|
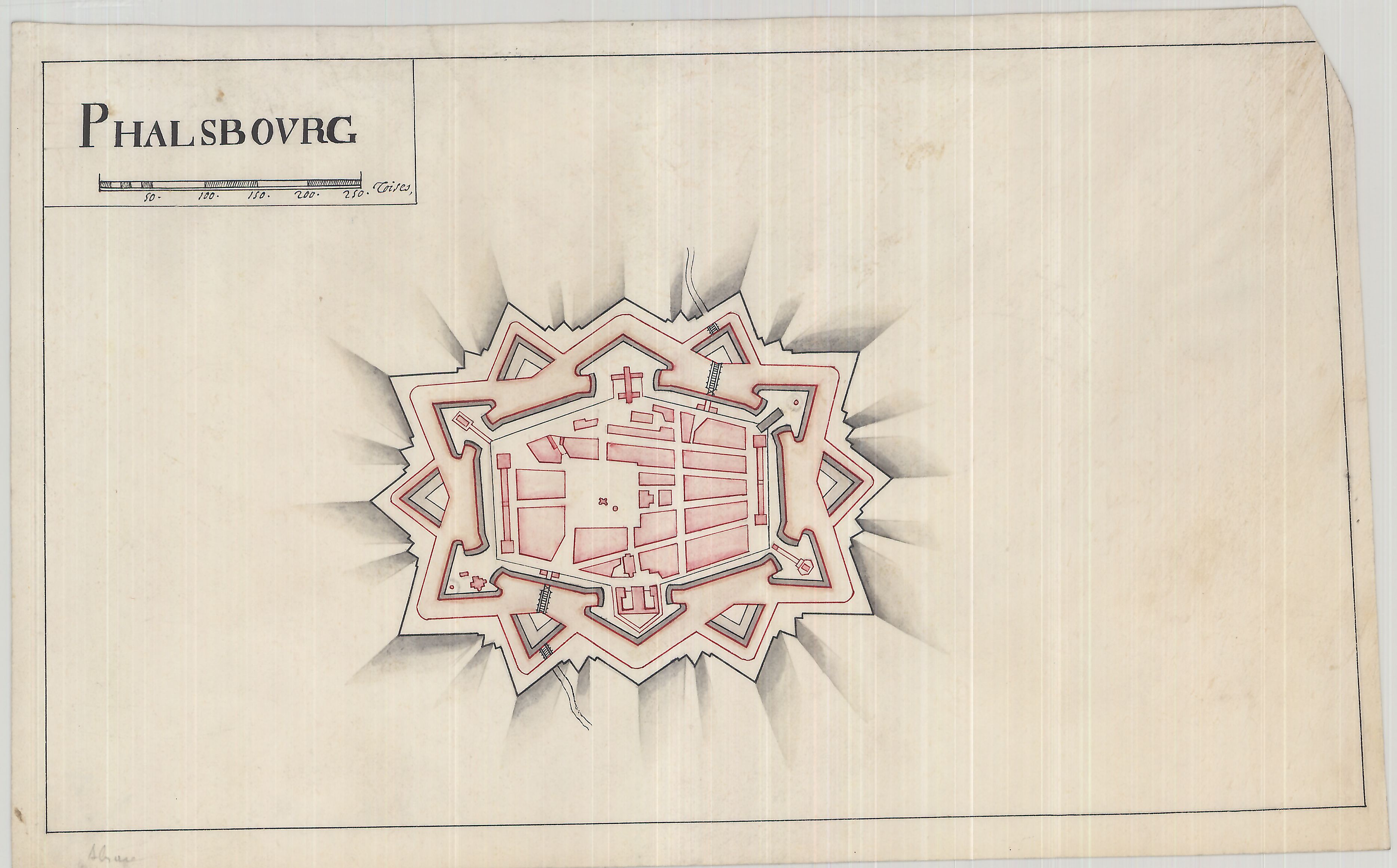
Phalsbourg
Phalsbourg (; ; Lorraine Franconian: ''Phalsburch'') is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France, with a population of about 5,000. It lies high on the west slopes of the Vosges, northwest of Strasbourg by rail. In 1911, it contained an Evangelical and a Roman Catholic church, a synagogue and a teachers' seminary. Its industries then included the manufacture of gloves, straw hats and liqueurs, and quarrying. History The area of the city of Phalsbourg, originally Pfalzburg, was originally part of the principality of Lützelstein, under the overlordship of Luxembourg, then the bishops of Metz and of Strasbourg, before becoming possessed by the Dukes of Palantine Veldenz, all within the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation. In 1570, Duke Georg Johann I of Palantine Veldenz founded the town of Pfalzburg as a refuge for Reformed Protestants expelled from of the Duchy of Lorraine, and as an administrative center of his holdings. But the cost f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Combat Helicopter Regiment
The 1st Combat Helicopter Regiment (1er Régiment d'Hélicoptères de Combat) (1er RHC) is based at Quartier La Horie (Phalsbourg). History The 1st Combat Helicopter Regiment was created on 1 August 1977, but traces its origins back to the 1950s. It carries the traditions of the 1st then the 21st Artillery Observation Groups which achieved particular fame during the First Indochina War, winning six citations. The 1st Aerial Artillery Observation Group was established on 20 November 1945, and became the 21st Aerial Artillery Observation Group on 1 October 1950. From 1945 to February 1946 it was stationed at Camp de Valdahon. It was dissolved on 31 December 1953.1° Groupe aérien d'observation d'artillerie – 1st GAOA – 21st GAOA. Mis sur pied au camp de Valdahon le 20 novembre 1945, embarque à Marseille le 1 Décember on the "Boissevin" . It arrived at Saïgon on 18 December. Devant faire mouvement sur le Tonkin, a détachement est embarqué au Cap-Saint-Jacques, on the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erckmann-Chatrian
Erckmann-Chatrian was the name used by French authors Émile Erckmann (1822–1899) and Alexandre Chatrian (1826–1890), nearly all of whose works were jointly written.Mary Ellen Snodgrass, ''Encyclopedia of Gothic Literature''. New York, Facts on File (2004). (p.104) History Both Erckmann and Chatrian were born in the ''département'' of Meurthe (now Moselle), in the Lorraine region in the extreme north-east of France. They specialised in military fiction and ghost stories in a rustic mode Hugh Lamb, "Erckmann-Chatrian", in Jack Sullivan, ''The Penguin Encyclopedia of Horror and the Supernatural'', New York City, U.S. : Viking, 1986. (pp. 144–5) Lifelong friends who first met in the spring of 1847, they finally quarreled during the mid-1880s, after which they did not produce any more stories jointly. During 1890 Chatrian died, and Erckmann wrote a few pieces under his own name. Many of Erckmann-Chatrian's works were translated into English by Adrian Ross. Tales of supern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Mouton
Georges Mouton, comte de Lobau (21 February 1770 – 27 November 1838) was a French soldier and political figure who rose to the rank of Marshal of France. Biography Born in Phalsbourg, Lorraine, he enlisted in the French Revolutionary Army in 1792. Serving in the early campaigns of the French Revolutionary Wars, he by 1800 he was promoted to the rank of colonel. He was promoted to ''général de brigade'' in 1805, after the establishment of the French Empire, and to ''général de division'' in 1807. Mouton distinguished himself in the battles of Jena, Landshut and Aspern-Essling. In 1810, he was created count of Lobau in recognition of his role in the battle of Aspern. During the Russian Campaign, he acted as a senior '' aide-de-camp'' to Emperor Napoleon I of France. He then served with distinction during the 1813 campaign, seeing action at the Battles of Lützen and Bautzen. After Dominique Vandamme was made prisoner during the battle of Kulm, Lobau commanded the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lixheim
Lixheim is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. The commune Vieux-Lixheim lies 1 km to the north-west. See also * Communes of the Moselle department The following is a list of the 725 communes of the Moselle department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Moselle (department) Duchy of Lorraine {{SarrebourgChâteauSalins-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Moselle Department
The following is a list of the 725 communes of the Moselle department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):BANATIC Périmètre des EPCI à fiscalité propre. Accessed 3 July 2020. * Metz Métropole * Communauté d'agglomération de Forbach Porte de France * Communauté d'agglomération Portes de F ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Est
Grand Est (; gsw-FR, Grossa Oschta; Moselle Franconian/ lb, Grouss Osten; Rhine Franconian: ''Groß Oschte''; german: Großer Osten ; en, "Great East") is an administrative region in Northeastern France. It superseded three former administrative regions, Alsace, Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine, on 1 January 2016 under the provisional name of Alsace-Champagne-Ardenne-Lorraine (; ACAL or, less commonly, ALCA), as a result of territorial reform which had been passed by the French Parliament in 2014. The region sits astride three water basins ( Seine, Meuse and Rhine), spanning an area of , the fifth largest in France; it includes two mountain ranges ( Vosges and Ardennes). It shares borders with Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany and Switzerland. As of 2017, it had a population of 5,549,586 inhabitants. The prefecture and largest city, by far, is Strasbourg. The East of France has a rich and diverse culture, being situated at a crossroads between the Latin and Germanic worlds. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Petite-Pierre
La Petite-Pierre (; german: Lützelstein; Rhine Franconian: ''Lítzelstain'') is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It lies in the historical and cultural region of Alsace (Elsass in German). Petit-Pierre literally means ''little rock''. The town lies in the Northern Vosges Regional Nature Park which has its headquarter in the château (Maison du Parc). History Lützelstein castle was built by Count Hugo, who was the son of Hugh, Count of Blieskastel. It was claimed by the Bishop of Strasbourg in 1223, but the count successfully defended it. After Count Friedrich died without a male successor, the county was subject to a protracted inheritance dispute between his uncle, Frederick Burkhard, and his sister, who was married to John of Leiningen. Both John and the sons of Burkhard died within a short time and without heirs, so the entire county was passed to the Electoral Palatinate in 1462. During the partition of the House of Wittelsba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative divisions, administrative division in the France, French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipality, municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlet (place), hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Forces In Europe
United may refer to: Places * United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Arts and entertainment Films * ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film * ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two film Literature * ''United!'' (novel), a 1973 children's novel by Michael Hardcastle Music * United (band), Japanese thrash metal band formed in 1981 Albums * ''United'' (Commodores album), 1986 * ''United'' (Dream Evil album), 2006 * ''United'' (Marvin Gaye and Tammi Terrell album), 1967 * ''United'' (Marian Gold album), 1996 * ''United'' (Phoenix album), 2000 * ''United'' (Woody Shaw album), 1981 Songs * "United" (Judas Priest song), 1980 * "United" (Prince Ital Joe and Marky Mark song), 1994 * "United" (Robbie Williams song), 2000 * "United", a song by Danish duo Nik & Jay featuring Lisa Rowe Television * ''United'' (TV series), a 1990 BBC Two documentary series * ''United!'', a soap opera that aired on BBC One from 1965 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand II (9 July 1578 – 15 February 1637) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1619 until his death in 1637. He was the son of Archduke Charles II of Inner Austria and Maria of Bavaria. His parents were devout Catholics, and, in 1590, they sent him to study at the Jesuits' college in Ingolstadt because they wanted to isolate him from the Lutheran nobles. In July that same year (1590), when Ferdinand was 12 years old, his father died, and he inherited Inner Austria–Styria, Carinthia, Carniola and smaller provinces. His cousin, the childless Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, who was the head of the Habsburg family, appointed regents to administer these lands. Ferdinand was installed as the actual ruler of the Inner Austrian provinces in 1596 and 1597. Rudolf II also charged him with the command of the defense of Croatia, Slavonia, and southeastern Hungary against the Ottoman Empire. Ferdinand regarded the regulation of religious issues as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |