|
Peltasts
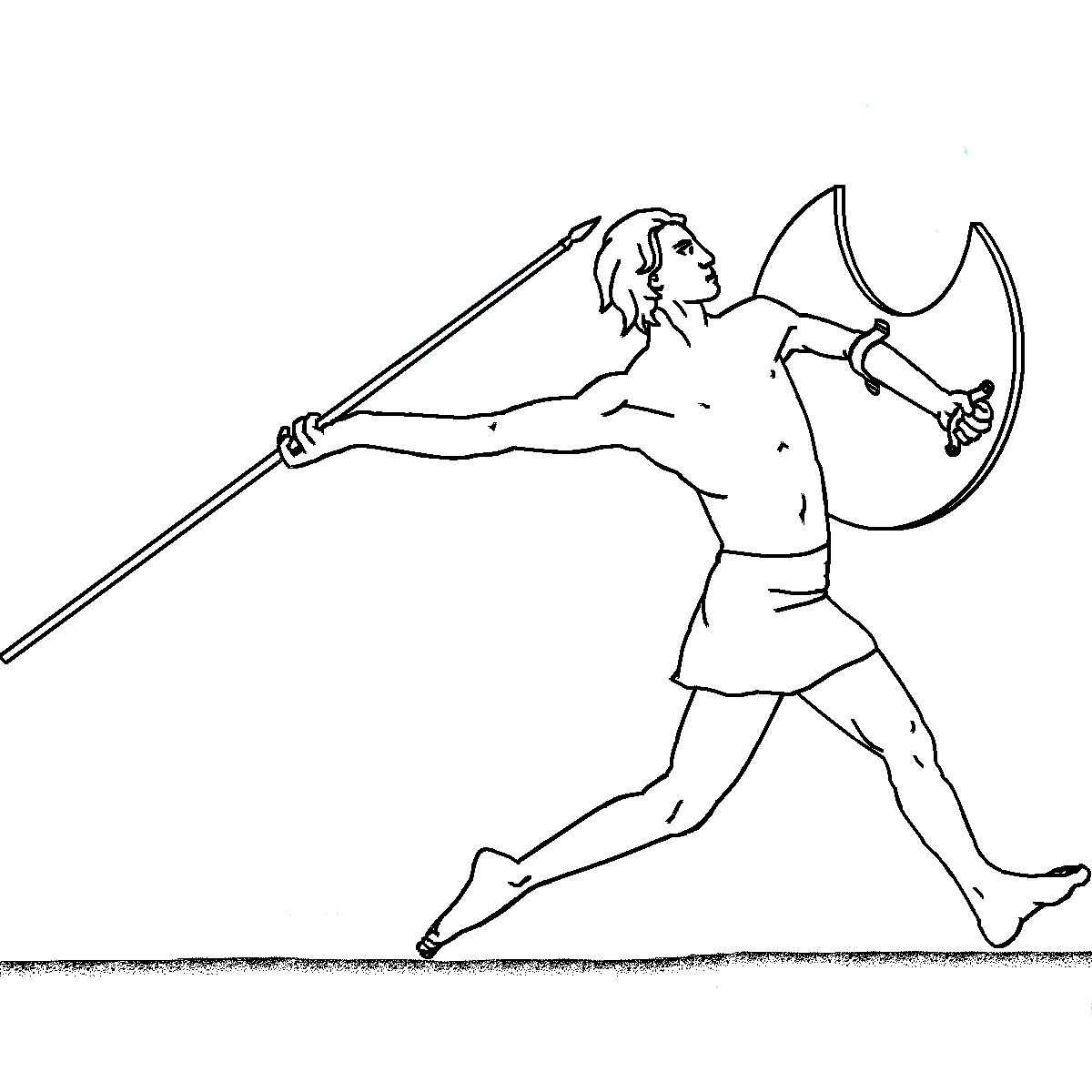
A ''peltast'' ( grc-gre, πελταστής ) was a type of light infantryman, originating in Thrace and Paeonia, and named after the kind of shield he carried. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis distinguishes the Thracian and Greek peltast troops. The peltast often served as a skirmisher in Hellenic and Hellenistic armies. In the Medieval period, the same term was used for a type of Byzantine infantryman. Description ''Pelte'' shield ''Peltasts'' carried a crescent-shaped wicker shield called a "''pelte''" (Ancient Greek grc, πέλτη, peltē, label=none; Latin: ) as their main protection, hence their name. According to Aristotle, the ''pelte'' was rimless and covered in goat- or sheepskin. Some literary sources imply that the shield could be round, but in art it is usually shown as crescent-shaped. It also appears in Scythian art and may have been a common type in Central Europe. The shield could be carried with a central stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javelins
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon, but today predominantly for sport. The javelin is almost always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distance, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraphic dating indicates that the weapons are about 400,000 year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenic Period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás'') was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word ''Hellenistic'' was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian invasion of the Achaemenid Empire in 330 BC and its disintegration shortly after, the Hellenistic kingdoms were established throughout south-west Asia (Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Pergamon), north-east Africa ( Ptolemaic Kingdom) and South Asia (Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Greek K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás'') was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word ''Hellenistic'' was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian invasion of the Achaemenid Empire in 330 BC and its disintegration shortly after, the Hellenistic kingdoms were established throughout south-west Asia ( Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Pergamon), north-east Africa ( Ptolemaic Kingdom) and South Asia ( Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
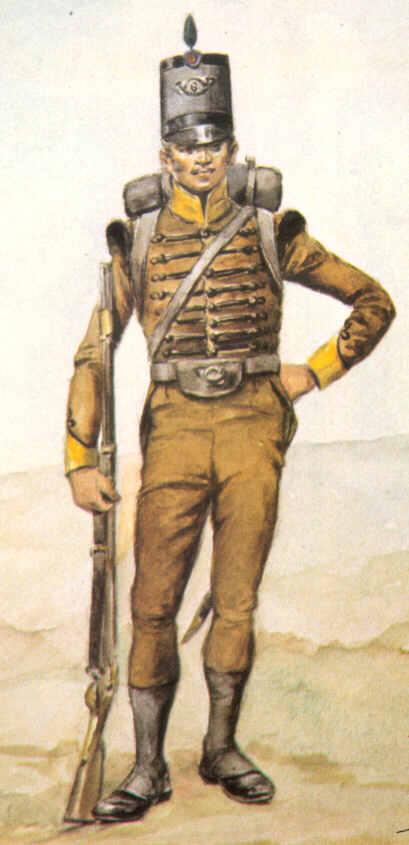
Light Infantry
Light infantry refers to certain types of lightly equipped infantry throughout history. They have a more mobile or fluid function than other types of infantry, such as heavy infantry or line infantry. Historically, light infantry often fought as scouts, raiders, and skirmishers. These are loose formations that fight ahead of the main army to harass, delay, disrupt supply lines, engage the enemy’s own skirmishing forces, and generally "soften up" an enemy before the main battle. Light infantrymen were also often responsible for screening the main body of a military formation. Post-World War II, the term "light infantry" evolved to include rapid-deployment units (including commandos and airborne units) that emphasize speed and mobility over armor and firepower. Some units or battalions that historically held a skirmishing role have kept their designation "light infantry" for the sake of tradition. History Ancient history The concept of a skirmishing screen is a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuirass
A cuirass (; french: cuirasse, la, coriaceus) is a piece of armour that covers the torso, formed of one or more pieces of metal or other rigid material. The word probably originates from the original material, leather, from the French '' cuirace'' and Latin word '' coriacea''. The use of the term "cuirass" generally refers to both the chest plate (or breastplate) and the back piece together; whereas a breastplate only protects the front, a cuirass protects both the front and the back. Description In Hellenistic and Roman times, the musculature of the male torso was idealized in the form of the muscle cuirass or "heroic cuirass" (in French the ''cuirasse esthétique'') sometimes further embellished with symbolic representation in relief, familiar in the Augustus of Prima Porta and other heroic representations in official Roman sculpture. As parts of the actual military equipment of classical antiquity, cuirasses and corsets of bronze, iron, or some other rigid substance were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Helmet
The Corinthian helmet originated in ancient Greece and took its name from the city-state of Corinth. It was a helmet made of bronze which in its later styles covered the entire head and neck, with slits for the eyes and mouth. A large curved projection protected the nape of the neck. Out of combat, a Greek hoplite would wear the helmet tipped upward for comfort. This practice gave rise to a series of variant forms in Italy, where the slits were almost closed, since the helmet was no longer pulled over the face but worn cap-like. Although the classical Corinthian helmet fell out of use among the Greeks in favour of more open types, the Italo-Corinthian types remained in use until the 1st century AD, being used, among others, by the Roman army. Physical evidence Apparently (judging from artistic and archaeological evidence) the most popular helmet during the Archaic and early Classical periods, the style gradually gave way to the more open Thracian helmet, Chalcidian helmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Mercenaries
There is evidence of mercenaries (''misthophoroi (plural), misthios (singular male), misthia (singular female)'' in Greek) being hired in Ancient Greece from the 6th century BC. The tyrants of that time hired bodyguards from other city-states. It is not known if earlier Aegean armies and navies, such as the Minoans and Mycenaeans, used mercenaries. Mercenary troops from Caria and Ionia are known to have fought with Psamtik I against the Assyrians. These were the "bronze men from the sea" whose arrival in Egypt, according to Herodotus, was foretold to Psamtik by an oracle. They entered the country as raiders but Psamtik made a truce with them and hired them to his cause. Afterwards, he granted land to them alongside the Nile and they are traditionally held to have been the first Greeks to settle in Egypt. In the 5th century BC, Arcadian soldiers fought for Xerxes I in 480 when he led the Persian invasion of Greece. Later in the century, many Greek mercenaries were employed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian Art
Scythian art is the art associated with Scythian cultures, primarily decorative objects, such as jewellery, produced by the nomadic tribes of the area known as Scythia, which encompassed Central Asia, parts of Eastern Europe east of the Vistula River, and parts of South Asia, with the eastern edges of the region vaguely defined by ancient Greeks. The identities of the nomadic peoples of the steppes is often uncertain, and the term "Scythian" should often be taken loosely; the art of nomads much further east than the core Scythian territory exhibits close similarities as well as differences, and terms such as the "Scytho-Siberian world" are often used. Other Eurasian nomad peoples recognised by ancient writers, notably Herodotus, include the Massagetae, Sarmatians, and Saka, the last a name from Persian sources, while ancient Chinese sources speak of the Xiongnu or Hsiung-nu. Modern archaeologists recognise, among others, the Pazyryk, Tagar, and Aldy-Bel cultures, with the furt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazons
In Greek mythology, the Amazons (Ancient Greek: Ἀμαζόνες ''Amazónes'', singular Ἀμαζών ''Amazōn'', via Latin ''Amāzon, -ŏnis'') are portrayed in a number of ancient epic poems and legends, such as the Labours of Hercules, the ''Argonautica'' and the ''Iliad''. They were a group of female warriors and hunters, who beat men in physical agility and strength, in archery, riding skills, and the arts of combat. Their society was closed for men and they only raised their daughters, either killing their sons or returning them to their fathers, with whom they would only socialize briefly in order to reproduce. Courageous and fiercely independent, the Amazons, commanded by their queen, regularly undertook extensive military expeditions into the far corners of the world, from Scythia to Thrace, Asia Minor and the Aegean Islands, reaching as far as Arabia and Egypt. Besides military raids, the Amazons are also associated with the foundation of temples and the est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. It comprises southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece ( Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey ( East Thrace). The region's boundaries are based on that of the Roman Province of Thrace; the lands inhabited by the ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into the region of Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'' was first used by the Greeks when referring to the Thracian tribes, from ancient Greek Thrake (Θρᾴκη), descending from ''Thrāix'' (Θρᾷξ). It referred originally to the Thracians, an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' first referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)



