|
Paradox Formation
In geology, the Paradox Formation Is a Pennsylvanian age formation which consists of abundant evaporites with lesser interbedded shale, sandstone, and limestone. The evaporites are largely composed of gypsum, anhydrite, and halite. The formation is found mostly in the subsurface, but there are scattered exposures in anticlines in eastern Utah and western Colorado. These surface exposures occur in the Black Mesa, San Juan and Paradox Basins and the formation is found in the subsurface in southwestern Colorado, southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona and northeastern New Mexico. The formation is notable both for its petroleum resources and for its salt tectonics, which are responsible for many distinctive geologic features of the eastern Colorado Plateau. In addition to the anticline valleys, these include the grabens of the Needles District of Canyonlands National Park and the fins and arches of Arches National Park. Description The Paradox Formation was deposited in the Para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Mesa Basin
Black Mesa (also called Big Mountain) is an upland mountainous mesa of Arizona, north-trending in Navajo County, west and southeast-trending in Apache County. In Navajo it is called ('Black Mountain') and during Mexican rule of Arizona it was called Mesa de las Vacas (Spanish for 'mesa of the cows'). It derives its dark appearance from its pinyon-juniper and mixed conifer woodlands. Geography The mesa is located on the Colorado Plateau near Kayenta, Arizona, and rises to over 8168 feet. Its highest peak is located on Black Mesa's northern rim, a few miles south of the town of Kayenta. Reliable springs surfacing at several locations mean the mesa is more suitable for continuous habitation than much of the surrounding desert area. It is now split between the Hopi and Diné (Navajo) tribal reservations. Black Mesa is also the name of a small Navajo community off BIA-8066, which lies 17 miles west of Rough Rock, 20 miles north of Blue Gap and 25 miles northeast of Pinon. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honaker Trail Formation Over Paradox Formation (Pennsylvanian; Goosenecks Of The San Juan River, Utah, USA) 6 (49103736132)
Honaker is a town in Russell County, Virginia, United States. The population was 1,449 at the 2010 census. History Honaker was settled as early as 1772 when William Ferrill established a homesite in the area. During Dunmore's War of 1774 a fort, known as New Garden Fort, was established to protect the settlers from Indian raids. The Honaker Commercial Historic District was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2009. Geography Honaker is located in the Clinch River watershed. According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 0.6 square miles (1.4 km2), all of it land. Demographics As of the census of 2010, there were 1,449 people and 684 households. The racial makeup of the town was 98.83% White, 0.20% African American, 0.28% Native American, and 0.69% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were .35% of the population. There were 684 households in 2010, out of which 23.39% had children under the age of 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.Potash USGS 2008 Minerals Yearbook The name derives from ''pot ash'', plant ashes or soaked in water in a pot, the primary means of manufacturing potash before the . The word '''' is derived from ''potash''. Potash is produced worldwide in amounts exceeding 90 million |
Dolomite (mineral)
Dolomite () is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally The term is also used for a sedimentary carbonate rock composed mostly of the mineral dolomite. An alternative name sometimes used for the dolomitic rock type is dolostone. History As stated by Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure the mineral dolomite was probably first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1768. In 1791, it was described as a rock by the French naturalist and geologist Déodat Gratet de Dolomieu (1750–1801), first in buildings of the old city of Rome, and later as samples collected in the mountains now known as the Dolomite Alps of northern Italy. Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure first named the mineral (after Dolomieu) in March 1792. Properties The mineral dolomite crystallizes in the trigonal-rhombohedral system. It forms white, tan, gray, or pink crystals. Dolomite is a double carbonate, having an alternating structural arrangement of calcium and magnesium ions. Unless it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
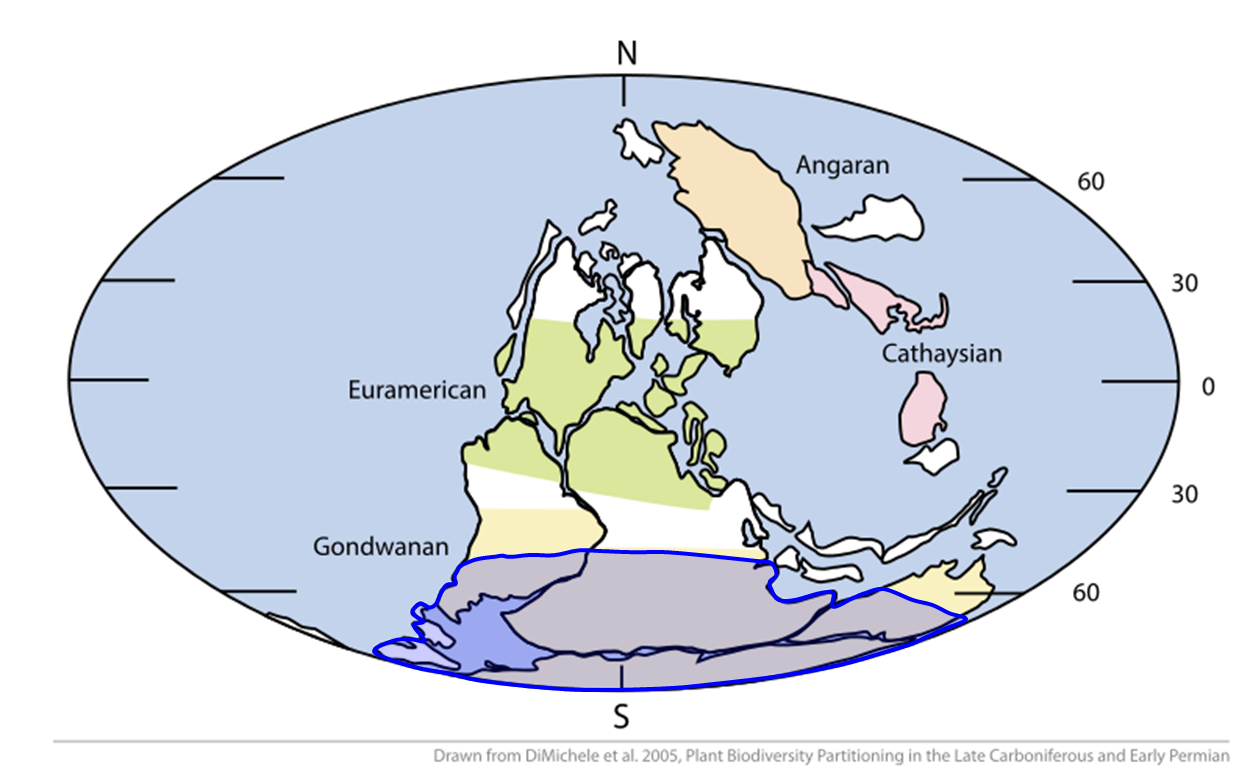
Late Paleozoic Icehouse
The late Paleozoic icehouse, also known as the Late Paleozoic Ice Age (LPIA) and formerly known as the Karoo ice age, was an ice age that began in the Late Devonian and ended in the Late Permian, occurring from 360 to 255 million years ago (Mya), and large land-based ice-sheets were then present on Earth's surface. It was the second major icehouse period of the Phanerozoic. It is named after the tillite ( Dwyka Group) found in the Karoo Basin of western South Africa, where evidence for the ice age was first clearly identified in the 19th century. The tectonic assembly of the continents of Euramerica and Gondwana into Pangaea, in the Hercynian- Alleghany Orogeny, made a major continental land mass within the Antarctic region, and the closure of the Rheic Ocean and Iapetus Ocean saw disruption of warm-water currents in the Panthalassa Ocean and Paleotethys Sea and an increase in carbon sequestration via silicate weathering, which led to progressive cooling of summers, and the sno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope movement. Processes that lead to subsidence include dissolution of underlying carbonate rock by groundwater; gradual compaction of sediments; withdrawal of fluid lava from beneath a solidified crust of rock; mining; pumping of subsurface fluids, such as groundwater or petroleum; or warping of the Earth's crust by tectonic forces. Subsidence resulting from tectonic deformation of the crust is known as tectonic subsidence and can create accommodation for sediments to accumulate and eventually lithify into sedimentary rock. Ground subsidence is of global concern to geologists, geotechnical engineers, surveyors, engineers, urban planners, landowners, and the public in general.National Research Council, 1991. ''Mitigating losses from land subsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
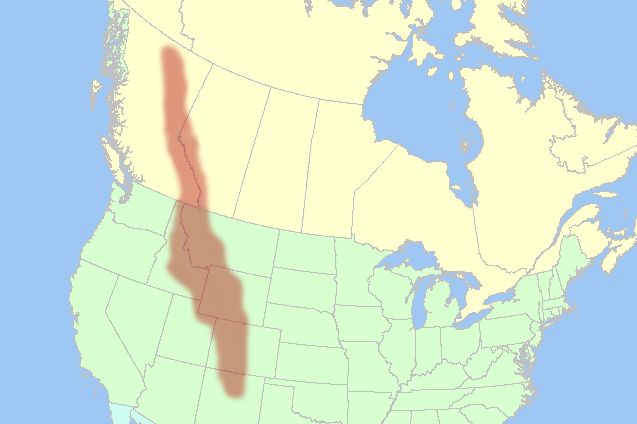
Ancestral Rocky Mountains
The geology of the Rocky Mountains is that of a discontinuous series of mountain ranges with distinct geological origins. Collectively these make up the Rocky Mountains, a mountain system that stretches from Northern British Columbia through central New Mexico and which is part of the great mountain system known as the North American Cordillera. The rocky cores of the mountain ranges are, in most places, formed of pieces of continental crust that are over one billion years old. In the south, an older mountain range was formed 300 million years ago, then eroded away. The rocks of that older range were reformed into the Rocky Mountains. The Rocky Mountains took shape during an intense period of plate tectonic activity that resulted in much of the rugged landscape of the western North America. The Laramide orogeny, about 80–55 million years ago, was the last of the three episodes and was responsible for raising the Rocky Mountains. Subsequent erosion by glaciers has created the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arches National Park
Arches National Park is a national park in eastern Utah, United States. The park is adjacent to the Colorado River, north of Moab, Utah. More than 2,000 natural sandstone arches are located in the park, including the well-known Delicate Arch, as well as a variety of unique geological resources and formations. The park contains the highest density of natural arches in the world. The park consists of of high desert located on the Colorado Plateau. The highest elevation in the park is at Elephant Butte, and the lowest elevation is at the visitor center. The park receives an average of less than of rain annually. Administered by the National Park Service, the area was originally named a national monument on April 12, 1929, and was redesignated as a national park on November 12, 1971. The park received more than 1.6 million visitors in 2018. Park purpose As stated in the foundation document in U.S. National Park Service website: Geology The national park lies above an unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canyonlands National Park
Canyonlands National Park is an American national park located in southeastern Utah near the town of Moab. The park preserves a colorful landscape eroded into numerous canyons, mesas, and buttes by the Colorado River, the Green River, and their respective tributaries. Legislation creating the park was signed into law by President Lyndon Johnson on September 12, 1964. The park is divided into four districts: the Island in the Sky, the Needles, the Maze, and the combined rivers—the Green and Colorado—which carved two large canyons into the Colorado Plateau. While these areas share a primitive desert atmosphere, each retains its own character. Author Edward Abbey, a frequent visitor, described the Canyonlands as "the most weird, wonderful, magical place on earth—there is nothing else like it anywhere." History In the early 1950s, Bates Wilson, then superintendent of Arches National Monument, began exploring the area to the south and west of Moab, Utah. After seeing what is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
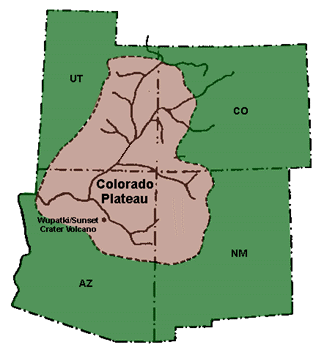
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Tectonics
upright=1.7 Salt tectonics, or halokinesis, or halotectonics, is concerned with the geometries and processes associated with the presence of significant thicknesses of evaporites containing rock salt within a stratigraphic sequence of rocks. This is due both to the low density of salt, which does not increase with burial, and its low strength. Salt structures (excluding undeformed layers of salt) have been found in more than 120 sedimentary basins around the world. Passive salt structures Structures may form during continued sedimentary loading, without any external tectonic influence, due to gravitational instability. Pure halite has a density of 2160 kg/m3. When initially deposited, sediments generally have a lower density of 2000 kg/m3, but with loading and compaction their density increases to 2500 kg/m3, which is greater than that of salt. Once the overlying layers have become denser, the weak salt layer will tend to deform into a characteristic series of rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |