|
Paine Run Rockshelter
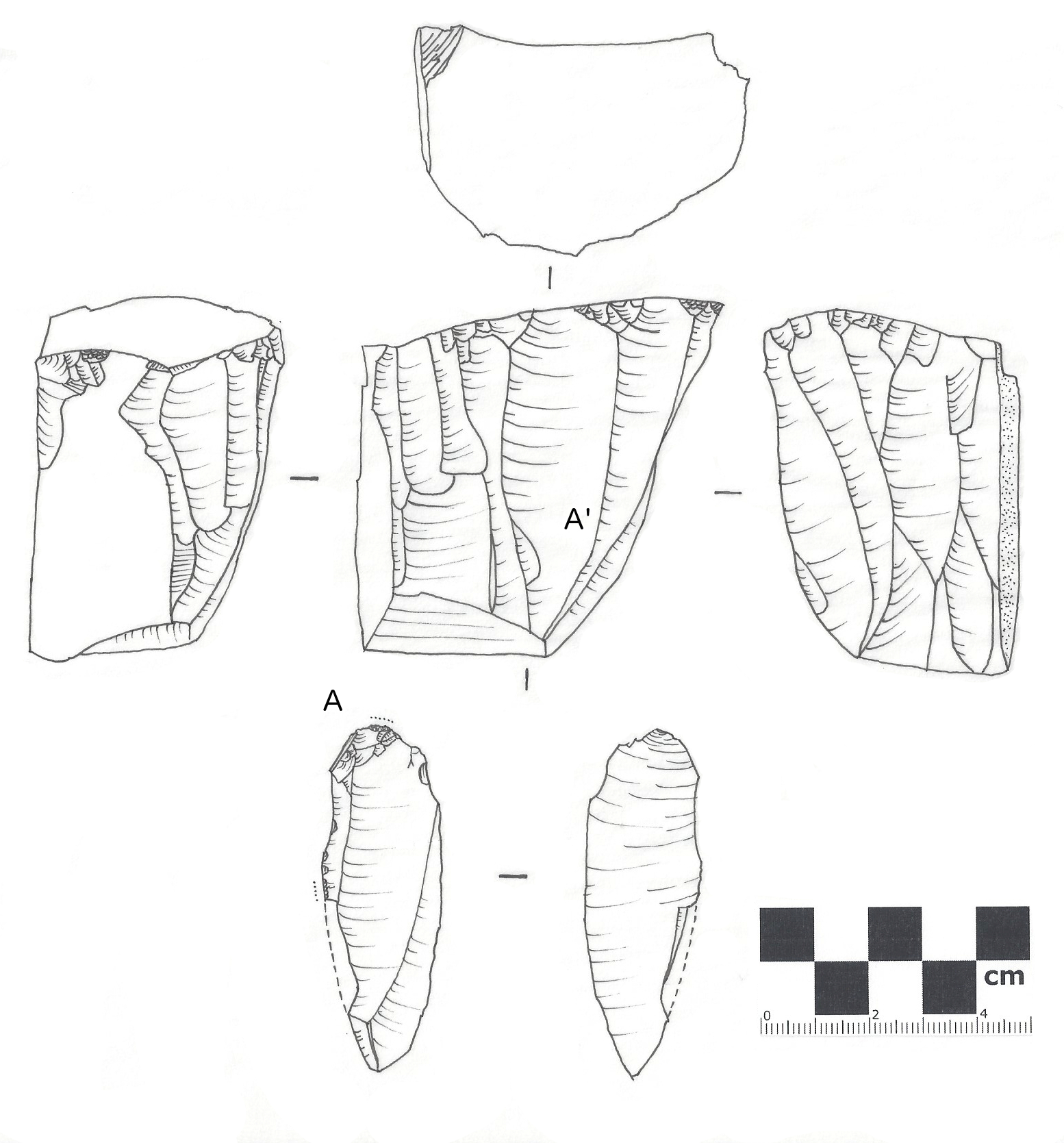
The Paine Run Rockshelter ( 44-AU-158) is an archaeological site in Shenandoah National Park, in Augusta County, Virginia, United States. The site was discovered during the early 1970s as part of a comprehensive survey of the national park. It is one of fifteen sites that the survey found along Paine Run,Foss, Robert Ward. ''Man and Mountain: An Archaeological Overview of the Shenandoah National Park''. Thesis U of Virginia, 1977. a group that also includes archaeological site 44-AU-154 and the Blackrock Springs Site. Located in a mountainside hollow, near three other rockshelters, the site is deeply stratified. It is a small shelter, only about in area, and little taller than the average man. The shelter faces northward, toward the narrow floodplain and Paine Run, which flows approximately away; it sits just east of site 44-AU-154. While other archaeological sites in Paine Run Hollow date primarily from the Archaic period, the rockshelter appears to have been occupi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grottoes, Virginia
Grottoes is an incorporated town in Augusta and Rockingham counties in the U.S. state of Virginia. The population was 2,668 at the 2010 census. The Rockingham County portion of Grottoes is part of the Harrisonburg Metropolitan Statistical Area, while the small portion that extends into Augusta County is part of the Staunton– Waynesboro Micropolitan Statistical Area. Only seven of the town's 2,668 residents reside in Augusta County. Grottoes is home to the Grand Caverns, America's oldest show cave. History The town was incorporated in 1892 under the name Shendun. In 1912 the name was changed to Grottoes. ("Grottoes" means caves). The Stephen Harnsberger House was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1982. Geography Grottoes is located at (38.267385, −78.824868). According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 1.3 square miles (3.4 km2), all land. Transportation The main highways providing access to Grottoes are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptocrystalline
Cryptocrystalline is a rock microstructure, rock texture made up of such minute crystals that its crystalline nature is only vaguely revealed even microscopically in thin section by transmitted polarized light. Among the sedimentary rocks, chert and flint are cryptocrystalline. carbonado (diamond), Carbonado, a form of diamond, is also cryptocrystalline. Volcanic rocks, especially of the felsic type such as felsites and rhyolites, may have a cryptocrystalline matrix (geology), groundmass as distinguished from pure obsidian (felsic) or tachylyte (mafic), which are natural rock glasses. Agate and onyx are examples of cryptocrystalline silica (chalcedony). See also * List of rock textures * Macrocrystalline * Microcrystalline * Nanocrystalline * Rock microstructure References Crystals Lithics Petrology concepts {{Petrology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places In Augusta County, Virginia
__NOTOC__ This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Augusta County, Virginia. This is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Augusta County, Virginia, United States. The locations of National Register properties and districts for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in an online map. There are 55 properties and districts listed on the National Register in the county, including 1 National Historic Landmark. Current listings See also *List of National Historic Landmarks in Virginia *National Register of Historic Places listings in Virginia *National Register of Historic Places listings in Staunton, Virginia *National Register of Historic Places listings in Waynesboro, Virginia __NOTOC__ This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Waynesboro, Virginia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites On The National Register Of Historic Places In Virginia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Shelters In The United States
Rock most often refers to: * Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids * Rock music, a genre of popular music Rock or Rocks may also refer to: Places United Kingdom * Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales * Rock, Cornwall, a village in England * Rock, County Tyrone, a village in Northern Ireland * Rock, Devon, a location in England * Rock, Neath Port Talbot, a location in Wales * Rock, Northumberland, a village in England * Rock, Somerset, a location in Wales * Rock, West Sussex, a hamlet in Washington, England * Rock, Worcestershire, a village and civil parish in England United States * Rock, Kansas, an unincorporated community * Rock, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Rock, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Rock, Rock County, Wisconsin, a town in southern Wisconsin * Rock, Wood County, Wisconsin, a town in central Wisconsin Elsewhere * Corregidor, an island in the Philippines also known as "The Rock" * Jamaica, an isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Core
In archaeology, a lithic core is a distinctive artifact that results from the practice of lithic reduction. In this sense, a core is the scarred nucleus resulting from the detachment of one or more flakes from a lump of source material or tool stone, usually by using a hard hammer precursor such as a hammerstone. The core is marked with the positive scars of these flakes. The surface area of the core which received the blows necessary for detaching the flakes is referred to as the striking platform. The core may be discarded or shaped further into a core tool, such as can be seen in some types of handaxe. The purpose of core reduction may be to rough out a blank for later refinement into a projectile point, knife, or other stone tool, or it may be performed in order to obtain sharp flakes, from which a variety of simple tools can be made. Generally, the presence of a core is indicative of the latter process, since the former process usually leaves no core. Because the morpholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectile Point
In North American archaeological terminology, a projectile point is an object that was hafted to a weapon that was capable of being thrown or projected, such as a javelin, dart, or arrow. They are thus different from weapons presumed to have been kept in the hand, such as knives, spears, axes, hammers, and maces. Stone tools, including projectile points, can survive for long periods, were often lost or discarded, and are relatively plentiful, especially at archaeological sites. They provide useful clues to the human past, including prehistoric trade. A distinctive form of point, identified though lithic analysis of the way it was made, is often a key diagnostic factor in identifying an archaeological industry or culture. Scientific techniques exist to track the specific kinds of rock or minerals that were used to make stone tools in various regions back to their original sources. As well as stone, projectile points were also made of worked wood, bone, antler, horn, or ivory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90°) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Excavation
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be conducted over a few weeks to several years. Excavation involves the recovery of several types of data from a site. This data includes artifacts (portable objects made or modified by humans), features (non-portable modifications to the site itself such as post molds, burials, and hearths), ecofacts (evidence of human activity through organic remains such as animal bones, pollen, or charcoal), and archaeological context (relationships among the other types of data).Kelly&Thomas (2011). ''Archaeology: down to earth'' (4th ed.). Belmont, Calif.: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. Before excavating, the presence or absence of archaeological remains can often be suggested by, non-intrusive remote sensing, such as ground-penetrating radar. Basic informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 Common Era, BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 CE to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric, prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Tools
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone Age) cultures that have become extinct. Archaeologists often study such prehistoric societies, and refer to the study of stone tools as lithic analysis. Ethnoarchaeology has been a valuable research field in order to further the understanding and cultural implications of stone tool use and manufacture. Stone has been used to make a wide variety of different tools throughout history, including arrowheads, spearheads, hand axes, and querns. Stone tools may be made of either ground stone or knapped stone, the latter fashioned by a flintknapper. Knapped stone tools are made from cryptocrystalline materials such as chert or flint, radiolarite, chalcedony, obsidian, basalt, and quartzite via a process known as lithic reduction. One simple form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)