|
Paunsaugunt Plateau
The Paunsaugunt Plateau (pronounced "PAWN-suh-gant") is a dissected plateau, rising to an elevation of , in southwestern Utah in the United States. Located in northern Kane County and southwestern Garfield County, it is approximately wide, and extends southward from the Sevier Plateau approximately , terminating in the Pink Cliffs at the southern end. It is drained by the East Fork Sevier River which flows northward on the plateau, to the meet the main branch (Sevier River) which flows in a valley along the western side of the plateau. The plateau is highly dissected along the eastern flank, which is drained by the Paria River in the Colorado River watershed, and is protected as Bryce Canyon National Park. A section of the Great Basin Divide is along the plateau, and much of the plateau is part of Dixie National Forest. The plateau receives approximately of snow per year and experiences approximately 200 days of freeze-and-thaw cycles. Utah's Highway 12, an All-American Roa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bald Knoll
Bald Knoll, also called Black Knoll, Buck Knoll or Corral Knoll, is a cinder cone in Utah, in the Southwestern United States. It is the youngest volcano at the southwest portion of the Paunsaugunt Plateau and it consists of basaltic lava with a well-preserved volcanic crater A volcanic crater is an approximately circular depression in the ground caused by Volcano, volcanic activity. It is typically a bowl-shaped feature containing one or more vents. During Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions, molten magm ... at its summit. References Volcanoes of Utah Cinder cones of the United States Basin and Range Province Landforms of Kane County, Utah {{Utah-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah Scenic Byway 12
State Route 12 or Scenic Byway 12 (SR-12), also known as ''"Highway 12 — A Journey Through Time Scenic Byway"'', is a state highway designated an All-American Road located in Garfield County and Wayne County, Utah, United States. Route description Proceeding west to east for 122 miles (nearly 200 km), the highway starts south of Panguitch at an intersection with US-89, crosses part of Dixie National Forest and Bryce Canyon National Park, continues through the small towns of Tropic, Cannonville, and Henrieville. It crosses various parts of Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument (GS-ENM), continues northeast through Escalante and over the Escalante River, then over the Hogback, a narrow ridge with no guardrails or shoulders and steep drop-offs on each side. It then proceeds north through more of GS-ENM, Boulder, the Aquarius Plateau, Grover, ending in Torrey at an intersection with SR-24, five miles (8 km) west of Capitol Reef National Park. The long por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plateaus Of Utah
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides have deep hills or escarpments. Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, and erosion by water and glaciers. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones. Formation Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, Plate tectonics movements and erosion by water and glaciers. Volcanic Volcanic plateaus are produced by volcanic activity. The Columbia Plateau in the north-western United States is an example. They may be formed by upwelling of volcanic magma or extrusion of lava. The un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of The Great Basin
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bryce Canyon
Bryce Canyon National Park () is an American national park located in southwestern Utah. The major feature of the park is Bryce Canyon, which despite its name, is not a canyon, but a collection of giant natural amphitheaters along the eastern side of the Paunsaugunt Plateau. Bryce is distinctive due to geological structures called hoodoos, formed by frost weathering and stream erosion of the river and lake bed sedimentary rocks. The red, orange, and white colors of the rocks provide spectacular views for park visitors. Bryce Canyon National Park is much smaller and sits at a much higher elevation than nearby Zion National Park. The rim at Bryce varies from . The Bryce Canyon area was settled by Mormon pioneers in the 1850s and was named after Ebenezer Bryce, who homesteaded in the area in 1874. The area around Bryce Canyon was originally designated as a national monument by President Warren G. Harding in 1923 and was redesignated as a national park by Congress in 1928. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational properties with various title designations. The U.S. Congress created the agency on August 25, 1916, through the National Park Service Organic Act. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., within the main headquarters of the Department of the Interior. The NPS employs approximately 20,000 people in 423 individual units covering over 85 million acres in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and US territories. As of 2019, they had more than 279,000 volunteers. The agency is charged with a dual role of preserving the ecological and historical integrity of the places entrusted to its management while also making them available and accessible for public use and enjoyment. History Yellowstone National Park was created as the first national par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Bryce Canyon Area
The exposed geology of the Bryce Canyon area in Utah shows a record of deposition that covers the last part of the Cretaceous Period and the first half of the Cenozoic era in that part of North America. The ancient depositional environment of the region around what is now Bryce Canyon National Park varied from the warm shallow sea (called the Cretaceous Seaway) in which the Dakota Sandstone and the Tropic Shale were deposited to the cool streams and lakes that contributed sediment to the colorful Claron Formation that dominates the park's amphitheaters. Other formations were also formed but were mostly eroded following uplift from the Laramide orogeny which started around 70 million years ago ( mya). This event raised the Rocky Mountains far to the east and caused the retreat of the sea that covered the Bryce Canyon area. After Laramide mountain building came to an end, about 15 mya, a large part of western North America began to be stretched into the nearby Basin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Staircase-big
Grand may refer to: People with the name * Grand (surname) * Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor * Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist * Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper Places * Grand, Oklahoma * Grand, Vosges, village and commune in France with Gallo-Roman amphitheatre * Grand Concourse (other), several places * Grand County (other), several places * Grand Geyser, Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone * Grand Rounds National Scenic Byway, a parkway system in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States * Le Grand, California, census-designated place * Grand Staircase, a place in the US. Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Grand'' (Erin McKeown album), 2003 * ''Grand'' (Matt and Kim album), 2009 * ''Grand'' (magazine), a lifestyle magazine related to related to grandparents * ''Grand'' (TV series), American sitcom, 1990 * Grand piano, musical instrument * Grand Production, Serbian record label company * The Grand Tour, a new British automobile show Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoodoo (geology)
A hoodoo (also called a tent rock, fairy chimney, or earth pyramid) is a tall, thin spire of rock formed by erosion. Hoodoos typically consist of relatively soft rock topped by harder, less easily eroded stone that protects each column from the elements. They generally form within sedimentary rock and volcanic rock formations. Hoodoos range in size from the height of an average human to heights exceeding a 10-story building. Hoodoo shapes are affected by the erosional patterns of alternating hard and softer rock layers. Minerals deposited within different rock types can cause hoodoos to have different colors throughout their height. Etymology In certain regions of western North America these rocky structures are called hoodoos. The name is derived from Hoodoo spirituality, in which certain natural forms are said to possess certain powers, but by the late 19th century, this spirituality became associated with bad luck. Prior to the English name for these geographic formations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint (geology)
A rock in Abisko fractured along existing joints possibly by mechanical frost weathering A joint is a break (fracture) of natural origin in a layer or body of rock that lacks visible or measurable movement parallel to the surface (plane) of the fracture ("Mode 1" Fracture). Although joints can occur singly, they most frequently appear as joint sets and systems. A ''joint set'' is a family of parallel, evenly spaced joints that can be identified through mapping and analysis of their orientations, spacing, and physical properties. A ''joint system'' consists of two or more intersecting joint sets. The distinction between joints and faults hinges on the terms ''visible'' or ''measurable,'' a difference that depends on the scale of observation. Faults differ from joints in that they exhibit visible or measurable lateral movement between the opposite surfaces of the fracture ("Mode 2" and "Mode 3" Fractures). Thus a joint may be created by either strict movement of a rock la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
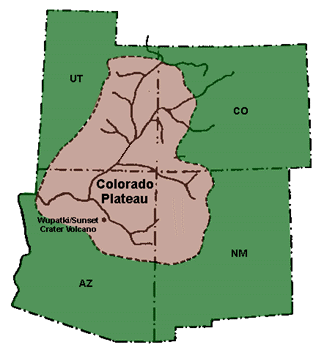
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)