow in the dark". Mechanism The mechanism underlying this phenomenon is not fully understood. However, the phenomenon of persistent luminescence must not be mistaken for fluorescence and phosphorescence (see for definitions and ). Indeed, in fluorescence, the lifetime of the excited state is in the order of a few nanoseconds and in phosphorescence, even if the lifetime of the emission can reach several seconds, the reason of the long emission is due to the deexcitation between two electronic states of different spin multiplicity. For persistent luminescence, it has been known for a long time that the phenomenon involved energy traps (such as electron or hole trap) in a material which are filled during the excitation. After the end of the excitation, the stored energy is gradually released to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay ( ), beta decay ( ), and gamma decay ( ), all of which involve emitting one or more particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force. A fourth type of common decay is electron capture, in which an unstable nucleus captures an inner electron from one of the electron shells. The loss of that electron from the shell results in a cascade of electrons dropping down to that lower shell resulting in emission of discrete X-rays from the transitions. A common example is iodine-125 commonly used in medical settings. Radioactive decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forbidden Mechanism
In spectroscopy, a forbidden mechanism (forbidden transition or forbidden line) is a spectral line associated with absorption or emission of photons by atomic nuclei, atoms, or molecules which undergo a transition that is not allowed by a particular selection rule but is allowed if the approximation associated with that rule is not made. For example, in a situation where, according to usual approximations (such as the electric dipole approximation for the interaction with light), the process cannot happen, but at a higher level of approximation (e.g. magnetic dipole, or electric quadrupole) the process is allowed but at a low rate. An example is phosphorescent glow-in-the-dark materials, which absorb light and form an excited state whose decay involves a spin flip, and is therefore forbidden by electric dipole transitions. The result is emission of light slowly over minutes or hours. Should an atomic nucleus, atom or molecule be raised to an excited state and should the transitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir George Stokes
Sir George Gabriel Stokes, 1st Baronet, (; 13 August 1819 – 1 February 1903) was an Irish English physicist and mathematician. Born in County Sligo, Ireland, Stokes spent all of his career at the University of Cambridge, where he was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics from 1849 until his death in 1903. As a physicist, Stokes made seminal contributions to fluid mechanics, including the Navier–Stokes equations; and to physical optics, with notable works on polarization and fluorescence. As a mathematician, he popularised "Stokes' theorem" in vector calculus and contributed to the theory of asymptotic expansions. Stokes, along with Felix Hoppe-Seyler, first demonstrated the oxygen transport function of hemoglobin and showed color changes produced by aeration of hemoglobin solutions. Stokes was made a baronet by the British monarch in 1889. In 1893 he received the Royal Society's Copley Medal, then the most prestigious scientific prize in the world, "for his researches and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their atomic nucleus, nuclei, including the pure Chemical substance, substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any chemical reaction. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as its atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z'') – all atoms with the same atomic number are atoms of the same element. Almost all of the Baryon#Baryonic matter, baryonic matter of the universe is composed of chemical elements (among rare exceptions are neutron stars). When different elements undergo chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged into new chemical compounds, compounds held together by chemical bonds. Only a minority of elements, such as silver and gold, are found uncombined as relatively pure native element minerals. Nearly all other naturally occurring element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the "Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
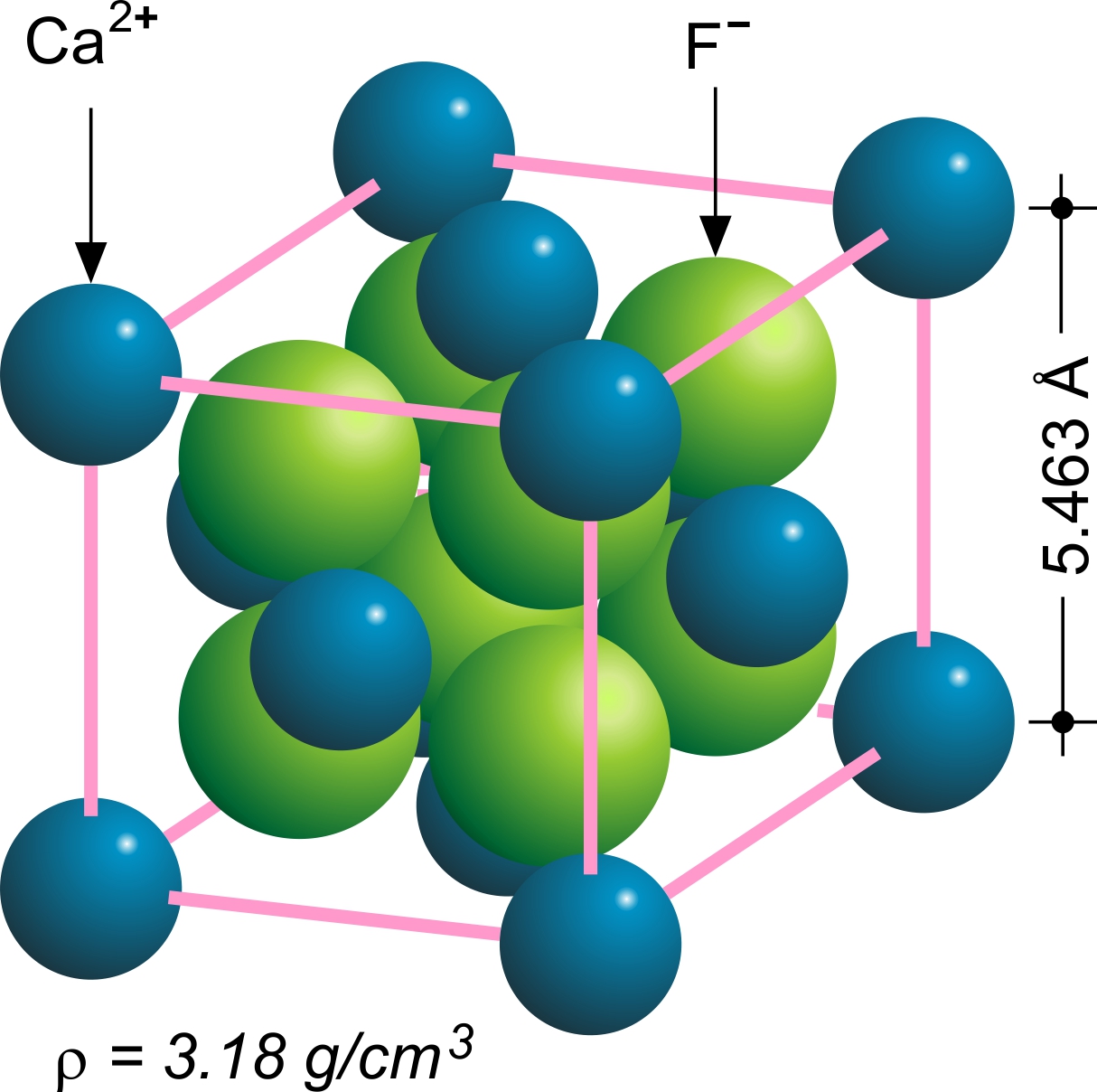
Fluorspar
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite. Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite lenses have low dispersion, so lenses made from it exhibit less chromatic aberration, making them valuable in microscopes and telescopes. Fluorite optics are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
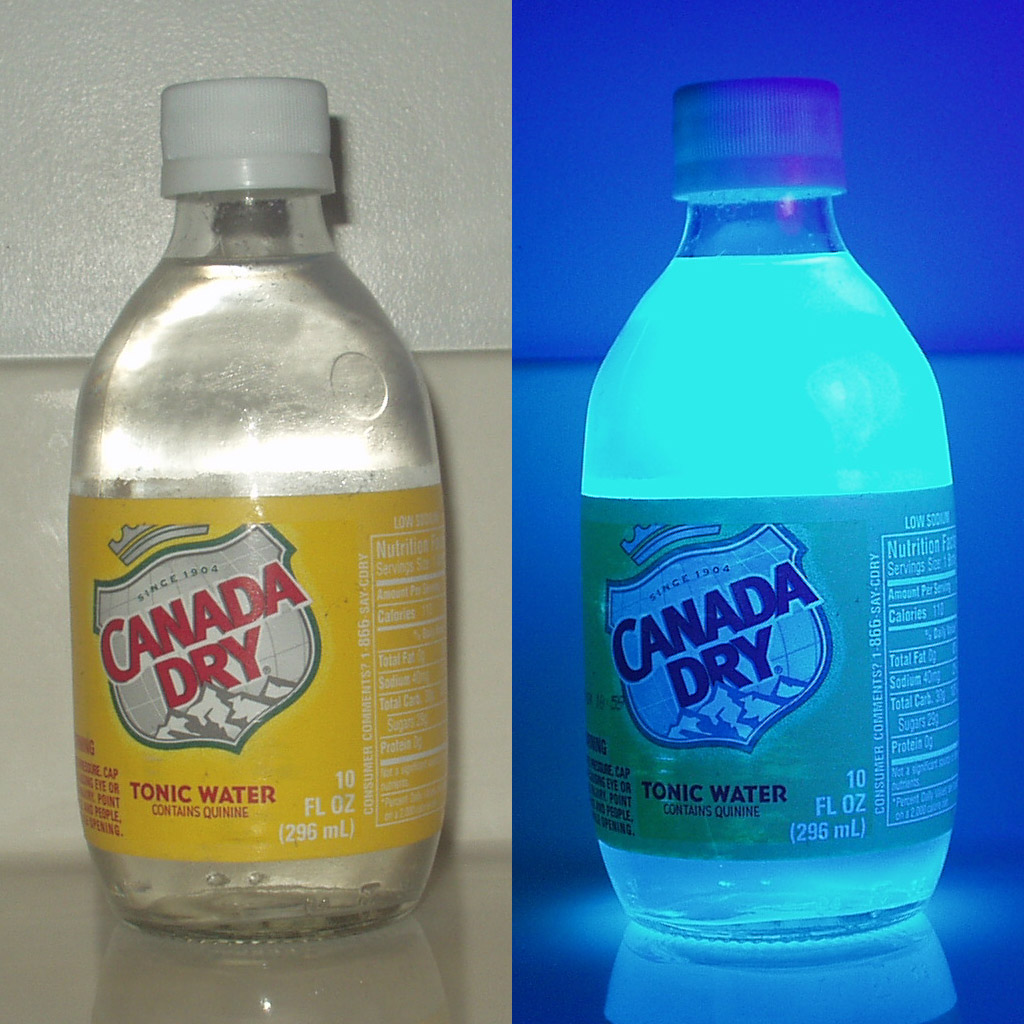
Quinine Sulfate
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg cramps, quinine is not recommended for this purpose due to the risk of serious side effects. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously. Malaria resistance to quinine occurs in certain areas of the world. Quinine is also used as an ingredient in tonic water to impart a bitter taste. Common side effects include headache, ringing in the ears, vision issues, and sweating. More severe side effects include deafness, low blood platelets, and an irregular heartbeat. Use can make one more prone to sunburn. While it is unclear if use during pregnancy causes harm to the baby, treating malaria during pregnancy with quinine when appropriate is still recommended. Quinine is an alkaloid, a naturally occurring chemical compound. How it works as a medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




%2C_black_and_white.png)