|
Persecution In Lyon
The persecution in Lyon in AD 177 was a legendary persecution of Christians in Lugdunum, Roman Gaul (present-day Lyon, France), during the reign of Marcus Aurelius (161–180). As there is no coeval account of this persecution the earliest source is a letter preserved in Eusebius's ''Ecclesiastical History'', book 5, chapter 1, written 150 years later in palestine. Gregory of Tours describes the persecution in the 6th century in ''De Gloria martyrum''. Background Lugdunum was an important Roman city in Gaul. Founded on the Rhone river in 43 BC by Lucius Munatius Plancus, it served as the capital of the Roman province Gallia Lugdunensis. The emperor Claudius was born in Lugdunum. The first known Christian community established in Lugdunum some time in the 2nd century was led by a bishop named Pothinus from Asia Minor. In the first two centuries of the Christian era, it was local Roman officials who were largely responsible for persecutions. In the second century, the Caesars w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugdunum
Lugdunum (also spelled Lugudunum, ; modern Lyon, France) was an important Roman city in Gaul, established on the current site of Lyon. The Roman city was founded in 43 BC by Lucius Munatius Plancus, but continued an existing Gallic settlement with a likely population of several thousands. It served as the capital of the Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis and was an important city in the western half of the Roman Empire for centuries. Two emperors, Claudius and Caracalla, were born in Lugdunum. In the period 69–192 AD, the city's population may have numbered 50,000 to 100,000, and possibly up to 200,000 inhabitants. The original Roman city was situated west of the confluence of the Rhône and Saône, on the Fourvière heights. By the late centuries of the empire much of the population was located in the Saône River valley at the foot of Fourvière. Name The Roman city was founded as ''Colonia Copia Felix Munatia'', a name invoking prosperity and the blessing of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decius
Gaius Messius Quintus Traianus Decius ( 201 ADJune 251 AD), sometimes translated as Trajan Decius or Decius, was the emperor of the Roman Empire from 249 to 251. A distinguished politician during the reign of Philip the Arab, Decius was proclaimed emperor by his troops after putting down a rebellion in Moesia. In 249, he defeated and killed Philip near Verona and was recognized as emperor by the Senate afterwards. During his reign, he attempted to strengthen the Roman state and its religion, leading to the Decian persecution, where a number of prominent Christians (including Pope Fabian) were put to death. In the last year of his reign, Decius co-ruled with his son Herennius Etruscus, until they were both killed by the Goths in the Battle of Abritus. Early life and rise to power Gaius Messius Quintus Traianus Decius was an Illyrian born at Budalia, Illyricum, near Sirmium in Pannonia Inferior. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persecution Of Early Christians
Persecution is the systematic mistreatment of an individual or group by another individual or group. The most common forms are religious persecution, racism, and political persecution, though there is naturally some overlap between these terms. The inflicting of suffering, harassment, imprisonment, internment, fear or pain are all factors that may establish persecution, but not all suffering will necessarily establish persecution. The threshold of severity has been a source of much debate. International law As part of the Nuremberg Principles, crimes against humanity are part of international law. Principle VI of the Nuremberg Principles states that Telford Taylor, who was Counsel for the Prosecution at the Nuremberg Trials wrote " tthe Nuremberg war crimes trials, the tribunals rebuffed several efforts by the prosecution to bring such 'domestic' atrocities within the scope of international law as 'crimes against humanity". Several subsequent international treaties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Ponticus
Ponticus was a boy martyred in 177 AD during the persecution in Lyons with a group of other Christians, including Saint Pothinus and Saint Blandina. He is venerated by the Roman Catholic Church as a martyr A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa .... References 177 deaths Christian child saints 2nd-century Christian martyrs Year of birth unknown {{saint-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipodius And Alexander
Epipodius (french: Épipode) and his companion Alexander (died 178) are venerated as Christian saints. Their feast day is 22 April, and Alexander is additionally commemorated on April 24 in the Eastern Orthodox Church. Epipodius was a native of Lyon; Alexander was said to be a native of Phrygia, and a physician by profession. They were both martyred during the reign of Marcus Aurelius. Life The earliest mention of Epipodius and Alexander is in a homily of St. Eucherius, about 440. Epipodius was born in Lyon and Alexander was a Greek, originally from Phrygia. Of distinguished birth, they were close friends since their childhood schooldays. Epipodius is said to have been a confirmed celibate bachelor, who devoted his time to Christian works. In the aftermath of the Persecution in Lyon in the summer of 177, Epipodius and Alexander, having been denounced as Christians, left the city and retired to a nearby village. There they found refuge in the house of a poor Christian widow situat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blandina
Saint Blandina (french: Blandine, c. 162–177 AD) was a Christian martyr who died in Lugdunum (modern Lyon, France) during the reign of Emperor Marcus Aurelius. Context In the first two centuries of the Christian era, it was the local Roman officials who were largely responsible for the persecution of Christians. In the second century, the emperors treated Christianity as a local problem to be dealt with by their subordinates. The number and severity of persecutions of Christians in various locations of the empire seemingly increased during the reign of Marcus Aurelius. The extent to which Marcus Aurelius himself directed, encouraged, or was aware of these persecutions is unclear and much debated by historians. Traditional history The traditional account regarding Blandina is reported by Eusebius in his '' Historia Ecclesiastica''. She belongs to the band of martyrs of Lyon who, after some of their number had endured frightful tortures, suffered martyrdom in 177 in the reign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Eleutherius
Pope Eleutherius (died 24 May 189), also known as Eleutherus, was the bishop of Rome from c. 174 to his death. His pontificate is alternatively dated to 171-185 or 177-193. He is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church. He is linked to a number of legends, one of them credited him with receiving a letter from "Lucius, King of Britain", but which is now generally considered to be a forgery. Life According to the '' Liber Pontificalis'', he was a Greek born in Nicopolis in Epirus, Greece. His contemporary Hegesippus wrote that he was a deacon of the Roman Church under Pope Anicetus (c. 154–164), and remained so under Pope Soter, whom he succeeded around 174. Dietary law The 6th-century recension of ''Liber Pontificalis'' ('Book of the Popes') known as the "Felician Catalog" includes additional commentary to the work's earlier entry on Eleutherius. One addition ascribes to Eleutherius the reissuance of a decree: "And he again affirmed that no food should be repudiated by Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irenaeus
Irenaeus (; grc-gre, Εἰρηναῖος ''Eirēnaios''; c. 130 – c. 202 AD) was a Greek bishop noted for his role in guiding and expanding Christian communities in the southern regions of present-day France and, more widely, for the development of Christian theology by combating heterodox or Gnostic interpretations of Scripture as heresy and defining the Catholic and Orthodox doctrines of the Apostolic Churches. Originating from Smyrna, he had seen and heard the preaching of Polycarp, who in turn was said to have heard John the Evangelist, and thus was the last-known living connection with the Apostles. Chosen as bishop of Lugdunum, now Lyon, his best-known work is '' Against Heresies'', often cited as ''Adversus Haereses'', a refutation of gnosticism, in particular that of Valentinus. To counter the doctrines of the gnostic sects claiming secret wisdom, he offered three pillars of orthodoxy: the scriptures, the tradition handed down from the apostles, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Pothinus
Saint Pothinus (french: Saint Pothin) was the first bishop of Lyon and the first bishop of Gaul. He is first mentioned in a letter attributed to Irenaeus of Lyon. The letter was sent from the Christian communities of Lyon and Vienne to the Roman province of Asia. History According to Irenaeus, Pothinus was born around the year 87, probably at Smyrna. He was a disciple of Polycarp, bishop of Smyrna, and accompanied him to Rome in 158. Pope Anicetus sent him to evangelize the Gauls. Pothinus established himself at Lyons, and founded there a flourishing Church, over which he presided for almost twenty years. In asserting his own authority as bishop of Lyon, Irenaeus says that Pothinus had been his predecessor in the position, and the first holder of that office. By 177, a large number of the Christians in the area of Vienne and Lyons were Greeks from Asia. A violent persecution was there against them while Pothinus was bishop of Lyons, and Irenæus, who had been sent there by Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
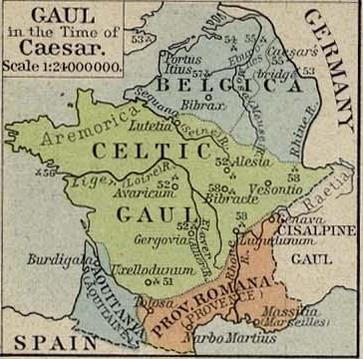
Roman Gaul
Roman Gaul refers to GaulThe territory of Gaul roughly corresponds to modern-day France, Belgium and Luxembourg, and adjacient parts of the Netherlands, Switzerland and Germany. under provincial rule in the Roman Empire from the 1st century BC to the 5th century AD. History During the Republic The Roman Republic's influence began in southern Gaul. By the mid-2nd century BC, Rome was trading heavily with the Greek colony of Massilia (modern Marseille) and entered into an alliance with them, by which it agreed to protect the town from local Gauls, including the nearby Aquitani and from sea-borne Carthaginians and other rivals, in exchange for land that it wanted in order to build a road to Hispania, to assist in troop movements to its provinces there. The Mediterranean settlements on the coast continued to be threatened by the powerful Gallic tribes to the north and in 122 BC the Roman general Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus campaigned in the area and defeated the Allobrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |